IoT: Understanding the Internet of Things
Categories:
3 minute read
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a revolutionary technology, connecting everyday objects to the internet, creating a vast network of interconnected devices. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT is transforming industries and reshaping our daily lives.
This comprehensive blog post will delve into the intricacies of IoT, exploring its fundamental concepts, applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding IoT
IoT refers to the interconnection of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other objects embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and network connectivity. These devices collect and exchange data, enabling them to communicate and interact with each other.
Key Components of IoT:
Devices: These include sensors, actuators, and microcontrollers that collect, process, and transmit data.
Connectivity: Networks like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular, and low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) provide communication channels for IoT devices.
Data Processing: Cloud computing and edge computing platforms handle data analysis, storage, and processing.
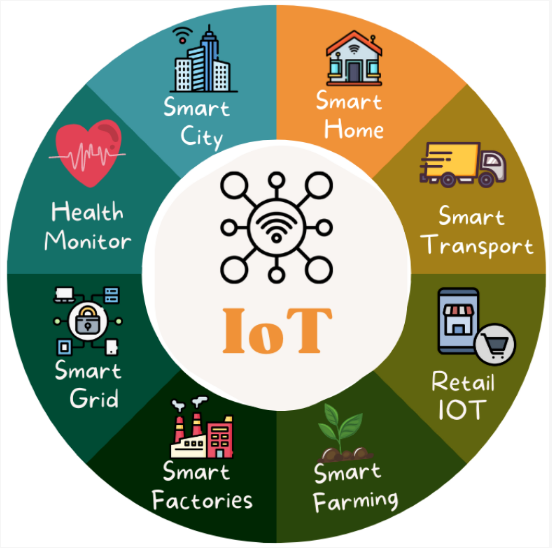
Applications: IoT solutions are implemented across various domains, from smart cities and healthcare to agriculture and manufacturing. Applications of IoT
IoT has found applications in numerous sectors, revolutionizing the way we live, work, and interact with our environment. Here are some prominent examples:
Smart Homes:
Home automation: Control lights, thermostats, security systems, and appliances remotely.
Energy management: Optimize energy consumption and reduce costs.
Smart appliances: Appliances with built-in IoT capabilities. Healthcare:
Remote patient monitoring: Track vital signs and provide timely medical assistance.
Wearable devices: Monitor health metrics and fitness activities.
Medical IoT: Improve patient care and efficiency in healthcare facilities. Agriculture:
Precision agriculture: Optimize farming practices using data-driven insights.
Smart irrigation: Efficiently manage water usage based on soil moisture and weather conditions.
** Livestock monitoring:** Track animal health and behavior. Manufacturing:
Industrial IoT (IIoT): Enhance productivity, efficiency, and quality control in manufacturing processes.
Predictive maintenance: Prevent equipment failures and reduce downtime.
Supply chain management: Optimize logistics and inventory management. Transportation:
Connected vehicles: Improve safety, traffic management, and fuel efficiency.
Autonomous vehicles: Self-driving cars and trucks.
Smart parking: Optimize parking space utilization. Cities:
Smart cities: Improve urban infrastructure, resource management, and citizen services.
Smart grids: Optimize energy distribution and consumption.
Traffic management: Reduce congestion and improve transportation efficiency. Benefits of IoT
IoT offers numerous benefits across various industries and applications, including:
Increased efficiency: Streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve productivity.
Enhanced decision-making: Data-driven insights enable informed decision-making.
Improved customer experience: Personalized services and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Enhanced safety: Monitor safety conditions and prevent accidents.
Sustainability: Optimize resource usage and reduce environmental impact. Challenges and Considerations
Despite its immense potential, IoT faces several challenges:
Security: Protecting IoT devices and data from cyber threats is a major concern.
Privacy: Ensuring privacy and data protection in IoT applications is crucial.
Interoperability: Ensuring compatibility and seamless communication between different IoT devices and systems.
Scalability: Handling the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices and ensuring scalability.
Cost: The initial investment in IoT infrastructure and devices can be significant. the Future of IoT**
The future of IoT is promising, with continued advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various sectors. Some key trends to watch include:
Edge computing: Processing data closer to the source to reduce latency and improve responsiveness.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning: Leveraging AI to extract valuable insights from IoT data.
5G connectivity: Providing faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity for IoT devices.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Transforming healthcare with connected medical devices.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Driving digital transformation in manufacturing and industry. Conclusion
IoT is a transformative technology that is reshaping the way we live, work, and interact with the world. By connecting everyday objects to the internet, IoT enables new possibilities, improves efficiency, and enhances our quality of life. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and benefits in the years to come.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.